Abstract
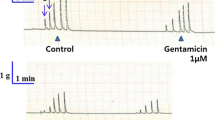
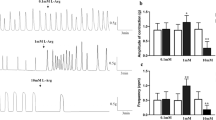
The effects of GABA receptor agonists were investigated on guinea-pig isolated ileum longitudinal muscle with intact myenteric plexus. Electrical field stimulation (1 Hz, 10 s) of the histamine (1 μM)-precontracted preparation caused a contraction followed by a relaxation. Relaxations were inhibited by l-N G-nitro-arginine (l-NA; EC50 3 μM) in a concentration-dependent manner. The inhibitory action of 10 μM l-NA was blocked by 10 μM l-arginine but not by d-arginine, which indicates that the relaxation was largely mediated by endogenous nitric oxide (NO). Tetrodotoxin (1 μM) reduced the relaxation only by about 50%. GABA and the GABAB agonist, baclofen, inhibited the field stimulation-induced longitudinal muscle relaxation in a concentration-dependent manner. The GABAB receptor antagonist, saclofen (10 μM), antagonised the effect of baclofen (apparent pA 2 of saclofen: 5.6). Muscimol (10 μM) similarly inhibited the relaxation, and this inhibition was prevented by bicuculline (1 μM). It is concluded that nitrergic nerves of the guinea-pig myenteric plexus are endowed with GABAA and GABAB receptors which mediate inhibition of NO release.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 February 1999 / Accepted: 22 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilbinger, H., Ginap, T. & Erbelding, D. GABAergic inhibition of nitric oxide-mediated relaxation of guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 359, 500–504 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005382
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005382