Abstract
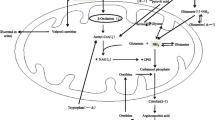
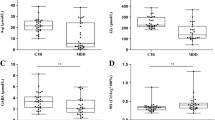
Twenty-four acutely ill schizophrenic patients (DSM-III-R), 18–42 years old, were treated for 6 weeks with sulpiride. Sulpiride was administered in three different daily dosages (starting with 400, 800 or 1200 mg) according to a double blind randomized administration schedule. The monoamine metabolites (MAM) homovanillic acid (HVA), 5-hydroxy-indoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenylglycol (HMPG) and the amino acids tyrosine, tryptophan, glutamate and glutamine were measured in serum before treatment and once a week during treatment. There were no significant differences between healthy controls and schizophrenic patients in serum levels of monoamine metabolites and amino acids before treatment. There was no dose-response effect of sulpiride on serum levels of the monoamine metabolites or the amino acids. The results are therefore based on the whole group of patients. During treatment the HMPG levels were reduced at all points in time. The serum level of HVA was significantly reduced after 6 weeks. The 5-HIAA and the amino acid levels were not changed during treatment. There were no significant correlations among the monoamine metabolites before treatment. During treatment, however, significant correlations were found among MAM and amino acids. Since the biochemical findings during the treatment were not related to the dose or the concentration of sulpiride the results may be related to secondary biochemical effects of sulpiride and/or to changes in the clinical state following treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfredsson G, Sedvall G, Wiesel F-A (1979) Quantitative analysis of sulpiride in body fluids by high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr Biomed Appl 164:187–193
Alfredsson G, Wiesel F-A, Lindberg M (1988a) Glutamate and glutamine in cerebrospinal fluid and serum from healthy volunteers — analytical aspects. J Chromatogr Biomed Appl 424:378–384
Alfredsson G, Wiesel F-A, Tylec A (1988b) Relationships between glutamate and monoamine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid and serum. Biol Psychiatry 23:689–697
Beck O, Hesselgren T (1980) Method for the determination of tryptophan in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. J Chromatogr Biomed Appl 181:100–102
Bjerkenstedt L, Härnryd C, Sedvall G (1979) Effect of sulpiride on monoaminergic mechanisms in psychotic women. Psychopharmacology 64:135–139
Bjerkenstedt L, Edman G, Hagenfeldt L, Sedvall G, Wiesel F-A (1985) Plasma amino acids in relation to cerebrospinal fluid monoamine metabolites in schizophrenic patients and healthy controls. Br J Psychiatry 147:276–282
Chang WM, Chen TY, Lee CF, Hung JC, Hu WM, Yeh EK (1987) Plasma homovanillic acid and subtyping of schizophrenia. Psychiatr Res 23:239–244
Chéramy A, Romo R, Godeheu G, Baruch P, Glowinski J (1986) In vivo presynaptic control of dopamine release in the cat caudate nucleus-II. Facilitatory or inhibitory influence of l-glutamate. Neuroscience 19:1081–1090
Davidsson M, Davis KL (1988) A comparison of plasma homovanillic acid concentrations in schizophrenic patients and normal controls. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:561–563
Doran AR, Pickar D, Labarca R, Douillet P, Wolkowitz OM, Thomas JW, Roy A, Paul SM (1985) Evidence for a daily rhythm of plasma HVA in normal controls but not in schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacol Bull 21:694–697
Farde L, Wiesel F-A, Halldin C, Sedvall G (1988) Central D2-dopamine receptor occupancy in schizophrenic patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:71–76
Hagenfeldt L, Bjerkenstedt L, Edman G, Sedvall G, Wiesel F-A (1984) Amino acids and monoamine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid — interrelationships in healthy subjects. J Neurochem 42:833–837
Harris PQ, Brown SJ, Friedman MJ, Bacopoulos NG (1984) Plasma drug and homovanillic acid levels in psychotic patients receiving neuroleptics. Biol Psychiatry 19:849–860
Hunneman DH (1983) Mass fragmentographic determination of homovanillic and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy mandelic acids in 50 μl plasma. Clin Chim Acta 135:169–174
