Abstract
Rationale
Associative learning during classical trace eyeblink conditioning has been shown to be regulated by serotonin 5-HT2A receptors and to be critically dependent on the integrity of frontal cortex. Chronic administration of 5-HT2A ligands has been shown to produce a selective up- or down-regulation of 5-HT2A receptors in frontal cortex.
Objectives
We examined whether alterations in 5-HT2A receptor density had a functional significance with respect to associative learning.
Methods
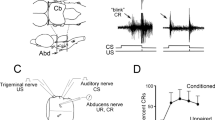
Animals received chronic injections of LSD, BOL or MDL11,939 and 1 day later began classical trace conditioning of the eyeblink response.
Results
The density of 5-HT2A receptors in frontal cortex was significantly increased at 1–4 days after the cessation of chronic injections of the selective 5-HT2A receptor ligand MDL11,939. Rabbits demonstrated an enhancement of associative learning when training began at 1 day after cessation of chronic MDL11,939 injections, but acquired at the same rate as controls when training began at 8 days after cessation of injections, a time when receptor density had returned to control levels. Animals that began training 1 day after chronic injections of BOL or LSD, drugs that produce decreases in 5-HT2A receptor density, demonstrated normal rates of acquisition.
Conclusions
These results indicate that increases in the density of 5-HT2A receptors in frontal cortex are associated with increases in the rate of associative learning, and further support an important role for this receptor in cortical circuitry that mediates learning. More generally, these results suggest an approach for functional remodeling of brain regions in the adult animal.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK, Marek GJ (1997) Serotonin induces excitatory postsynaptic potentials in apical dendrites of neocortical pyramidal cells. Neuropharmacology 36:589–599
Aghajanian GK, Marek GJ (2000) Serotonin model of schizophrenia: emerging role of glutamate mechanisms. Brain Res Rev 31:302–312
Aloyo VJ, Harvey JA (2000) Antagonist binding at 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors in the rabbit: high correlation with the profile for the human receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 406:163–169
Aloyo VJ, Dave KD, Rahman T, Harvey JA (2001) Selective and divergent regulation of cortical 5-HT2A receptors in the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:1066–1072
Andreasen NC, O’Leary DS, Flaum M, Nopoulos P, Watkins GL, Boles Ponto LL, Hichwa RD (1997) Hypofrontality in schizophrenia: distributed dysfunctional circuits in neuroleptic-naive patients. Lancet 349:1730–1734
Arora RC, Meltzer HY (1991) Serotonin2 (5-HT2) receptor binding in the frontal cortex of schizophrenic patients. J Neural Transm 85:19–29
Buchanan SL, Powell DA (1982) Cingulate cortex: its role in Pavlovian conditioning. J Comp Physiol Psychol 96:755–774
Burnet PWJ, Eastwood SL, Harrison PJ (1996) 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptor mRNAs and binding sites are differentially altered in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:442–455
Clark RE, Squire LR (1998) Classical conditioning and brain systems: the role of awareness. Science 280:77–81
Corbetta M, Miezin FM, Dobmeyer S, Shulman GL, Petersen SE (1991) Selective and divided attention during visual discriminations of shape, color and speed: functional anatomy by positron emission tomography. J Neurosci 11:2383–2402
Fuxe K, Agnati LF, Pich EM, Meller E, Goldstein M (1987) Evidence for a fast receptor turnover of D1 dopamine receptors in various forebrain regions of the rat. Neurosci Lett 81:183–187
Gabriel M, Kubota Y, Sparenborg S, Straube K, Vogt BA (1991) Effects of cingulate cortical lesions on avoidance learning and training-induced unit activity in rabbits. Exp Brain Res 86:585–600
Goldman-Rakic PS (1987) Circuitry of the prefrontal cortex and the regulation of behavior by representational knowledge. In: Plum F, Mountcastle V (eds) Handbook of physiology (vol 5). American Physiological Society, Bethesda, Md., pp 373–417
Harvey JA (1996) Serotonergic regulation of associative learning. Behav Brain Res 73:47–50
Harvey JA (2003) Role of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor in learning. Learn Mem (in press)
Hasuo H, Matsuoka T, Akasu T (2002) Activation of presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptors facilitates excitatory synaptic transmission via protein kinase C in the dorsolateral septal nucleus. J Neurosci 22:7509–7517
Hernandez I, Sokolov BP (2000) Abnormalities in 5-HT2A receptor mRNA expression in frontal cortex of chronic elderly schizophrenics with varying histories of neuroleptic treatment. J Neurosci Res 59:218–225
Hoyer D, Pazos A, Probst A, Palacios JM (1986) Serotonin receptors in the human brain: II. Characterization and autoradiographic localization of 5-HT1C and 5-HT2 recognition sites. Brain Res 376:97–107
