Abstract
Rationale
The hallucinatory effect and potential abuse of salvinorin A, the major ingredient of Salvia divinorum, has not been documented in animals.
Objective
The effects of salvinorin A on the zebrafish (Danio rerio) model, through its swimming behavior and conditioned place preference (CPP) task, was studied.
Materials and methods
Swimming activity was determined in a squared observational chamber after an i.m. treatment of salvinorin A (0.1–10 μg/kg). For the CPP test, zebrafish were given salvinorin A (0.2 and 1 μg/kg) or vehicle and evaluated in a two-compartment chamber.
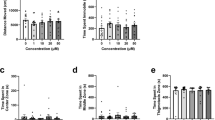
Results
Salvinorin A (0.1 and 0.2 μg/kg) induced accelerated swimming behavior in comparison with vehicle, whereas a “trance-like” effect, at doses as 5 and 10 μg/kg, was obtained. Pretreatment with the κ-opioid antagonist, nor-binaltorphimine (nor-BNI; 10 mg/kg) and the cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) antagonist, rimonabant (1 mg/kg), blocked salvinorin A-induced both stimulating and depressive effects obtained at a dose of 0.2 and 10 μg/kg, respectively. In the CPP test, salvinorin A (0.2 and 0.5 μg/kg) produced an increase in the time spent in the drug-associated compartment. A dose of 1 μg/kg produced no effect, whereas a dose of 80 μg/kg induced aversion. Pretreatment with nor-BNI or rimonabant fully reversed the reinforcing properties of salvinorin A (0.5 μg/kg).
Conclusions
Taken together, these results indicate that salvinorin A, as is sometimes reported in humans, exhibits rewarding effects, independently from its motor activity, suggesting the usefulness of the zebrafish model to study addictive behavior. These effects appear mediated by activation of both κ-opioid and cannabinoid CB1 receptors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson Ha, Evans LT (1954) Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD 25) II. Psychobiological effects on the Siamese fighting fish. Science 120:990–991
Ameri A (1999) The effects of cannabinoids on the brain. Prog Neurobiol 58:315–348
Anichtchik OV, Kaslin J, Peitsaro N, Scheinin M, Panula P (2004) Neurochemical and behavioural changes in zebrafish Danio rerio after systemic administration of 6-hydroxydopamine and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. J Neurochem 88:443–453
Bals-Kubik R, Herz A, Shippenberg TS (1989) Evidence that the aversive effects of opioid antagonists and kappa-agonists are centrally mediated. Psychopharmacology 98:203–206
Braida D, Iosue S, Pegorini S, Sala M (2004) Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced conditioned place preference and intracerebroventricular self-administration in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 506:63–69 (erratum in Eur J Pharmacol 511:75–76)
Bretaud S, Lee S, Guo S (2004) Sensitivity of zebrafish to environmental toxins implicated in Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicol Teratol 26:857–864
Bucheler R, Gleiter CH, Schwoerer P, Gaertner I (2005) Use of nonprohibited hallucinogenic plants: increasing relevance for public health? A case report and literature review on the consumption of Salvia divinorum (Diviner’s Sage). Pharmacopsychiatry 38:1–5
Busse GD, Lawrence ET, Riley AL (2004) The modulation of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference by alcohol: effects of cocaine dose. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28:149–155
Butelman ER, Harris TJ, Kreek MJ (2004) The plant-derived hallucinogen, salvinorin A, produces kappa-opioid agonist-like discriminative effects in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 172:220–224
Carlezon WA Jr, Beguin C, DiNieri JA, Baumann MH, Richards MR, Todtenkopf MS, Rothman RB, Ma Z, Lee DY, Cohen BM (2006) Depressive-like effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A on behavior and neurochemistry in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:440–447
Carroll FI, Harris LS, Aceto MD (2005) Effects of JDTic, a selective kappa-opioid receptor antagonist, on the development and expression of physical dependence on morphine using a rat continuous-infusion model. Eur J Pharmacol 524:89–94
