Summary
-
1.
mRNA transcripts for three isoforms of theα subunit of (Na, K)-ATPase have been previously identified in the rat nervous system and designatedα1,α2 andα3.
-
2.
In order to study the localization and expression of the differentα isoform mRNAs on a regional and cellular level in the brain, we prepared probes from the unique 3′ untranslated region of ratα1 cDNA and from a segment containing a portion of the translated region of ratα3 cDNA. These probes were used in dot blot andin situ hybridization assays of rat brain.
-
3.
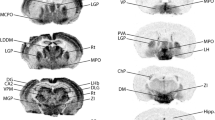
α1 mRNA was found predominantly in cerebral cortex, dentate gyrus of hippocampus, and specific isolated brain-stem nuclei such as locus ceruleus and motor nuclei V and VII. In contrastα3 mRNA was found predominantly in pyramidal neurons in the deep layers of cerebral cortex, in both pyramidal and dentate gyrus neurons of the hippocampus, and in neurons of most subcortical structures of the thalamus, basal ganglia, and brain-stem nuclei.
-
4.
In the cerebellum, Purkinje cells showed predominantlyα3, as did stellate and basket cells. The granule cells contained predominantlyα1.
-
5.
These experiments show that mRNAs for bothα1 andα3 isoforms of (Na, K)-ATPase are found in neurons of the CNS. The isoforms have unique cellular and regional distributions, which in some cases overlap.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers, R. W., Siegel, G. J., and Stahl, W. L. (1989). Membrane transport. InBasic Neurochemistry 4th edition (G. J. Siegel, B. W. Agranoff, R. W. Albers, and P. B. Molinoff, Eds.), Raven Press, New York, pp. 49–70.
Bevilacqua, A., Erickson, R. P., and Hieber, V. (1988). Antisense RNA inhibits endogenous gene expression in mouse preimplantation embryos: Lack of double-stranded RNA “melting” activity.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85831–835.
Filuk, P. E., Miller, M. A., Dorsa, D. M., and Stahl, W. L. (1989). Localization of messenger RNA encoding isoforms of the catalytic subunit of Na, K-ATPase in rat brain by in situ hybridization histochemistry.Neurosci. Res. Comm. 5155–162.
Hara, Y., Ohtsubo, M., Kojima, T., Noguch, S., Nakao, M., and Kawamura, M. (1989). Expression of active alpha-3 subunit of rat brain Na+, K+-ATPase from the messenger RNA injected into xenopus oocytes.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 163102–105.
Herrera, V. L., Emanuel, J. R., Ruiz Opazo, N., Levenson, R., and Nadal Ginard, B. (1987). Three differentially expressed Na, K-ATPase alpha subunit isoforms: Structural and functional implications.J. Cell Biol. 1051855–1865.
Hieber, V., Siegel, G. J., Desmond, T., Lee-Hwa Liu, J., and Ernst, S. A. (1989). Na, K-ATPase: Comparison of the cellular localization of alpha-subunit mRNA and polypeptide in mouse cerebellum, retina, and kidney.J. Neurosci. Res. 239–20.
Lytton, J. (1985). Insulin affects the sodium affinity of the rat adipocyte (Na, K)-ATPase.J. Biol. Chem. 26010075–10080.
Mata, M., Siegel, G. J., Hieber, V., Beaty, M. W., and Fink, D. J. Differential distribution of (Na, K)-ATPaseα isoform mRNAs in the peripheral nervous system.Brain Res. (in press).
McGrail, K. M., and Sweadner, K. J. (1989). Complex expression patterns for the Na, K+ ATPase isoforms in retina and optic nerve.Eur. J. Neurosci. 2170–176.
Orlowski, J., and Lingrel, J. B. (1988). Tissue-specific and developmental regulation of rat Na, K-ATPase catalytic alpha isoform and beta subunit mRNAs.J. Biol. Chem. 26310436–10442.
Orlowski, J., and Lingrel, J. B. (1990). Thyroid and glucocorticoid hormones regulate expression of multiple Na, K-ATPase genes in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes.J. Biol. Chem. 2653462–3470.
Price, E. M., and Lingrel, J. B. (1988). Structure-function relationships in the Na, K-ATPase alpha subunit: Site-directed mutagenesis of glutamine-11 to arginine and asparagine-122 to aspartic acid generates a ouabain resistant enzyme.Biochemistry 278400–8408.
Schneider, J. W., Mercer, R. W., Gilmore-Hebert, M., Utset, M. F., Lai, C., Greene, A., and Benz, E. J. (1988). Tissue specificity, localization in brain, and cell-free translation of mRNA encoding the A3 isoform of Na+, K+-ATPase.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85284–288.
Schulte, B. A., and Adams, J. C. (1990). Distribution of immunoreactive Na+, K+-ATPase in gerbil cochlea.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 37127–134.
Shull, G. E., Greeb, J., and Lingrel, J. B. (1986). Molecular cloning of three distinct forms of the Na+, K+-ATPase alpha-subunit from rat brain.Biochemistry 258125–8132.
Shyjan, A. W., and Levenson, R. (1989). Antisera specific for the alphal, alpha2, alpha3, and beta subunits of the Na, K-ATPase: Differential expression of alpha and beta subunits in rat tissue membranes.Biochemistry 284531–4535.
Shyjan, A. W., Cena, V., Klein, D. C., and Levenson, R. (1990). Differential expression and enzymatic properties of the Na, K-ATPase alpha3 isoenzyme in rat pineal glands.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,871178–1182.
Spicer, S. F., Schulte, B. A., and Adams, J. C. (1990). Immunolocalization of Na+, K+-ATPase and carbonic anhydrase in the gerbil vestibular system.Hear. Res. 43205–217.
Sweadner, K. J. (1979). Two molecular forms of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated ATPase in brain. Separation and difference in affinity for strophanthidin.J. Biol. Chem. 2546060–6067.
Sweadner, K. J. (1988). Preparation of the alpha(+) isozyme of the Na+, K+-ATPase from mammalian axolemma.Methods Enzymol. 15665–71.
Sweadner, K. J. (1989). Isozymes of the Na/K-ATPase.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 988185–220.
Urayama, O., and Sweadner, K. J. (1988). Ouabain sensitivity of the alpha 3 isozyme of rat Na, K-ATPase.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 156796–800.
Urayama, O., Shutt, H., and Sweadner, K. J. (1989). Identification of three isozyme proteins of the catalytic subunit of the Na, K-ATPase in rat brain.J. Biol. Chem. 2648271–8280.
Watson, S. J., Sherman, J. G., Kelsey, J. E., Burke, S., and Akil, H. (1987). Anatomical localization of mRNA: In situ hybridization of neuropeptide systems. InIn Situ Hybridization: Applications to Neurobiology (K. L. Valentino, J. H. Eberwine, and J. D. Barchas, Eds.), Oxford University Press, New York, pp. 126–145.
Yang-Feng, T. L., Schneider, J. W., Lindgren, V., Shull, M. M., Benz, E. J., Lingrel, J. B., and Francke, U. (1988). Chromosomal localization of human Na, K-ATPase alpha and beta subunit genes.Genomics 2128–138.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hieber, V., Siegel, G.J., Fink, D.J. et al. Differential distribution of (Na, K)-ATPaseα isoforms in the central nervous system. Cell Mol Neurobiol 11, 253–262 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00769038
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00769038