Abstract
Rationale
A high comorbidity between depression and alcoholism has been reported in several studies, but the mechanisms underlying this relationship remain unknown.
Objectives
We tested whether learned helplessness in rats as a model for depression is associated with enhanced alcohol intake and relapse behavior.
Methods
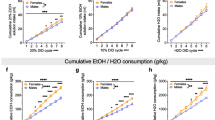
Congenital learned helplessness (cLH) and congenital non-learned helplessness (cNLH) rats were selectively bred for differences in an escape paradigm. Sucrose preference was tested at the first hour of the dark phase. In order to study an association with alcohol drinking behavior, rats underwent a free-choice procedure with access to water, and 5% and 20% alcohol solutions for 6 weeks. After acquisition of alcohol drinking behavior, the alcohol deprivation effect (ADE) was assessed. Sensitivity to the sedative-hypnotic effect of alcohol was measured by loss of the righting reflex.
Results
cLH rats showed significantly lower preference for sucrose solutions during the second half hour of the dark phase than cNLH rats. Alcohol intake of male cLH rats was not significantly different from that of male cNLH rats. In contrast, cLH female rats consumed higher amounts of alcohol than female cNLH rats. The ADE was more pronounced in female animals, although the magnitude of the ADE was similar in both cNLH and cLH female rats. The time to regain the righting reflex was significantly higher in both male and female cLH rats than in cNLH rats.
Conclusions
In summary, these data suggest that an inborn depressive-like behavior in female rats is associated with enhanced alcohol intake.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MG (1976) Twin studies of affective illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry 33:1476–1478
Almeida OF, Shoaib M, Deicke J, Fischer D, Darwish MH, Patchev VK (1998) Gender differences in ethanol preference and ingestion in rats. The role of the gonadal steroid environment. J Clin Invest 101:2677–2685
Angst J, Sellaro R, Ries Merikangas K (2002) Multimorbidity of psychiatric disorders as an indicator of clinical severity. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 252:147–154
Becker JB, Molenda H, Hummer DL (2001) Gender differences in the behavioral responses to cocaine and amphetamine. Implications for mechanisms mediating gender differences in drug abuse. Ann NY Acad Sci 937:172–187
Bell RL, Stewart RB, Woods JE II, Lumeng L, Li TK, Murphy JM, McBride WJ (2001) Responsivity and development of tolerance to the motor impairing effects of moderate doses of ethanol in alcohol-preferring (P) and -nonpreferring (NP) rat lines. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:644–650
Ciccocioppo R, Panocka I, Froldi R, Colombo G, Gessa GL, Massi M (1999) Antidepressant-like effect of ethanol revealed in the forced swimming test in Sardinian alcohol-preferring rats. Psychopharmacology 144:151–157
Cloninger CR (1987) Neurogenetic adaptive mechanisms in alcoholism. Science 236:410–416
Colombo G, Agabio R, Carai MA, Lobina C, Pani M, Reali R, Vacca G, Gessa GL (2000) Different sensitivity to ethanol in alcohol-preferring sP and -nonpreferring sNP rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:1603–1608
D’Aquila PS, Newton J, Willner P (1997) Diurnal variation in the effect of chronic mild stress on sucrose intake and preference. Physiol Behav 62:421–426
Davidson KM (1995) Diagnosis of depression in alcohol dependence: changes in prevalence with drinking status. Br J Psychiatry 166:199–204
Davidson KM, Ritson EB (1993) The relationship between alcohol dependence and depression. Alcohol Alcohol 28:147–155
Dixit AR, Crum RM (2000) Prospective study of depression and the risk of heavy alcohol use in women. Am J Psychiatry 157:751–758
Dunne FJ, Galatopoulos C, Schipperheijn JM (1993) Gender differences in psychiatric morbidity among alcohol misusers. Compr Psychiatry 34:95–101