Jakab RL, Goldman-Rakic PS (1998) 5-Hydroxytryptamine2A serotonin receptors in the primate cerebral cortex: possible site of action of hallucinogenic and antipsychotic drugs in pyramidal cell apical dendrites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:735–740
Kronforst-Collins MA, Disterhoft JF (1998) Lesions of the caudal area of rabbit medial prefrontal cortex impair trace eyeblink conditioning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 69:147–162
Lambe EK, Goldman-Rakic PS, Aghajanian GK (2000) Serotonin induces EPSCs preferentially in layer V pyramidal neurons of the frontal cortex in the rat. Cereb Cortex 10:974–980
Lennox BR, Park SBG, Medley I, Morris PG, Jones PB (2000) The functional anatomy of auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia. Psychiatr Res Neuroimaging 100:13–20
Leysen JE, Pauwels PJ (1990) 5-HT2A receptors, roles and regulation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 600:183–191
Liddle PF, Morris DL (1991) Schizophrenic syndromes and frontal lobe performance. Br J Psychiatry 158:340–345
López-Giménez JF, Vilaró MT, Palacios JM, Mengod G (1998) [3H]MDL100,907 labels 5-HT2A receptors selectively in primate brain. Neuropharmacology 37:1147–1158
Marek GJ, Aghajanian GK (1994) Excitation of interneurons in piriform cortex by 5-hydroxytryptamine: blockade by MDL100,907, a highly selective 5-HT2A receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 259:137–141
Marek GJ, Aghajanian GK (1996) LSD and the phenethylamine hallucinogen DOI are potent partial agonists at 5-HT2A receptors on interneurons in rat piriform cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:1373–1382
McCarthy G, Puce A, Constable RT, Krystal JH, Gore JC, Goldman-Rakic P (1996) Activation of human prefrontal cortex during spatial and nonspatial working memory tasks measured by functional MRI. Cereb Cortex 6:600–611
Meltzer HY (1999) The role of serotonin in antipsychotic drug action. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:106S–115S
Mesulam MM, Geschwind N (1978) On the possible role of neocortex and its limbic connections in the process of attention and schizophrenia: clinical cases of inattention in man and experimental anatomy in monkey. J Psychiatr Res 14:249–259
Munson PJ, Rodbard D (1980) LIGAND: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem 107:220–239
Pazos A, Cortes R, Palacios JM (1985) Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. II. Serotonin-2 receptors. Brain Res 346:231–249
Quirion R, Richard J, Dam TV (1985) Evidence for the existence of serotonin type-2 receptors on cholinergic terminals in rat cortex. Brain Res 333:345–349
Raghupathi RK, Brousseau DA, McGonigle P (1996) Time-course of recovery of 5-HT1A receptors and changes in 5-HT1A receptor mRNA after irreversible inactivation with EEDQ. Mol Brain Res 38:233–242
Rinaldi-Carmona M, Bouaboula M, Congy C, Oury-Donat F, Simiand J, Shire D, Casellas P, Soubrie P, Breliere JC, Le Fur G (1993) Up-regulation of 5-HT2 receptors in the rat brain by repeated administration of SR 46349B, a selective 5-HT2 antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 246:73–80
Romano AG, Bormann NM, Harvey JA (1991) A unique enhancement of associative learning produced by methylenedioxyamphetamine. Behav Pharmacol 2:225–231
Sheldon PW, Aghajanian GK (1991) Excitatory responses to serotonin (5-HT) in neurons of the rat piriform cortex: evidence for mediation by 5-HT1C receptors in pyramidal cells and 5-HT2 receptors in interneurons. Synapse 9:208–218
Tanaka E, North RA (1993) Actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine on neurons of the rat cingulate cortex. J Neurophysiol 69:1749–1757
Weiner DM, Burstein ES, Nash N, Croston GE, Currier EA, Vanover KE, Harvey SC, Donohue E, Hansen HC, Andersson CM, Spalding TA, Gibson DFC, Krebs-Thomson K, Powell SB, Geyer MA, Hacksell U, Brann MR (2001) 5-Hydroxytryptamine2A receptor inverse agonists as antipsychotics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:268–276
Welsh SE, Kachelries WJ, Romano AG, Simansky KJ, Harvey JA (1998) Effects of LSD, ritanserin, 8-OH-DPAT and lisuride on classical conditioning in the rabbit. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59:469–475
Williams GV, Rao SG, Goldman-Rakic PS (2002) The physiological role of 5-HT2A receptors in working memory. J Neurosci 22:2843–2854
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institute of Mental Health Grant MH16841-36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harvey, J.A., Quinn, J.L., Liu, R. et al. Selective remodeling of rabbit frontal cortex: relationship between 5-HT2A receptor density and associative learning. Psychopharmacology 172, 435–442 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1687-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1687-4