Summary
Commercial ruthenium red has been tested for its purity by spectrophotometry. Impurities detected by this method could be abolished by nitric acid-precipitation of ruthenium brown. This substance has no effect on cell surface staining and converts almost completely to ruthenium red under the conditions used in electron microscopy. It was found, by photometric analysis, that in the ruthenium red-osmium tetroxide-cacodylate combination, generally used for cell surface staining, chemical reactions between ruthenium red and osmium tetroxide occur. As aerial oxidation of hexammineruthenium2+ leads to a product with some surface staining capability, it is suggested that an oxidazed product of ruthenium red is responsible for binding to cellular components, and that a reduced product of osmium tetroxide gives an additional contrast enhancement.
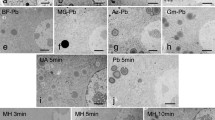
In ruthenium red-osmium dioxide combinations ruthenium red seems to bind to cell surfaces without any molecular alteration, and contrast is gained by the model proposed by Blanquet (1976b). The latter method could open a way for investigating the binding of ruthenium red to certain natural compounds involved in calcium transport, as postulated by a number of authors.
Both ruthenium-osmium combinations differ in their cell surface staining ability. The ruthenium red-osmium dioxide combination tends to form distinct subunits, whereas the osmium tetroxide variety stains homogeneously. In combination with osmium dioxide, the surface staining is affected by EDTA, and, in contrast to osmium tetroxide, a successive application of ruthenium red and osmium dioxide as possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanquet, P.R.: Ultrahistochemical study on the ruthenium red surface staining, I. Processes which give rise to electron-dense marker. Histochemistry 47, 63–78 (1976a)
Blanquet, P.R.: Ultrahistochemical study on the ruthenium red surface staining. II. Nature and affinity of the electron-dense marker. Histochemistry 47, 175–189 (1976b)
Dierichs, R., Inczédy-Marcsek, M., Lindner, E.: Der Einfluß von Kalzium und EDTA auf den aktivierenden Effekt von Rutheniumrot an menschlichen Blutplättchen. Acta Histochem. (Jena) Suppl. 20, 299–306 (1977)
Dierichs, R., Inczédy-Marcsek, M., Lindner, E.: Effekt des Polykations Rutheniumrot auf die Oberflächenmorphologie und Bildung von Aggregaten menschlicher Thrombozyten. Verh. Anat. Ges. 72, 387–389 (1978a)
Dierichs, R., Inczédy-Marcsek, M., Lindner, E.: Darstellung und Reinigung von Rutheniumamminoverbindungen und ihre Anwendungsmöglichkeit in der elektronenmikroskopischen Histochemie. Acta Histochem. (Jena) Suppl. 21, (1978 b in press)
Dierichs, R., Lindner, E.: Methods of heavy metal electron microscopic histochemistry applied to frog lung surfactant. Histochemistry 61, 199–212 (1979)
Endicott, J.F., Taube, H.: Studies on oxidation-reduction reactions of ruthenium ammines. Inorg. Chem. 4, 437–445 (1965)
Fletcher, J.M., Greenfield, B.F., Hardy, C.J., Scargill, D., Woodhead, J.L.: Ruthenium red. J. Chem. Soc. 1961, 2000–2006
Griffith, W.P.: The chemistry of the rarer platinum metals (Os, Ru, Ir and Rh). London, New York, Sydney: Interscience Publishers, Division of John Wiley & Sons 1967
Hartmann, H., Buschbeck, Ch.: Lichtabsorption und magnetisches Verhalten von Komplexverbindungen des Ru(III). Z. Phys. Chem. Neue Folge 11, 120–135 (1957)
Huet, Ch., Herzberg, M.: Effects of enzymes and EDTA on ruthenium red and concanavalin A labeling of the cell surface. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 42, 186–199 (1973)
Inczédy-Marscek, M.: Untersuchungen über die Bedeutung filamentöser Strukturen für die Haftung, Pseudopodienbildung und Aggregation der Thrombozyten. Diss. (Regensburg 1973)
Johansen, B. V.: A high performance Wehnelt grid for transmission electron microscopes. Micron 4, 121–135 (1973)
Kamino, K., Ogawa, M., Uyesaka, N., Inouye, A.: Calcium-binding of synaptosomes isolated from rat brain cortex. IV. Effects of ruthenium red on the co-operative nature of calcium-binding. J. Membrane Biol. 26, 345–356 (1976)
Lever, F.M., Powell, A.R.: Aminine complexes of ruthenium. J. Chem. Soc. (A) 1477–1482 (1969)
Luft, J.H.: Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat. Rec. 171, 347–368 (1971a)
Luft, J.H.: Ruthenium red and violet, II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat. Rec. 171, 369–416 (1971b)
Moore, C.L.: Specific inhibition of mitochondrial Ca++ transport by ruthenium red. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 42, 298–305 (1971)
Reed, K.C., Bygrave, F.L.: The inhibition of mitochondrial calcium transport by lanthanides and ruthenium red. Biochem. J. 140, 143–155 (1974a)
Reed, K.C., Bygrave, F.L.: A low molecular weight ruthenium complex inhibitory to mitochondrial Ca2+ transport. FEBS Lett. 46, 109–114 (1974b)
Spurr, A.R.: A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26, 31–43 (1969)
Vasington, F.D., Gazzotti, P., Tiozzo, R., Carafoli, E.: The effect of ruthenium red on Ca2+ transport and respiration in rat liver mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 256, 43–54 (1972)
Warner, W., Carchman, R.A.: Effects of ruthenium red, A 23187 and D-600 on steroidogenesis in Y-1 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 528, 409–415 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dierichs, R. Ruthenium red as a stain for electron microscopy. Some new aspects of its application and mode of action. Histochemistry 64, 171–187 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00490097
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00490097