George FR (1993) Genetic models in the study of alcoholism and substance abuse mechanisms. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 17:345–361
Godfrey CD, Froehlich JC, Stewart RB, Li TK, Murphy JM (1997) Comparison of rats selectively bred for high and low ethanol intake in a forced-swim-test model of depression: effects of desipramine. Physiol Behav 62:729–733
Henniger MSH, Spanagel R, Wigger S, Landgraf R, Hölter SM (2002) Alcohol self-administration in two Wistar rat lines selectively bred for extremes in anxiety-related behaviour. Neuropsychopharmacology 26:729–736
Hesselbrock MN, Meyer RE, Keener JJ (1985) Psychopathology in hospitalized alcoholics. Arch Gen Psychiatry 42:1050–1055
Hölter SM, Engelmann M, Kirschke C, Liebsch G, Landgraf R, Spanagel R (1998) Long-term ethanol self-administration with repeated ethanol deprivation episodes changes ethanol drinking pattern and increases anxiety-related behaviour during ethanol deprivation in rats. Behav Pharmacol 9:41–48
Kessler RC, McGonagle KA, Zhao S, Nelson CB, Hughes M, Eshleman S, Wittchen HU, Kendler KS (1994) Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of DSM-III-R psychiatric disorders in the United States. Results from the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:8–19
Khanna JM, Kalant H, Shah G, Sharma H (1990) Comparison of sensitivity and alcohol consumption in four outbred strains of rats. Alcohol 7:429–434
Kiianmaa K, Stenius K, Sinclair JD (1991) Determinants of alcohol preference in the AA and ANA rat lines selected for differential ethanol intake. Alcohol Alcohol 26:115–120
Kuehner C (2003) Gender differences in unipolar depression: an update of epidemiological findings and possible explanations. Acta Psychiatr Scand 108:163–174
Lancaster FE (1995) Gender differences in animal studies. Implications for the study of human alcoholism. Recent Dev Alcohol 12:209–215
Li TK, Spanagel R, Colombo G, McBride WJ, Porrino LJ, Suzuki T, Rodd-Henricks ZA (2001) Alcohol reinforcement and voluntary ethanol consumption. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:117S–126S
Markou A, Kosten TR, Koob GF (1998) Neurobiological similarities in depression and drug dependence: a self-medication hypothesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 18:135–174
Matsumoto H, Fukui Y (2002) Pharmacokinetics of ethanol: a review of the methodology. Addict Biol 7:5–14
Merikangas KR, Risch NJ, Weissman MM (1994) Comorbidity and co-transmission of alcoholism, anxiety and depression. Psychol Med 24:69–80
Merikangas KR, Angst J, Eaton W, Canino G, Rubio-Stipec M, Wacker H, Wittchen HU, Andrade L, Essau C, Whitaker A, Kraemer H, Robins LN, Kupfer DJ (1996) Comorbidity and boundaries of affective disorders with anxiety disorders and substance misuse: results of an international task force. Br J Psychiatry 168:58–67
Overmier JB, Seligman ME (1967) Effects of inescapable shock upon subsequent escape and avoidance responding. J Comp Physiol Psychol 63:28–33
Overstreet DH (2002) Behavioral characteristics of rat lines selected for differential hypothermic responses to cholinergic or serotonergic agonists. Behav Genet 32:335–348
Overstreet DH, Rezvani AH, Janowsky DS (1992) Genetic animal models of depression and ethanol preference provide support for cholinergic and serotonergic involvement in depression and alcoholism. Biol Psychiatry 31:919–936
Pare AM, Pare WP, Kluczynski J (1999) Negative affect and voluntary alcohol consumption in Wistar–Kyoto (WKY) and Sprague–Dawley rats. Physiol Behav 67:219–225
Piccinelli M, Wilkinson G (2000) Gender differences in depression. Critical review. Br J Psychiatry 177:486–492
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N, Jalfre M (1978) Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 47:379–391
