Abstract
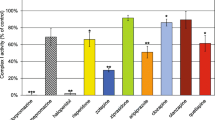
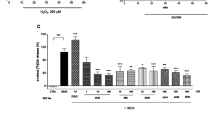
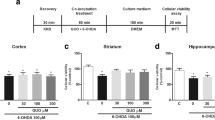
Since the discovery of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced parkinsonism, it has been postulated that (a) MPTP-like toxin(s) such as 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline (TIQ) may induce Parkinson's disease. As the neuronal degeneration in MPTP-induced parkinsonism is thought to be caused by the inhibition of the mitochondrial respiration by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+), we studied the effects of TIQ-like alkaloids including dopaminederived ones on the mitochondrial respiration using mouse brains. TIQ, tetrahydropapaveroline (THP), and tetrahydropapaverine (THPV) produced significant inhibition of the state 3 and 4 respiration and respiratory control ratio supported by glutamate + malate, the activity of Complex 1 and the ATP synthesis. Among those compounds, THPV was most potent. Toxic properties of these compounds on mitochondria were quite similar to that of MPP+. Our results support the hypothesis that (a) MPTP- or MPP+-like substance(s) may be responsible for the nigral degeneration in Parkinson's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MPTP:
-
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- MPP+ :
-
1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion
- ATP:
-
adenosine triphosphate
- ADP:
-
Adenosine diphosphate
- TCL:
-
tricarboxylic acid
- TIQ:
-
cycle: 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline
- THPV:
-
Tetrahydropapaverine
- THP:
-
Tetrahydropaveroline
References
Langston, J. W., Ballard, P., Tetrud, J. W. and Irwin, I. 1983. Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science. 219:979–980.
Langston, J. W., Irwin, I., Langston, E. B., and Forno, L. S. 1984. 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+): Identification of metabolite of MPTP, A toxin selective to the substantia nigra. Neurosci. Lett. 48:87–92.
Irwin, I., and Langston, J. W. 1985. Selective accumulation of MPP+ in the substantia nigra: A key to neurotoxicity. Life Sci. 36:207–212.
Jenner, P., Rupniak, N. M. J., Rose, S., Kelly, E., Kilpatrick, G., Lees, A., and Marsden, C. D. 1984. 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced parkinsonism in the common marmoset. Neurosci. Lett. 50:85–90.
Langston, J. W. 198. MPTP neurotoxicity: An overview and characterization of phases of toxicity. Life Sci. 36:201–206.
Heikkila, R. E., Nicklas, W. J., Vyas, I., and Duvoisin, R. C. 1985. Dopaminergic toxicity of rotenone and the 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion after their stereotaxic administration to rats: Implication for the mechanism of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine toxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 62:389–394.
Ramsay, R. R., Salach, J. I., and Singer, T. P. 1986. Uptake of the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine (MPP+) by mitochondria and its relation to the inhibition of the mitochondrial oxidation of NAD+-linked substrates by MPP+. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 134:743–748.
Mizuno, Y., Saitoh, T., and Sone, N. 1987. Inhibition of mitochondrial NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 143:294–299.
Mizuno, Y., Saitoh, T., and Sone, N. 1987. Inhibition of mitochondrial alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 143:971–976.
Mizuno, Y., Suzuki, K., Sone, N., and Saitoh, T. 1987c. Inhibition of ATP synthesis by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+) in isolated mitochondria from mouse brains. Neurosci. Lett. 81:204–208.
Mizuno, Y., Sone, N., and Saitoh, T. 1987d. Effects of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine and 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion on activities of the enzymes in the electron transport system in mouse brain. J Neurochem. 48:1787–1793.
Mizuno, Y., Sone, N., Suzuki, K., and Saitoh, T. 1988a. Studies on the toxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+) against mitochondria of mouse brain. J. Neurol. Sci. 86:97–110.
