Abstract.
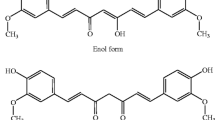
Curcumin is the active ingredient in the traditional herbal remedy and dietary spice turmeric (Curcuma longa). Curcumin has a surprisingly wide range of beneficial properties, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic activity. The pleiotropic activities of curcumin derive from its complex chemistry as well as its ability to influence multiple signaling pathways, including survival pathways such as those regulated by NF-κB, Akt, and growth factors; cytoprotective pathways dependent on Nrf2; and metastatic and angiogenic pathways. Curcumin is a free radical scavenger and hydrogen donor, and exhibits both pro- and antioxidant activity. It also binds metals, particularly iron and copper, and can function as an iron chelator. Curcumin is remarkably non-toxic and exhibits limited bioavailability. Curcumin exhibits great promise as a therapeutic agent, and is currently in human clinical trials for a variety of conditions, including multiple myeloma, pancreatic cancer, myelodysplastic syndromes, colon cancer, psoriasis and Alzheimer’s disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 1 October 2007; received after revision 16 January 2008; accepted 24 January 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatcher, H., Planalp, R., Cho, J. et al. Curcumin: From ancient medicine to current clinical trials. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 1631–1652 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-7452-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-7452-4