Summary
-
1.
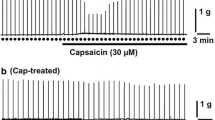
Capsaicin applied on the serosal surface of the urinary bladder in urethane-anaesthetized rats produces two distinct types of motor effects: a) a tetrodotoxin-, hexamethonium- and lidocaine-insensitive ‘tonic’ contraction and b) a series of tetrodotoxin-, hexamethonium- and lidocaine-sensitive rhythmic contractions.
-
2.
Both ‘tonic’ and rhythmic contractions are abolished by bladder denervation indicating their neurogenic origin. The rhythmic but not the ‘tonic’ component of the contractile effect of capsaicin is abolished by spinal cord transection indicating activation of a supraspinal micturition reflex.
-
3.
The motor effects of topical capsaicin are unaffected by pretreatment with indomethacin or diphenhydramine plus cimetidine.
-
4.
Pretreatment with a large dose of subcutaneous (SC) capsaicin increases both volume and pressure threshold for micturition while amplitude of micturition contraction is unaffected. Moreover the spinal somatovesical reflex elicited by pinching of the perineal skin is unaffected by capsaicindesensitization.
-
5.
The intracerebroventricular (ICV) administration of capsaicin reproduces the effects of SC capsaicin on the bladder response to saline filling. Rats pretreated with ICV capsaicin are as sensitive as controls in reacting to noxious heat (hot plate test) while the wiping response to instillation of capsaicin into one eye was abolished.
-
6.
These findings provide functional evidence for the presence in the rat urinary bladder of a capsaicin-sensitive innervation which subserves a sensory function in relaying volume/pressure information from detrusor muscle to central nervous system. Information carried through these capsaicin-sensitive fibers appears to be relevant for initiation of a supraspinal vesico-vesical micturition reflex. Functional evidence indicates that these fibers may terminate at supraspinal level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alm P, Elmer M (1975) Adrenergic and cholinergic innervation of the rat urinary bladder. Acta Physiol Scand 94:36–45
Blaivas J (1982) The neurophysiology of micturition: a clinical study of 550 patients. J Urol 127:958–963
Cervero F, McRitchie HA (1982) Neonatal capsaicin does not affect unmyelinated efferent fibers of the autonomic nervous system: functional evidence. Brain Res 239:283–288
Coleridge JC, Coleridge HM (1977) Afferent C fibers and cardiorespiratory reflexes. Am Rev Respir Dis 115:251–260
Fitzgerald M (1983) Capsaicin and sensory neurons — A review. Pain 15:109–130
Gamse R, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1980) Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurons and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol 68:207–213
Gamse R, Wax A, Zigmond RE, Leeman SE (1981a) Immunoreactive substance P in sympathetic ganglia: distribution and sensitivity toward capsaicin. Neuroscience 6:437–441
Gamse R, Leeman SE, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1981b) Differential effects of capsaicin on the content of somatostatin, substance P and neurotensin in the nervous system of the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 317:140–148
Holzer P, Bucsics A, Lembeck F (1982) Distribution of capsaicin sensitive nerve fibres containing immunoreactive substance p in cutaneous and visceral tissues of the rat. Neurosci Letters 31:253–257
Holzer-Petsche U, Lembeck F (1984) Systemic capsaicin treatment impairs the micturition reflex in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 83:935–941
Jancsó G, Kiraly E, Jacsó-Gabor A (1980) Direct evidence for an axonal site of action of capsaicin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 313:91–94
Jhamandas K, Yaksh TL, Harty G, Szolcsányi J, Go VLW (1984) Action of intrathecal capsaicin and its structural analogues on the content and release of spinal substance P: selectivity of action and relationship to analgesia. Brain Res 306:215–225
Juan H, Lembeck F, Seewann S, Hack U (1980) Nociceptor stimulation and PGE release by capsaicin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 312:139–143
Lembeck F, Gamse R (1982) Substance P in peripheral sensory processes in: Substance P in the nervous system (Ciba Foundation Symposium 91). Pitman, London, pp 35–54
Lembeck F, Skofitsch G (1982) Visceral pain reflex after pretreatment with capsaicin and morphine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 321:116–122
Ljungdahl A, Hokfelt T, Nilsson G (1978) Distribution of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat I Cell bodies and nerve terminals. Neuroscience 3:861–943
