Abstract
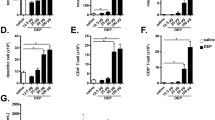
Although several studies have demonstrated that airway exposure to diesel exhaust particles (DEP) induces lung inflammation, the signaling pathways involved in the pathogenesis remain unclear. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are generally accepted to be pathogen recognition receptors in mammalians. In the present study, we investigated the role of TLR-4 in DEP-induced lung inflammation and cytokine expression in the lung in TLR-4 point mutant (C3H/HeJ) mice and corresponding control (C3H/HeN) mice. Both the types of mice were randomized into four experimental groups that received vehicle or DEP (12 mg/kg body weight) by intratracheal instillation (n=8–10 in each group). Cellular profile of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid, expressions of cytokines and chemokines in the lung, and circulatory fibrinogen levels were evaluated 24 h after the instillation.DEP challenge revealed a significant increase in the numbers of total cells and neutrophils in the BAL fluid as compared to vehicle challenge, however, the numbers were less in C3H/HeJ mice than in C3H/HeN mice. DEP exposure significantly induced the lung expression of interleukin (IL)-1β, keratinocyte chemoattractant (KC), and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1α when compared to vehicle challenge in both genotypes of mice. In the presence of DEP, the level of MIP-1α was significantly lower in C3H/HeJ mice than in C3H/HeN mice, however, the levels of IL-1β, KC, and fibrinogen showed opposite findings. These results suggest that TLR-4 is one of recognition receptors against DEP in the airways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreotti F, Burzotta F, Maseri A (1999) Fibrinogen as a marker of inflammation: a clinical view. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 10:S3–S4
Becker S, Fenton MJ, Soukup JM (2002) Involvement of microbial components and toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in cytokine responses to air pollution particles. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 27:611–618
Becker S, Dailey L, Soukup JM, Silbajoris R, Devlin RB (2005) TLR-2 is involved in airway epithelial cell response to air pollution particles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203:45–52
Beutler B, Poltorak A (2000) The search for Lps: 1993–1998. J Endotoxin Res 6:269–293
Driscoll KE (1994) Macrophage inflammatory proteins: biology and role in pulmonary inflammation. Exp Lung Res 20:473–490
Hollingsworth JW 2nd, Cook DN, Brass DM, Walker JK, Morgan DL, Foster WM, Schwartz DA (2004) The role of toll-like receptor 4 in environmental airway injury in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:126–132
Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Ogawa T, Takeda Y, Takeda K, Akira S (1999) Cutting edge: toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J Immunol 162:3749–3752
Ichinose T, Furuyama A, Sagai M (1995) Biological effects of diesel exhaust particles (DEP). II. Acute toxicity of DEP introduced into lung by intratracheal instillation. Toxicology 99:153–167
Inoue K, Takano H, Yanagisawa R, Sakurai M, Shimada A, Morita T, Sato M, Yoshino S, Yoshikawa T, Tohyama C (2004) Protective role of interleukin-6 in coagulatory and hemostatic disturbance induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Thromb Haemost 91:1194–1201
Inoue K, Takano H, Yanagisawa R, Ichinose T, Shimada A, Yoshikawa T (2005) Pulmonary exposure to diesel exhaust particles induces airway inflammation and cytokine expression in NC/Nga mice. Arch Toxicol (in press)
Johnson GB, Brunn GJ, Platt JL (2004) Cutting edge: an endogenous pathway to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)-like reactions through toll-like receptor 4. J Immunol 172:20–24
Lim HB, Ichinose T, Miyabara Y, Takano H, Kumagai Y, Shimojyo N, Devalia JL, Sagai M (1998) Involvement of superoxide and nitric oxide on airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness induced by diesel exhaust particles in mice. Free Radic Biol Med 25:635–644
Matsumoto T, Yokoi K, Mukaida N, Harada A, Yamashita J, Watanabe Y, Matsushima K (1997) Pivotal role of interleukin-8 in the acute respiratory distress syndrome and cerebral reperfusion injury. J Leukoc Biol 62:581–587
McClellan RO (1987) Health effects of exposure to diesel exhaust particles. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 27:279–300
Ohashi K, Burkart V, Flohe S, Kolb H (2000) Cutting edge: heat shock protein 60 is a putative endogenous ligand of the toll-like receptor-4 complex. J Immunol 164:558–561
Okamura Y, Watari M, Jerud ES, Young DW, Ishizaka ST, Rose J, Chow JC, Strauss JF 3rd (2001) The extra domain A of fibronectin activates toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem 276:10229–10233
Parker LC, Whyte MK, Dower SK, Sabroe I (2005) The expression and roles of toll-like receptors in the biology of the human neutrophil. J Leukoc Biol 77:886–892
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B (1998) Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 282:2085–2088
Sagai M, Furuyama A, Ichinose T (1996) Biological effects of diesel exhaust particles (DEP). III. Pathogenesis of asthma like symptoms in mice. Free Radic Biol Med 21:199–209
Sanbongi C, Takano H, Osakabe N, Sasa N, Natsume M, Yanagisawa R, Inoue K, Kato Y, Osawa T, Yoshikawa T (2003) Rosmarinic acid inhibits lung injury induced by diesel exhaust particles. Free Radic Biol Med 34:1060–1069
Singer M, Sansonetti PJ (2004) IL-8 is a key chemokine regulating neutrophil recruitment in a new mouse model of Shigella-induced colitis. J Immunol 173:4197–4206
Smiley ST, King JA, Hancock WW (2001) Fibrinogen stimulates macrophage chemokine secretion through toll-like receptor 4. J Immunol 167:2887–2894
Takano H, Yoshikawa T, Ichinose T, Miyabara Y, Imaoka K, Sagai M (1997) Diesel exhaust particles enhance antigen-induced airway inflammation and local cytokine expression in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:36–42
Takano H, Yanagisawa R, Ichinose T, Sadakane K, Yoshino S, Yoshikawa T, Morita M (2002) Diesel exhaust particles enhance lung injury related to bacterial endotoxin through expression of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:1329–1335
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, Ki., Takano, H., Yanagisawa, R. et al. The role of toll-like receptor 4 in airway inflammation induced by diesel exhaust particles. Arch Toxicol 80, 275–279 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-005-0040-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-005-0040-6