Chavkin C, Sud S, Jin W, Stewart J, Zjawiony JK, Siebert DJ, Toth BA, Hufeisen SJ, Roth BL (2004) Salvinorin A, an active component of the hallucinogenic sage Salvia divinorum is a highly efficacious kappa-opioid receptor agonist: structural and functional considerations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:1197–1203
Clements S, Schreck CB, Larsen DA, Dickhoff WW (2002) Central administration of corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulates locomotor activity in juvenile chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Gen Comp Endocrinol 125:319–327
Cui CL, Wu LZ, Han JS (2000) Spinal kappa-opioid system plays an important role in suppressing morphine withdrawal syndrome in the rat. Neurosci Lett 295:45–48
Darland T, Dowling JE (2001) Behavioral screening for cocaine sensitivity in mutagenized zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11691–11696
Dlugos CA, Rabin RA (2003) Ethanol effects on three strains of zebrafish: model system for genetic investigations. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:471–480
Dooley K, Zon LI (2000) Zebrafish: a model system for the study of human disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:252–256
Gerlai R, Lahav M, Guo S, Rosenthal A (2000) Drinks like a fish: zebra fish (Danio rerio) as a behavior genetic model to study alcohol effects. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:773–782
Giacomini NJ, Rose B, Kobayashi K, Guo S (2006) Antipsychotics produce locomotor impairment in larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 28:245–250
Giroud C, Felber F, Augsburger M, Horisberger B, Rivier L, Mangin P (2000) Salvia divinorum: an hallucinogenic mint which might become a new recreational drug in Switzerland. Forensic Sci Int 112:143–150
Gonzalez-Nuñez V, Barrallo A, Traynor JR, Rodriguez RE (2006) Characterization of opioid-binding sites in zebrafish brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:900–904
Hampson RE, Mu J, Deadwyler SA (2000) Cannabinoid and kappa opioid receptors reduce potassium K current via activation of G(s) proteins in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 84:2356–2364
Iwamoto ET (1989) Characterization of dynorphin A(1–17)-induced place preference in rats. NIDA Res Monogr 95:308–309
Lam CS, Rastegar S, Strahle U (2006) Distribution of cannabinoid receptor 1 in the CNS of zebrafish. Neuroscience 138:83–95
Levin ED, Chen E (2004) Nicotinic involvement in memory function in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 26:731–735
Levin ED, Limpuangthip J, Rachakonda T, Peterson M (2006) Timing of nicotine effects on learning in zebrafish. Psychopharmacology 184:547–552
Lockwood B, Bjerke S, Kobayashi K, Guo S (2004) Acute effects of alcohol on larval zebrafish: a genetic system for large-scale screening. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 77:647–654
McCurdy CR, Sufka KJ, Smith GH, Warnick JE, Nieto MJ (2006) Antinociceptive profile of salvinorin A, a structurally unique kappa opioid receptor agonist. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 83:109–113
Mendizabal V, Zimmer A, Maldonado R (2006) Involvement of kappa/Dynorphin system in WIN 55,212-2 self-Administration in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1957–1966
Mori T, Nomura M, Nagase H, Narita M, Suzuki T (2002) Effects of a newly synthesized kappa-opioid receptor agonist, TRK-820, on the discriminative stimulus and rewarding effects of cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology 161:17–22
Mowry M, Mosher M, Briner W (2003) Acute physiologic and chronic histologic changes in rats and mice exposed to the unique hallucinogen salvinorin A. J Psychoact Drugs 35:379–382
Ninkovic J, Folchert A, Makhankov YV, Neuhauss SC, Sillaber I, Straehle U, Bally-Cuif L (2006) Genetic identification of AChE as a positive modulator of addiction to the psychostimulant d-amphetamine in zebrafish. J Neurobiol 66:463–475
