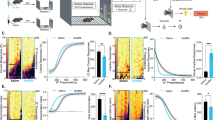
Abstract
Background
Disruptions in perception and cognition are characteristic of psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia. Studies of pharmacological agents that alter perception and cognition in humans might provide a better understanding of the brain substrates of these complex processes. One way to study these states in rodents is with tests that require attention and visual perception for correct performance.
Methods
We examined the effects of two drugs that cause disruptions in perception and cognition in humans—the kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) agonist salvinorin A (salvA; 0.125–4.0 mg/kg) and the non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist ketamine (0.63–20 mg/kg)—on behavior in rats using the 5-choice serial reaction time task (5CSRTT), a food-motivated test that quantifies attention. We also compared the binding profiles of salvA and ketamine at KORs and NMDA receptors.
Results
SalvA and ketamine produced the same pattern of disruptive effects in the 5CSRTT, characterized by increases in signs often associated with reduced motivation (omission errors) and deficits in processing (elevated latencies to respond correctly). Sessions in which rats were fed before testing suggest that reduced motivation produces a subtly different pattern of behavior. Pretreatment with the KOR antagonist JDTic (10 mg/kg) blocked all salvA effects and some ketamine effects. Binding and function studies revealed that ketamine is a full agonist at KORs, although not as potent or selective as salvA.
Conclusions
SalvA and ketamine have previously under-appreciated similarities in their behavioral effects and pharmacological profiles. By implication, KORs might be involved in some of the cognitive abnormalities observed in psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amitai N, Semenova S, Markou A (2007) Cognitive disruptive effects of the psychotomimetic phencyclidine and attenuation by atypical antipsychotic medications. Psychopharmacol 193:521–537
Baker LE, Panos JJ, Killinger BA, Peet MM, Bell LM, Haliw LA, Walker SL (2009) Comparison of the discriminative stimulus effects of salvinorin A and its derivatives to U69,593 and U50,488 in rats. Psychopharmacol 203:203–211
Beardsley PM, Howard JL, Shelton KL, Carroll FI (2005) Differential effects of the novel kappa opioid receptor antagonist, JDTic, on reinstatement of cocaine-seeking induced by footshock stressors vs cocaine primes and its antidepressant-like effects in rats. Psychopharmacol 183:118–126
Carlezon WA Jr, Thomas M (2009) Biological substrates of reward and aversion: a nucleus accumbens activity hypothesis. Neuropharmacol 56(Suppl 1):122–-132
Carlezon WA Jr, Béguin C, DiNieri JA, Baumann MH, Richards ME, Todtenkopf MS, Rothman RB, Ma Z, Y-W LD, Cohen BM (2006) Depressive-like effects of the κ-opioid receptor agonist Salvinorin A on behavior and neurochemistry in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:440–447
Chavkin C, Sud S, Jin W, Stewart J, Zjawiony JK, Siebert DJ, Toth BA, Hufeisen SJ, Roth BL (2004) Salvinorin A, an active component of the hallucinogenic sage Salvia divinorum is a highly efficacious kappa-opioid receptor agonist: structural and functional considerations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:1197–1203
Chen WJ, Faraone SV (2000) Sustained attention deficits as markers of genetic susceptibility to schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 97:52–57
Clark L, Iversen S, Goodwin G (2002) Sustained attention deficit in bipolar disorder. Br J Psychiatry 180:133–139
Cornblatt BA, Malhotra AK (2001) Impaired attention as an endophenotype for molecular genetic studies of schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 105:11–15
Crawford CA, McDougall SA, Bolanos CA, Hall S, Berger SP (1995) The effects of the kappa agonist U-50,488 on cocaine-induced conditioned and unconditioned behaviors and Fos immunoreactivity. Psychopharmacol 120:392–399
Davis JA (2008) Mouse and rat anesthesia and analgesia. Curr Protoc Neurosci 42:A.4B.1–A.4B.21
Fibiger HC, Fibiger HP, Zis AP (1973) Attenuation of amphetamine-induced motor stimulation and stereotypy by 6-hydroxydopamine in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 47:683–692
González D, Riba J, Bouso JC, Gómez-Jarabo G, Babanoj MJ (2006) Pattern of use and subjective effects of Salvia divinorum among recreational users. Drug Alcohol Depend 85:157–162
Hancock PJ, Stamford JA (1999) Stereospecific effects of ketamine on dopamine efflux and uptake in the rat nucleus accumbens. Br J Anaesth 82:603–608
