Abstract
Rationale
Recent studies have suggested that the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) plays an important role in the development of sensitization to cocaine. In particular, a recent report proposed that sensitization is associated with a decreased dopamine D2 receptor function in the mPFC. The present study was designed to further examine the involvement of mPFC dopamine D2 receptors in cocaine sensitization.
Objectives
The experiments described below sought to determine the effects of acute or repeated intra-mPFC injections of the dopamine D2 antagonist sulpiride on subsequent motor-stimulant and nucleus accumbens dopamine responses to cocaine.
Methods
Rats received bilateral cannulae implants above the ventral mPFC for microinjections and above the nucleus accumbens for in vivo microdialysis. Initial studies examined the effects of intra-mPFC sulpiride pretreatment on the acute motor-stimulant and nucleus accumbens dopamine responses to cocaine. Follow-up studies determined the effects of repeated intra-mPFC sulpiride injections on subsequent behavioral and nucleus accumbens dopamine responses to a cocaine challenge.
Results
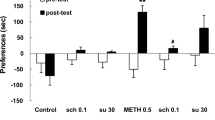
Intra-mPFC sulpiride enhanced the cocaine-induced increases in motor activity and dopamine overflow in the nucleus accumbens. Repeated intra-mPFC sulpiride induced behavioral and neurochemical cross-sensitization to cocaine.
Conclusions
The data support previous findings that sensitization is associated with a decrease in dopamine D2 receptor function in the mPFC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
al-Tikriti MS, Roth RH, Kessler RM, Innis RB (1992) Autoradiographic localization of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in rat cerebral cortex following unilateral neurotoxic lesions. Brain Res 575:39–46
Amtage J, Schmidt WJ (2003) Context-dependent catalepsy intensification is due to classical conditioning and sensitization. Behav Pharmacol 14:563–567
Bernard ML, Peterson YK, Chung P, Jourdan J, Lanier SM (2001) Selective interaction of AGS3 with G-proteins and the influence of AGS3 on the activation state of G-proteins. J Biol Chem 276:1585–1593
Beyer CE, Steketee JD (1999) Dopamine depletion in the medial prefrontal cortex induces sensitized-like behavioral and neurochemical responses to cocaine. Brain Res 833:133–141
Beyer CE, Steketee JD (2000) Intra-medial prefrontal cortex injection of quinpirole, but not SKF 38393, blocks the acute motor-stimulant response to cocaine in the rat. Psychopharmacology 151:211–218
Beyer CE, Steketee JD (2001) Characterization of the role of medial prefrontal cortex dopamine receptors in cocaine-induced locomotor activity. Behav Neurosci 115:1093–1100
Beyer CE, Steketee JD (2002) Cocaine sensitization: modulation by dopamine D2 receptors in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 12:526–535
Bowers MS, McFarland K, Lake RW, Peterson YK, Lapish CC, Gregory ML, Lanier SM, Kalivas PW (2004) Activator of g protein signaling 3; a gatekeeper of cocaine sensitization and drug seeking. Neuron 42:269–281
Chefer VI, Moron JA, Hope B, Rea W, Shippenberg TS (2000) Kappa-opioid receptor activation prevents alterations in mesocortical dopamine neurotransmission that occur during abstinence from cocaine. Neuroscience 101:619–627
Goeders NE, Smith JE (1983) Cortical dopaminergic involvement in cocaine reinforcement. Science 221:773–775
Grobin AC, Deutch AY (1998) Dopaminergic regulation of extracellular g-aminobutyric acid levels in the prefrontal cortex of the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:350–357
Gulledge AT, Jaffe DB (1998) Dopamine decreases the excitability of layer V pyramidal cells in the rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 18:9139–9151
Jayaram P, Steketee JD (2004) Effects of repeated cocaine on medial prefrontal cortical GABAB receptor modulation of neurotransmission in the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system. J Neurochem (in press)
Kalivas PW, Pierce RC, Cornish J, Sorg BA (1998) A role for sensitization in craving and relapse in cocaine addiction. J Psychopharmacol 12:49–53
Karler R, Calder LD, Thai DK, Bedingfield JB (1998) The role of dopamine in the mouse frontal cortex: a new hypothesis of behavioral sensitization to amphetamine and cocaine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:435–443
McFarland K, Kalivas PW (2001) The circuitry mediating cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior. J Neurosci 21:8655–8663
McFarland K, Lapish CC, Kalivas PW (2003) Prefrontal glutamate release into the core of the nucleus accumbens mediates cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior. J Neurosci 23:3531–3537
Milliken GA, Johnson DE (1984) Analysis of messy data, vol 1, designed experiments. Lifetime Learning, Toronto, Ontario, pp 326–337
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York
Pirot S, Godbout R, Mantz J, Tassin J-P, Glowinski J, Thierry A-M (1992) Inhibitory effects of ventral tegmental area stimulation on the activity of prefrontal cortical neurons: evidence for the involvement of both dopaminergic and GABAergic components. Neuroscience 49:857–865
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993) The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Rev 18:247–291
Sesack SR, Deutch AY, Roth RH, Bunney BS (1989) Topographical organization of the efferent projections of the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: an anterograde tract-tracing study with Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin. J Comp Neurol 290:213–242
Sorg BA, Davidson DL, Kalivas PW, Prasad BM (1997) Repeated daily cocaine alters subsequent cocaine-induced increase of extracellular dopamine in the medial prefrontal cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:54–61
Steketee JD (2003) Neurotransmitter systems in the medial prefrontal cortex: potential role in sensitization to psychostimulants. Brain Res Rev 41:203–228
Taber MT, Das S, Fibiger HC (1995) Cortical regulation of subcortical dopamine release: mediation via the ventral tegmental area. J Neurochem 65:1407–1410
Vincent SL, Khan Y, Benes FM (1993) Cellular distribution of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in rat medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 13:2551–2564
Vincent SL, Khan Y, Benes FM (1995) Cellular colocalization of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Synapse 19:112–120
Williams JM, Steketee JD (2005) Time dependent effects of repeated cocaine administration on dopamine transmission in the medial prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 48:51–61
Wu W-R, Li N, Sorg BA (2003) Prolonged effects of repeated cocaine on medial prefrontal cortex dopamine response to cocaine and a stressful predatory odor challenge in rats. Brain Res 991:232–239
Zhang K, Tarazi FI, Campbell A, Baldessarini RJ (2000) GABAB receptors: altered coupling to G-proteins in rats sensitized to amphetamine. Neuroscience 101:5–10
Acknowledgements
All research efforts were financially supported by grants DA13470 and DA15965 (J.D.S.) from the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steketee, J.D., Walsh, T.J. Repeated injections of sulpiride into the medial prefrontal cortex induces sensitization to cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology 179, 753–760 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2102-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2102-5