Novak CM, Jiang X, Wang C, Teske JA, Kotz CM, Levine JA (2005) Caloric restriction and physical activity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurosci Lett 383:99–104. DOI 10.1016/j. neulet.2005.03.048
Rink E, Wullimann MF (2001) The teleostean (zebrafish) dopaminergic system ascending to the subpallium (striatum) is located in the basal diencephalon (posterior tuberculum). Brain Res 889:316–330
Roth BL, Baner K, Westkaemper R, Siebert D, Rice KC, Steinberg S, Ernsberger P, Rothman RB (2002) Salvinorin A: a potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11934–11939
Scholz H, Ramond J, Singh CM, Heberlein U (2000) Functional ethanol tolerance in Drosophila. Neuron 28:261–271
Sheffler DJ, Roth BL (2003) Salvinorin A: the “magic mint” hallucinogen finds a molecular target in the kappa opioid receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:107–109
Shin JT, Fishman MC (2002) From zebrafish to human: modular medical models. Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet 3:311–340
Shippenberg TS, Herz A (1987) Place preference conditioning reveals the involvement of D1-dopamine receptors in the motivational properties of mu-kappa-opioid agonists. Brain Res 436:169–172
Siebert DJ (1994) Salvia divinorum and salvinorin A: new pharmacologic findings. J Ethnopharmacol 43:53–56
Smith MA, Bryant PA, McClean JM (2003) Social and environmental enrichment enhances sensitivity to the effects of kappa opioids: studies on antinociception, diuresis and conditioned place preference. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 76:93–101
Smith PB, Welch SP, Martin BR (1994) Interactions between delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and kappa opioids in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:1381–1387
Spanagel R, Almeida OF, Bartl C, Shippenberg TS (1994) Endogenous kappa-opioid systems in opiate withdrawal: role in aversion and accompanying changes in mesolimbic dopamine release. Psychopharmacology 115:121–127
Suzuki T, Shiozaki Y, Masukawa Y, Misawa M, Nagase H (1992) The role of mu- and kappa-opioid receptors in cocaine-induced conditioned place preference. Jpn J Pharmacol 58:435–442
Turner DM (1996) Salvinorin: The psychedelic essence of Salvia divinorum. Panther Press, San Francisco, CA
Valdes LJ, Butler WM, Hatfield GM, Paul AG, Koreeda M (1984) Divinorin A: a psychotropic terpenoid and divinorin B from the hallucinogenic Mexican mint Salvia divinorum. J Org Chem 49:4716–4720
Valdes LJ 3rd, Diaz JL, Paul AG (1983) Ethnopharmacology of ska Maria Pastora (Salvia divinorum, Epling and Jativa-M.). J Ethnopharmacol 7:287–312
Wang Y, Tang K, Inan S, Siebert D, Holzgrabe U, Lee DY, Huang P, Li JG, Cowan A, Liu-Chen LY (2005) Comparison of pharmacological activities of three distinct kappa ligands (Salvinorin A, TRK-820 and 3FLB) on kappa opioid receptors in vitro and their antipruritic and antinociceptive activities in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:220-230. DOI 10.1124/jpet.104.073668
Wasson RG (1962) A new Mexican psychotropic drug from the mint family. Bot Mus Leaf Harv Univ 20:77–84
Wasson RG (1963) Notes on the present status of ololuiqui and the other hallucinogens of Mexico. Bot Mus Leaf Harv Univ 20:163–193
Zhang Y, Butelman ER, Schlussman SD, Ho A, Kreek MJ (2005) Effects of the plant-derived hallucinogen salvinorin A on basal dopamine levels in the caudate putamen and in a conditioned place aversion assay in mice: agonist actions at kappa opioid receptors. Psychopharmacology 179:551–558
Zon LI, Peterson RT (2005) In vivo drug discovery in the zebrafish. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:35–44
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful for the financial support from regione Lombardia-Direzione Famiglia e Solidarietà sociale (MDMA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braida, D., Limonta, V., Pegorini, S. et al. Hallucinatory and rewarding effect of salvinorin A in zebrafish: κ-opioid and CB1-cannabinoid receptor involvement. Psychopharmacology 190, 441–448 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0639-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0639-1