Hanes K (2001) Antidepressant effects of the herb Salvia divinorum: a case report. J Clin Psychopharmacol 21:634–635
Herberg LJ, Rose IC (1989) The effect of MK-801 and other antagonists of NMDA-type glutamate receptors on brain-stimulation reward. Psychopharmacol 99:87–90
Hetzler BE, Wautlet BS (1985) Ketamine-induced locomotion in rats in an open-field. Pharmacol Biochem Behav: 653–655
Imperato A, Scrocco MG, Bacchi S, Angelucci L (1990) NMDA receptors and in vivo dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and caudatus. Eur J Pharmacol 187:555–556
Imre G, Fokkema DS, Den Boer JA, Ter Horst GJ (2006) Dose–response characteristics of ketamine effect on locomotion, cognitive function and central neuronal activity. Brain Res Bull 69:338–345
Javitt DC, Zukin SR (1991) Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 148:1301–1308
Jensen NH, Roth BL (2008) Massively parallel screening of the receptorome. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 11:420–426
Jentsch JD, Roth RH (1999) The neuropsychopharmacology of phencyclidine: from NMDA receptor hypofunction to the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol 20:201–225
Knoll AT, Carlezon WA Jr (2010) Dynorphin, stress and depression. Brain Res 1314C:56–73
Knoll AT, Meloni EG, Thomas JB, Carroll FI, Carlezon WA Jr (2007) Anxiolytic-like effects of κ-opioid receptor antagonists in behavioral models of unlearned and learned fear in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:838–845
Kovács KJ, Larson AA (1998) Up-regulation of [3H]DTG but not [3H](+)-pentazocine labeled sigma sites in mouse spinal cord by chronic morphine treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 350:47–52
Krystal JH, D'Souza DC, Mathalon D, Perry E, Belger A, Hoffman R (2003) NMDA receptor antagonist effects, cortical glutamatergic function, and schizophrenia: toward a paradigm shift in medication development. Psychopharmacol 169:215–233
Krystal JH, Abi-Saab W, Perry E, D’Souza DC, Liu N, Gueorguieva R, McDougall L, Hunsberger T, Belger A, Levine L, Breier A (2005) Preliminary evidence of attenuation of the disruptive effects of the NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist, ketamine, on working memory by pretreatment with group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist, LY354740, in healthy human subjects. Psychopharmacol 179:303–309
Lahti AC, Weiler MA, Tamara Michaelidis BA, Parwani A, Tamminga CA (2001) Effects of ketamine in normal and schizophrenic volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacol 25:455–467
Leyton M, Stewart J (1992) The stimulation of central kappa opioid receptors decreases male sexual behavior and locomotor activity. Brain Res 594:56–74
Maeng S, Zarate CA Jr, Du J, Schloesser RJ, McCammon J, Chen G, Manji HK (2007) Cellular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant effects of ketamine: role of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors. Biol Psychiatry 63:349–352
Mague SD, Pliakas AM, Todtenkopf MS, Tomasiewicz HC, Zhang Y, Stevens WC Jr, Jones RM, Portoghese PS, Carlezon WA Jr (2003) Antidepressant-like effects of κ-opioid receptor antagonists in the forced swim test in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:323–330
Maisonneuve IM, Archer S, Glick SD (1994) U50,488, a κ-opioid receptor agonist, attenuates cocaine-induced increases in extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Neurosci Lett 181:57–60
McLaughlin JP, Land BB, Li S, Pintar JE, Chavkin C (2006) Prior activation of kappa opioid receptors by U50,488 mimics repeated forced swim stress to potentiate cocaine place preference conditioning. Neuropsychopharmacol 31:787–794
Mori T, Nomura M, Yoshizawa K, Nagase H, Sawaguchi T, Narita M, Suzuki T (2006) Generalization of NMDA-receptor antagonists to the discriminative stimulus effects of κ-opioid receptor agonists U-50,488H, but not TRK-820 in rats. J Pharmacol Sci 100:157–161
Morris BJ, Cochran SM, Pratt JA (2005) PCP: from pharmacology to modeling schizophrenia. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:101–106
Paine T, Olmstead M (2004) Cocaine disrupts both behavioural inhibition and conditional discrimination in rats. Psychopharmacol 175:443–450
Paine TA, Tomasiewicz HC, Zhang K, Carlezon WA Jr (2007) Sensitivity of the 5-choice serial reaction time task to the effects of various psychotropic drugs in Sprague–Dawley rats. Biol Psychiatry 62:687–693
Paine TA, Neve RL, Carlezon WA Jr (2009) Attention deficits and hyperactivity following inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) within the medial prefrontal cortex of rats. Neuropsychopharmacol 34:2143–2155