Preisig M, Fenton BT, Stevens DE, Merikangas KR (2001) Familial relationship between mood disorders and alcoholism. Compr Psychiatry 42:87–95
Schuckit MA (1998) Biological, psychological and environmental predictors of the alcoholism risk: a longitudinal study. J Stud Alcohol 59:485–494
Schuckit MA, Smith TL (1996) An 8-year follow-up of 450 sons of alcoholic and control subjects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:202–210
Schuckit MA, Pitts FN Jr, Reich T, King LJ, Winokur G (1969) Alcoholism. I. Two types of alcoholism in women. Arch Gen Psychiatry 20:301–306
Schuckit MA, Tipp JE, Bergman M, Reich W, Hesselbrock VM, Smith TL (1997) Comparison of induced and independent major depressive disorders in 2,945 alcoholics. Am J Psychiatry 154:948–957
Schuckit MA, Smith TL, Kalmijn J, Tsuang J, Hesselbrock V, Bucholz K (2000) Response to alcohol in daughters of alcoholics: a pilot study and a comparison with sons of alcoholics. Alcohol Alcohol 35:242–248
Spanagel R (2000) Recent animal models of alcoholism. Alcohol Res Health 24:124–131
Spanagel R, Holter SM (1999) Long-term alcohol self-administration with repeated alcohol deprivation phases: an animal model of alcoholism? Alcohol Alcohol 34:231–243
Swendsen JD, Merikangas KR, Canino GJ, Kessler RC, Rubio-Stipec M, Angst J (1998) The comorbidity of alcoholism with anxiety and depressive disorders in four geographic communities. Compr Psychiatry 39:176–184
Thomasson HR (1995) Gender differences in alcohol metabolism. Physiological responses to ethanol. Recent Dev Alcohol 12:163–179
Vengeliene V, Siegmund S, Singer MV, Sinclair JD, Li TK, Spanagel R (2003) A comparative study on alcohol-preferring rat lines: effects of deprivation and stress phases on voluntary alcohol intake. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:1048–1054
Vollmayr B, Henn FA (2001) Learned helplessness in the rat: improvements in validity and reliability. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 8:1–7
Vollmayr B, Faust H, Lewicka S, Henn FA (2001) Brain-derived-neurotrophic-factor (BDNF) stress response in rats bred for learned helplessness. Mol Psychiatry 6:471–474
Vollmayr B, Bachteler D, Vengeliene V, Gass P, Spanagel R, Henn FA (2004) Rats with congenital learned helplessness respond less to sucrose but show no deficits in activity or learning. Behav Brain Res 150:217–221
Weiss JM, Glazer HI (1975) Effects of acute exposure to stressors on subsequent avoidance-escape behavior. Psychosom Med 37:499–521
Weiss JM, Cierpial MA, West CH (1998) Selective breeding of rats for high and low motor activity in a swim test: toward a new animal model for depression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:49–66
Weissman MM, Olfson M (1995) Depression in women: implications for health care research. Science 269:799–801
Willner P (1984) The validity of animal models of depression. Psychopharmacology 83:1–16
Willner P (1991) Animal models as simulations of depression. Trends Pharmacol Sci 12:131–136
Willner P, Mitchell PJ (2002) The validity of animal models of predisposition to depression. Behav Pharmacol 13:169–188
Winokur G, Coryell W (1992) Familial subtypes of unipolar depression: a prospective study of familial pure depressive disease compared to depression spectrum disease. Biol Psychiatry 32:1012–1018
Wolffgramm J, Heyne A (1995) From controlled drug intake to loss of control: the irreversible development of drug addiction in the rat. Behav Brain Res 70:77–94
Acknowledgements
Supported in part by the BMBF FKZ EB 01011300/6 to R.S. and by the DFG VO 621/3-1 to B.V.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vengeliene, V., Vollmayr, B., Henn, F.A. et al. Voluntary alcohol intake in two rat lines selectively bred for learned helpless and non-helpless behavior. Psychopharmacology 178, 125–132 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2013-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2013-5