Nagatsu, T., and Hirata, Y. 1987. Inhibition of the tyrosine hydroxylase system by MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+) and the structurally related compounds in vitro and in vivo. Europ. Neurol. 26 (suppl.1):11–15.
Kohno, M., Ohta, S., and Hirobe, M. 1986. Tetrahydroisoquinoline and 1-methyl-tetrahydroisoquinoline as a novel endogenous amines in rat brains. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 140:448–454.
Niwa, T., Takeda, Kaneda, N., Hashizume, Y., and Nagatsu, T. 1987. Presence of tetrahydroisoquinoline and 2-methyl-tetrahydroquinoline in parkinsonian and human brains. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 144:1084–1089.
Ohta, S., Kohno, M., Makino, Y., Tachikawa, O., and Hirobe, M. 1987. Tetrahydroisoquinoline and 1-methyl-tetrahydroisoquinoline are present in the human brain: relation to Parkinson's disease. Biomed. Res. 8:453–456.
Nagatsu, T., and Yoshida, M. 1988. An endogenous substance of the brain, tetrahydroisoquinoline, produces parkinsonism in primates with decreased dopamine, tyrosine hydroxylase and biopterin in the nigrostriatal regions. Neurosci. Lett. 87:178–182.
Suzuki, K., Mizuno, Y., and Yoshida, M. 1988. Inhibition of mitochondrial NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase activity and ATP synthesis by tetrahydroisoquinoline. Neurosci. Lett. 86:105–108.
Sandler, M., and Carter, S. B. 1973. Tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloids: in vivo metabolites of L-dopa in man. Nature. 241:439–443.
Algeri, S., Baker, K. M., Frigerio, A., and Turner, A. J. 1973. Identification and quantitation of tetrahydropapaveroline in rat brain. Proc. Annu. Conf. Amer. Soc. Mass Spectrum., 21st, San Francisco, Calif. p. 301.
Davis, V. E., and Walsh, M. J. 1970. Alcohol, amines, and alkaloids: A possible biochemical basis for alcohol addiction. Science. 167:1005–1007.
Cohen, G., and Collins, M. 1970. Alkaloids from catecholamines in adrenal tissue: Possible role in alcoholism. Science. 167:1749–1751.
Whaley, W., and Govindachari, T. R. 1951. The pictet-spengler synthesis of tetrahydroisoquinolines and related compounds. Org. React. 6:151–190.
Weiner, C. D., and Collins, M. A. 1978. Tetrahydroisoquinolines derived from catecholamines or dopa: Effects on brain tyrosine hydroxylase activity. Biochem. Pharm. 27:2699–2703.
Shen, R-s., Smith, R. V., Davis, P. J., Brubaker, A., and Abell, C. W. 1982. Dopamine-derived tetrahydroisoquinolines. J. Biol. Chem. 257:7294–7297.
Niwa, T., Takeda, N., Tatematsu, A., Matsuura, S., Yoshida, M., and Nagatsu, T. 1988. Migration of tetrahydroisoquinoline, a possible parkinsonain neurotoxin, into monkey brain from blood as proved by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 452:85–91.
Dagani, F., Marzatico, F., and Curti, D. 1988. Oxidative metabolism of nonsynaptifc mitochondria isolated from rat brain hippocampus: a comparative regional study. J. Neurochem. 50:1233–1236.
Hertz, L., Drejer, J., and Schousboe, A. 1988. Energy metabolism in glutamatergic neurons, GABAergic neurons and astrocytes in primary cultures. Neurochem. Res. 13:605–610.
Lai, J. C. K., and Clark, J. B. 1979. Preparation of synaptic and nonsynaptic mitochondria from mammalian brain. Pages 51–60,in Fleischer, S., and Packer, L. (eds.), Methods in Enzymology, Vol 55, Academic Press, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, K., Mizuno, Y. & Yoshida, M. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration by 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-like endogenous alkaloids in mouse brain. Neurochem Res 15, 705–710 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00973651
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00973651