Härnryd C, Bjerkenstedt L, Björk K, Gullberg B, Oxenstierna G, Sedvall G, Wiesel F-A, Wik G, Åberg-Wistedt A (1984a) Clinical evaluation of sulpiride in schizophrenic patients — a doubleblind comparison with chlorpromazine. Acta Psychiatr Scand [Suppl 69] 311:7–30
Härnryd C, Bjerkenstedt L, Gullberg G, Oxenstierna G, Sedvall G, Wiesel F-A (1984b) Time course for effects of sulpiride and chlorpromazine on monoamine metabolites and prolactin levels in cerebrospinal fluid from schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand [Suppl 69] 311:75–92
Kim JS, Kornhuber HH, Schmid-Burgk W, Holzmuller B (1980) Low cerebrospinal fluid glutamate in schizophrenic patients and a new hypothesis on schizophrenia. Neurosci Lett 20:379–382
Kopin IJ, Gordon EK, Jimerson DC, Polinsky RJ (1983) Relation between plasma and cerebrospinal fluid levels of 3-methoxy-4-hydrocyphenylglycol. Science 219:73–75
Lindroth P, Mopper K (1979) High performance liquid chromatographic determination of subpicomole amounts of amino acids by precolumn fluorescence derivatization with o-phthaldialdehyde. Anal Chem 51:1667–1674
Maas JW, Contreras SA, Seleshi E, Bowden CL (1988) Dopamine metabolism and disposition in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:553–559
Pardridge WM, Oldendorf WH (1977) Transport of metabolic substrates through the blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem 28:5–12
Perry TL, Hansen S (1969) Technical pitfalls leading to errors in the quantitation of plasma amino acids. Clin Chim Acta 25:53–58
Pickar D, Labarca R, Linnoila M, Roy A, Hommer D, Everett D, Paul SM (1984) Neuroleptic-induced decrease in plasma homovanillic acid and antipsychotic activity in schizophrenic patients. Science 32:521–542
Rau RV, Bailey J, Bishop M, Coppen A (1981) A clinical and pharmacodynamic evaluation of sulpiride. Psychopharmacology 73:77–80
Roberts PJ, McBean GJ, Sharif NA, Thomas EM (1982) Striatal glutamatergic function: modifications following specific lesions. Brain Res 235:83–91
Sedvall G, Wode-Helgodt B (1980) Aberrant monoamine metabolite levels in CSF and family history of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 37:1113–1116
Sedvall G, Alfredsson G, Bjerkenstedt L, Eneroth P, Fyrö B, Härnryd C, Swahn C-G, Wiesel F-A, Wode-Helgodt B (1975) Selective effects of psychoactive drugs on levels of monoamine metabolites and prolactin in cerebrospinal fluid of psychiatric patients. In: Proc 6th Int Congress of Pharmacology 3:255–267
Sjöquist B, Lindström B, Änggård E (1975) Mass fragmentographic determination of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl-glycol (HPMG) in urine, cerebrospinal fluid, plasma and tissues using a deuterium-labelled internal standard. J Chromatogr 105:309–316
Spitzer RL, Williams JBW (ed.) (1987) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Washington, DC
Swahn C-G, Sandgärde B, Wiesel F-A, Sedvall G (1976) Simultaneous determination of the three major monoamine metabolites in brain tissue and body fluids by a mass fragmentographic method. Psychopharmacology 48:147–152
Toru M, Schimazonon Y, Miyasaka M, Kokubo T, Mori Y, Nasu T (1972) A double-blind comparison of sulpiride with chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. J Clin Pharmacol 12:221–229
Wiesel F-A, Alfredsson G, Jönsson E (1989) Dose-finding and serum concentrations of neuroleptics in the treatment of schizophrenic patients. Proc 5th Int Meeting of Clinical Pharmacology in Psychiatry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Wik G, Wiesel F-A, Eneroth P, Sedvall G, Åström G (1986) Dexamethasone suppression test in schizophrenic patients before and during neuroleptic treatment. Acta Psychiatr Scand 74:161–167
Wode-Helgodt B, Fyrö B, Gullberg B, Sedvall G (1977) Effects of chlorpromazine treatment on monoamine metabolite levels in cerebrospinal fluid of psychotic patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand 56:129–142
Wood K, Swade C, Harwood J, Eccleston E, Bishop M, Coppen A (1977) Comparison of methods for the determination of total and free tryptophan in plasma. Clin Chim Acta 80:299–303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alfredsson, G., Wiesel, FA. Monoamine metabolites and amino acids in serum from schizophrenic patients before and during sulpiride treatment. Psychopharmacology 99, 322–327 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00445551
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00445551