Abstract
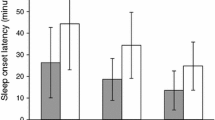
Rats were administered 0.5 mg/kg SC of haloperidol (H) or saline (S) daily from day 1 after birth until 20 days of age. At 60 days of age (40 days after the postnatal treatment with H or S was interrupted) the stereotyped behaviour and the effects on locomotor activity elicited by apomorphine in S- and H-pretreated rats were investigated. The intensity of apomorphine (0.5–1 mg/kg, SC)-induced stereotyped behaviour was significantly greater in the H-pretreated group than in S-pretreated animals and this was accompanied by a much more marked reduction of locomotor activity in H-pretreated than in S-pretreated rats. Finally, at 80 days of age (60 days after the postnatal treatment with H or S was interrupted) rats were subjected to a Differential Reinforcement of Low Rates schedule (DRL 15-s). The results indicate that the acquisition of the DRL task performance criterion (Rs/Rf≤2.5) was significantly more rapid in S-pretreated rats than in H-pretreated ones. In parallel biochemical experiments, acute H produced smaller increases in dopamine turnover in chronic H-treated rats compared with S-treated controls. These data indicate that H treatment in neonatal rats induces behavioural and biochemical changes which can be observed up to 60 days after H withdrawal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlenius S, Engel J, Lundborg P (1975) Antagonism by d-amphetamine of learning deficits in rats induced by exposure to antipsychotic drugs during early postnatal life. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 288:185–193
Ahlenius S, Engel J, Hard E, Larsson C, Lundborg P, Sinnerstedt P (1977) Open field behaviour and gross motor development in offspring of nursing rat mothers given penfluridol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:343–347
Cattabeni F, Racagni G, Spano PF, Costa E (eds) (1980) Long-term effects of neuroleptics. Advances in Biochem Psychopharm, vol 24. Raven Press, New York, p 1
Clark CVH, Gorman D, Vernadakis A (1970) Effects of prenatal administration of psychotropic drugs on behaviour of developing rats. Dev Psychobiol 3:225–235
Cortese I, Cristino R, Cuomo V (1981) Behavioural effects induced by low doses of methylmercury in rats. Br J Pharmacol (in press)
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1973) On the mode of action of apomorphine. Eur J Pharmacol 21:350–361
Coyle I, Wayer MJ, Singer G (1976) Behavioural teratogenesis: a critical evaluation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 4:191–200
Creese I, Iversen SD (1973) Blockage of amphetamine induced motor stimulation and stereotypy in the adult rat following neonatal treatment with 6-hydroxydopamine. Brain Res 55:369–382
Ferster CB, Skinner BF (1957) Schedules of reinforcement. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York
Gauron EF, Rowley VN (1973) Effects on offspring behaviour of parental early drug experience and cross-fostering. Psychopharmacologia 30:269–274
Golub M, Kornetsky C (1974) Seizure susceptibility and avoidance conditioning in adult rats treated prenatally with chlorpromazine. Dev Psychobiol 7:79–88
Holloway FA, Wansley RA (1973) Factors governing the vulnerability of DRL operant performance to the effects of ethanol. Psychopharmacologia 28:351–362
Karoum F, Gillin JC, Wyatt RJ (1975) Mass fragmentographic determination of some acidic and alcoholic metabolites of biogenic amines in the rat brain. J Neurochem 25:653–658
Kornetsky C (1970) Psychoactive drugs in the immature organism. Psychopharmacologia 17:195–196
Lison L (1961) Statistica applicata alla biologia sperimentale. Ambrosiana Milano
Oliverio A, Castellano C (1974) Genotype-dependent sensitivity and tolerance to morphine and heroin: dissociation between opiate-induced running and analgesia in the mouse. Psychopharmacologia 39:13–22
Rosengarten H, Friedhoff AJ (1979) Enduring changes in dopamine receptor cells of pups from drug administration to pregnant and nursing rats. Science 203:1133–1135
Sidman M (1955) Technique for assessing the effects of drugs on timing behavior. Science 122:925–928
Ungerstedt U (1979) Central dopamine mechanisms and unconditioned behaviour. In: Horn AS, Korf J, Westerink BHC (eds) The neurobiology of dopamine. Academic Press, New York, p 577
Werboff J, Dembicki EL (1962) Toxic effects of tranquilizers administered to gravid rats. J Neuropsychiatry 4:87–91
White BC, Tapp WN (1977) Unilateral catecholamine depletion of the corpus striatum and amphetamine induced turning: an ontogenetic study. Psychopharmacology 53:211–212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cuomo, V., Cagiano, R., Coen, E. et al. Enduring behavioural and biochemical effects in the adult rat after prolonged postnatal administration of haloperidol. Psychopharmacology 74, 166–169 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432686
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00432686