Maggi CA, Meli A (1982) An in vivo procedure for estimating spasmolytic activity in the rat by measuring smooth muscle contractions to topically applied acetylcholine. J Pharmacol Methods 8:39–46
Maggi CA, Meli A (1983) Reserpine induced detrusor hyperreflexia: an in vivo model for studying smooth muscle relaxants at urinary bladder level. J Pharmacol Methods 10:79–93
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1984a) The effects of topical capsaicin on rat urinary bladder motility in vivo. European J Pharmacol 103:41–50
Maggi CA, Evangelista S, Santicioli P, Grimaldi G, Giolitti A, Meli A (1984b) Evidence for the involvement of arachidonic acid metabolites in spontaneous and drung induced contractions of the rat urinary bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 230:500–514
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1985a) Evidence for the involvement of endogenous substance P in the motor effects of capsaicin in the rat urinary bladder. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:203–204
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1985b) The nonstop transvesical cystometrogram in urethane anaesthetized rats: a simple procedure for quantitative studies on the various phases of urinary bladder voiding cycle. J Pharmacol Methods (in press)
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1985c) Sympathetic inhibition of reflex activation of bladder motility during filling at a physiological-like rate in urethane anaesthetized rats. Neurourology Urodynamics 4:37–45
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Furio M, Meli A (1985d) Dual effect of clonidine on micturition reflex in urethane anaesthetized rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther (in press)
Maggi CA, Furio M, Santicioli P, Meli A (1985e) Intracisternal glycine activates micturition reflex in urethane anaesthetized rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 37:517–520
Maggi CA, Giuliani S, Santicioli P, Regoli D, Meli A (1985f) A comparison of the effects of substance P and substance K on blood pressure, salivation and urinary bladder motility in urethane anesthetized rats. Eur J Pharmacol 113:291–294
Mahony DT, Laferte RO, Blais DJ (1977) Integral storage and voiding reflexes. Urology 9:95–106
Nadelhaft I, Booth AM (1984) The location and morphology of preganglionic neurons and the distribution of visceral afferents from the rat pelvic nerve: a horseradish peroxidase study. J Comp Neurol 226:238–245
Santicioli P, Maggi CA, Meli A (1985) The effect of capsaicin pretretment on the cystometrogram of urethane anaesthetized rats. J Urol 133:700–704
Saria A, Lundberg JM, Hua X, Lembeck F (1983) Capsaicin-induced substance P release and sensory control of vascular permeability in the guinea pig ureter. Neurosci Letters 41:167–172
Saria A, Lundberg JM, Skofitsch G, Hua X, Lembeck F (1984) Neurogenic plasma extravasation in various organs in relation to capsaicin sensitive substance P neurons, In: Chahl LA, Szolcsányi J Lembeck F (eds) Antidromic vasodilatation and neurogenic inflammation. Akademiai Kiádo, Budapest, pp 245–258
Sato A, Sato Y, Shimada F, Torigata Y (1975) Changes in vesical function produced by cutaneous stimulation in rats. Brain Res 94:465–474
Satoh K, Shimizu N, Tohyama M, Maeda T (1978) Localization of the micturition reflex center at dorsolateral pontine tegmentum in the rat. Neurosci Letters 8:27–33
Sharkey KA, Williams RG, Schultzberg M, Dockray GJ (1983) Sensory substance P innervation of the urinary bladder: possible site of action of capsaicin in causing urine retention in rats. Neuroscience 10:861–868
Szolcsányi J (1984a) Capsaicin-sensitive chemoceptive neural system with dual sensory-efferent function. In: Chahl LA, Szolcsányi J, Lembeck F (eds) Antidromic vasodilatation and neurogenic inflammation. Akademiai Kiádo, Budapest, pp 26–52
Szolcsányi J (1984b) Capsaicin and neurogenic inflammation: History and early findings. In: Chahl LA, Szolcsányi J, Lembeck F (eds) Antidromic vasodilatation and neurogenic inflammation. Akademiai Kiádo, Budapest, pp 7–25
Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Hokfelt T, Lundberg JM, Forssmann WG, Reinecke M, Tschopp FA, Fischer JA (1984) Immunoreactive CGRP and substance P coexist in sensory neurons to the spinal cord and interact in spinal behaviour responses of the rat. Neurosci Letters 52:199–204
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maggi, C.A., Santicioli, P., Borsini, F. et al. The role of the capsaicin-sensitive innervation of the rat urinary bladder in the activation of micturition reflex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 332, 276–283 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00504867
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00504867