Parwani A, Weiler MA, Blaxton TA, Warfel D, Hardin M, Frey K, Lahti AC (2005) The effects of a subanesthetic dose of ketamine on verbal memory in normal volunteers. Psychopharmacol 183:265–274
Pfeiffer A, Brantl V, Herz A, Emrich HM (1986) Psychotomimesis mediated by kappa opiate receptors. Science 233:774–776
Potter D, Toitman MF, Cohen BM, Carlezon WA Jr, Chartoff EH (2009) Biphasic effects of the kappa opioid receptor agonist salvinorin A on hedonic state. Soc Neurosci Abs 39:564.14
Robbins T (2002) The 5-choice serial reaction time task: behavioural pharmacology and functional neurochemistry. Psychopharmacol 163:362–380
Rosvold HE, Mirsky AF, Saranson I, Bransome EB, Beck LH (1956) A continuous performance test of brain damage. J Consult Clin Psychol 20:343–350
Roth BL, Baner K, Westkaemper R, Siebert D, Rice KC, Steinberg S, Ernsberger P, Rothman RB (2002) Salvinorin A: a potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous κ opioid selective agonist. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 99:11934–11939
Shippenberg TS, LeFevour A, Heidbreder C (1996) kappa-Opioid receptor agonists prevent sensitization to the conditioned rewarding effects of cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276:545–554
Siebert DJ (1994) Salvia divinorum and Salvinorin A: new pharmacologic findings. J Ethnopharmacol 43:53–56
Thomas JB, Atkinson RN, Vinson NA, Catanzaro JL, Perretta CL, Fix SE, Mascarella SW, Rothman RB, Xu H, Dersch CM, Cantrell BE, Zimmerman DM, Carroll FI (2003) Identification of (3R)-7-hydroxy-N-((1S)-1-[[(3R, 4R)-4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)- 3, 4-dimethyl-1-piperidinyl]methyl]-2-methylpropyl)-1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydro-3-isoquinolinecarboxamide as a novel potent and selective opioid kappa receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 46:3127–3137
Todtenkopf MS, Marcus JF, Portoghese PS, Carlezon WA Jr (2004) Effects of kappa-opioid receptor ligands on intracranial self-stimulation in rats. Psychopharmacol 172:463–470
Tomasiewicz HC, Todtenkopf MS, Chartoff EH, Cohen BM, Carlezon WA Jr (2008) The kappa-opioid agonist U69,593 blocks cocaine-induced enhancement of brain stimulation reward. Biol Psychiatry 64:982–988
Valdes LJ 3rd (1994) Salvia divinorum and the unique diterpene hallucinogen, Salvinorin (divinorin) A. J Psychoactive Drugs 26:277–283
Vortherms TA, Roth BL (2006) Salvinorin A: from natural product to human therapeutics. Molec Interv 6:257–265
Wadenberg ML (2003) A review of the properties of spiradoline: a potent and selective kappa-opioid receptor agonist. CNS Drug Rev 9:187–198
Willmore-Fordham CB, Krall DM, McCurdy CR, Kinder DH (2007) The hallucinogen derived from Salvia divinorum, salvinorin A, has kappa-opioid agonist discriminative stimulus effects in rats. Neuropharmacol 53:481–486
Wise RA (2008) Dopamine and reward: the anhedonia hypothesis 30 years on. Neurotoxicol Res 14:169–183
Yan F, Bikbulatov RV, Mocanu V, Dicheva N, Parker CE, Wetsel WC, Mosier PD, Westkaemper RB, Allen JA, Zjawiony JK, Roth BL (2009) Structure-based design, synthesis, and biochemical and pharmacological characterization of novel salvinorin A analogues as active state probes of the kappa-opioid receptor. Biochem 48:6898–6908
Zarate CA Jr, Singh JB, Carlson PJ, Brutsche NE, Ameli R, Luckenbaugh DA, Charney DS, Manji HK (2006) A randomized trial of an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:856–864
Zhang J, Chiodo LA, Freeman AS (1992) Electrophysiological effects of MK-801 on rat nigrostriatal and mesoaccumbal dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res 590:153–163
Zhang Y, Butelman ER, Schlussman SD, Ho A, Kreek MJ (2005) Effects of the plant-derived hallucinogen salvinorin A on basal dopamine levels in the caudate putamen and in a conditioned place aversion assay in mice: agonist actions at kappa opioid receptors. Psychopharmacol 179:551–558
Acknowledgment
This study is supported by the National Institute of Mental Health (MH063266 to WAC, and RO1DA017204 to BLR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors Nemeth and Paine denote equal authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nemeth, C.L., Paine, T.A., Rittiner, J.E. et al. Role of kappa-opioid receptors in the effects of salvinorin A and ketamine on attention in rats. Psychopharmacology 210, 263–274 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1834-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1834-7