Summary
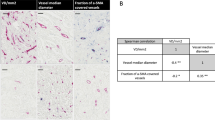
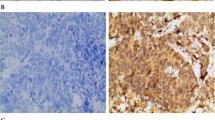
The importance of tumor angiogenesis in the process of tumor growth and progression in solid tumors has been widely accepted. We have investigated the significance of tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic indicator in a retrospective study including 328 primary breast cancer patients. The postoperative survey demonstrated that the microvessel density (MVD) evaluated by immunocytochemical staining for factor VIII-related antigen is a potent prognostic indicator. The relapse-free survival (RFS) rate of patients with over 100 microvessels/mm2 in a microscopic field was significantly worse compared to that of patients with less than 100 microvessels/mm2 (p<0.00001). The significance of MVD was found in both node-negative and node-positve patients (p< 0.005 and p<0.01, respectively). Multivariate analysis confirmed that MVD is an independent prognostic indicator for RFS. In the background factor analysis, MVD was significantly correlated with the number of metastatic nodes (p<0.01). In addition, the immunocytochemical analysis for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) demonstrated a close association between the increase in MVD and the expression of VEGF (p<0.001). VEGF status also was a significant prognostic indicator in univariate analysis for RFS (p<0.01). It was concluded that MVD is a potent prognostic indicator in primary breast cancer. Furthermore, it was also suggested that VEGF plays crucial roles in the promotion of angiogenesis in breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MVD:
-
microvessel density
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Folkman J: What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 82:4–6, 1990.
Bicknell R, Harris AL: Novel growth regulatory factors and tumor angiogenesis. Eur J Cancer 27: 781–784, 1991.
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua P, Allred EN, Moore DH, Meli S, Gasparini G: Tumor angiogenesis: a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 84:1875–1887, 1992.
Horak ER, Leek R, Klenk N, Lejeune S, Smith K, Stuart N, Greenall M, Stepniewska K, Harris AL: Angiogenesis, assessed by platelet/ endothelial cell adhesion molecule antibodies, as indicator of node metastases and survival in breast cancer. Lancet 340: 1120–1124, 1992.
Toi M, Kashitani J, Tominaga T: Tumor angiogenesis is an independent prognostic indicator in primary breast carcinoma. Int J Cancer, 55:371–374, 1993.
Gasparini G, Weidner N, Bevilacqua P, Maluta S, Dalla Palma P, Caffo O, Barbareschi M, Boracchi P, Marubini E, Pozza F: Tumor microvessel density, p53 expression, tumor size, and peritumoral lymphatic invasion are relevant prognostic markers in node-negative breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 12:454–466, 1994.
Macchiarini P, Fontanini G, Hardin MJ, Sqartini F, Angeletti CA: Relation of neovasculature to metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 340: 145–146, 1992.
Wakui S, Furusato M, Itoh T: Tumor angiogenesis in prostatic carcinoma with and without bone marrow metastasis: a morphometric study. J Pathol 168: 257–262, 1992.
Gasparini G, Weidner N, Maluta S, et al: Intratumoral microvessel density and p53 protein: Correlation with metastasis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 55:739–744, 1993.
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis — correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 324:1–8, 1991.
Toi M, Tominaga T, Osaki A, Toge T: Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in primary breast cancer: results of a biochemical study and an immunocytochemical study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 29:51–58, 1994.
Ferrara N, Houck KA, Jakeman LB, Winer J, Leung DW: The vascular endothelial growth factor family of polypeptides. J Cell Biochem 47:211–218, 1991.
Cox DR: Analysis of Binary Data. Methuen, London, 1970.
Bosari S, Lee AK, DeLellis R, Wiley BD, Heatley GJ, Silverman ML: Microvessel quantitation and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol 23: 755–761, 1992.
Sahin A, Sneige N, Singletary E, Ayala A: Tumor angiogenesis detected by factor VIII immunostaining in node negative breast carcinoma (NNBC): a possible predictor of distant metastasis. Lab Invest 66:17, 1992.
Fox SB, Leek RD, Smith K, Harris AL: Tumor angiogenesis in node-negative breast carcinomas — relationship to epidermal growth factor receptor, estrogen receptor, and survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat 29: 109–116, 1994.
Hall NR, Fish DE, Hunt N, Goldin RD, Guillou PJ, Monson JRT: Is the relatioship between angiogenesis and metastasis in breast cancer real? J Surg Oncol 23:755–761, 1992.
Van Hoef MEHM, Know WF, Dhesi SS, Howell A, Schor AM: Assessment of tumor vascularity as a prognostic factor in lymph node negative invasive breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 29A:1141–1145, 1993.
Esch F, Baird A, Ling N, Ueno N, Hill F, Deneroy L, Klepper R, Gospadarowicz D, Bohlen P, Guillemin R: Primary structure of bovine basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:6507–6511, 1985.
Ishikawa F, Miyazono K, Hellman U, Drexler H, Wernstedt C, Hagiwara K, Usuki K, Takaku F, Risau W, Heldin C-H: Identification of angiogenic activity and the cloning and expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor. Nature 338:557–562, 1989.
Bussolino F, Di Renzo MF, Ziche M, Bocchietto E, Olivero M, Naldini L, Gaudino G, Tamagnone L, Coffer A, Comoglio PM: Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J Cell Biol 119:629–641, 1992.
Toi M, Harris AL, Bicknell R: Interleukin-4 is a potent mitogen for capillary endothelium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 174:1287–1293, 1991.
Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi CA, Harvey VS, Dvorak HF: Tumor cells secrete a vascular permiability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science 219:983–985, 1983.
Ferrara N, Henzel WJ: Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161:851–858, 1989.
Toi M, Hoshina S, Takayanagi T, Tominaga T: Association of vascular endothelial growth factor expression with tumor angiogenesis and early response in primary breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res 85:1045–1049, 1994.
Ingber D, Fujita T, Kishimoto S, Sudo K, Kanamaru T, Berm H, Folkman J: Synthetic analogues of fumagillin that inhibit angiogenesis and suppress tumor growth. Nature 348:555–557, 1990.
Toi M, Yamamoto Y, Imazawa T, Takayanagi T, Akutsu K, Tominaga T: Antitumor effect of the angiogenesis inhibitor AGM-1470 and its combination effect with tamoxifen in DMBA induced mammary tumors in rats. Int J Oncol 3:525–528, 1993.
Kato T, Sato K, Kakinuma H, Matsuda Y: Enhanced suppression of tumor growth by combination of angiogenesis inhibitor O-(chloroacetyl-carbamoyl) fumagillol (TNP-470) and cytotoxic agents in mice. Cancer Res 54:5143–5147, 1994.
Kim KJ, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett N, Phillips HS, Ferrara N: Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Nature 362:841–844, 1993.
Kondo S, Asano M, Suzuki H: Significance of vascular endothelial growth factor / vascular permeability factor for solid tumor growth, and its inhibition by the antibody. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 194:1234–1241, 1993.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toi, M., Inada, K., Suzuki, H. et al. Tumor angiogenesis in breast cancer: Its importance as a prognostic indicator and the association with vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Breast Cancer Res Tr 36, 193–204 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00666040
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00666040