Abstract
Objective
High-density lipoprotein (HDL)-associated antioxidant paraoxonase (PON) may reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation and prevent atherosclerosis. The aim of this present study was to investigate the effect of the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor atorvastatin on hydrogen-peroxide-induced DNA damage by comet assay and the correlation between oxidative DNA damage and antioxidant PON activity.
Methods
Thirteen type-II/a hyperlipidemic patients were enrolled in the study. We examined the effect of 10 mg/day atorvastatin treatment on lipid levels and the degree of DNA damage in lymphocytes separated from hyperlipidemic patients, nitric oxide (NO), thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS), PON levels and activity.
Results
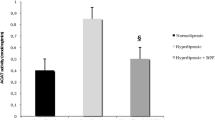
After 6 months, atorvastatin treatment significantly decreased serum cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol levels. The triglyceride level did not change, and there was no significant change in the HDL cholesterol level. The visual score characteristic to the degree of DNA damage in comet assay was significantly decreased, as well as the TBARS level, while the level of NO was non-significantly increased. PON activity and the PON/HDL ratio were significantly increased after atorvastatin treatment. There was a negative correlation between DNA damage and PON activity, as well as between DNA damage and the PON/HDL ratio before and after atorvastatin treatment.
Conclusion
These findings show that atorvastatin treatment favorably affected the lipid profile, increasing the activity of HDL-associated PON and decreasing the cytotoxic effect of oxidative stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steinberg D, Parthasarathy S, Carew TE, Khoo JC, Witztum JL (1989) Beyond cholesterol. Modification of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med 320:915–924
Schmitz G, Orso E, Rothe G, Klucken J (1997) Scavenging, signalling and adhesion coupling in macrophages: implications for atherogenesis. Curr Opin Lipidol 8:287–300
Hessler JR, Robertson AL Jr, Chisolm GM III (1979) LDL-induced cytotoxicity and its inhibition by HDL in human vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells in culture. Atherosclerosis 32:213–229
Parthasarathy S, Barnett J, Fong LG (1990) High-density lipoprotein inhibits the oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1044:275–283
Maier JA, Barenghi L, Pagani F, Bradamante S, Comi P, Ragnotti G (1994) The protective role of high-density lipoprotein on oxidized-low-density-lipoprotein-induced U937/endothelial cell interactions. Eur J Biochem 221:35–41
La Du BN (1992) Human serum paraoxonase/arylesterase. In: Kalow W (ed) Pharmacogenetics of drug metabolism. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 51–91
Kelso GJ, Stuart WD, Richter RJ, Furlong CE, Jordan-Starck TC, Harmony JA (1994) Apolipoprotein J is associated with paraoxonase in human plasma. Biochemistry 33:832–839
Watson AD, Berliner JA, Hama SY, La Du BN, Faull KF, Fogelman AM, Navab M (1995) Protective effect of high density lipoprotein associated paraoxonase. Inhibition of the biological activity of minimally oxidized low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest 96:2882–2891
Mackness MI, Arrol S, Abbott CA, Durrington PN (1993) Is paraoxonase related to atherosclerosis. Chem Biol Interact 87:161–171
Paragh Gy, Seres I, Balogh Z, Varga Zs, Karpati I, Matyus J, Ujhelyi L, Kakuk Gy (1998) The serum paraoxonase activity in patients with chronic renal failure and hyperlipidemia. Nephron 80:166–170
Paragh Gy, Asztalos L, Seres I, Balogh Z, Locsey L, Kárpáti I, Matyus J, Katona E, Harangi M, Kakuk Gy (1999) Serum paraoxonase activity changes in uremic and kidney transplanted patients. Nephron 83:126–131
Beckman JS, Koppenol WH (1994) Reactions and diffusion of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite. Biochemist 16:8–10
Berliner JA, Navab M, Fogelman AM, Frank JS, Demer LL, Edwards PA, Watson AD, Lusis AJ (1995) Atherosclerosis: basic mechanism. Oxidation, inflammation, and genetics. Circulation 91:2488–2496
Vaca CE, Wilhelm J, Harms-Ringdahl M (1988) Interaction of lipid peroxidation products with DNA. A review. Mutat Res 195:137–149
Naoumova RP, O‘Neill FH, Dunn S, Neurwirth CK, Taylor GW, Axelson M, Thompson GR (1999) Effect of inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase on 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one, a marker of bile acid synthesis: contrasting findings in patients with and without prior up-regulation of the latter pathway. Eur J Clin Invest 29:404–412
Cilla DD Jr, Whitfield LR, Gibson DM, Sedman AJ, Posvar EL (1996) Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of atorvastatin, an inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 60:687–695
Aviram M, Dankner G, Cogan U, Hochgraf E, Brook JG (1992) Lovastatin inhibits low-density lipoprotein oxidation and alters its fluidity and uptake by macrophages: in vitro and in vivo studies. Metabolism 41:229–235
Aviram M (1996) Oxidized low density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) interaction with macrophages in atherosclerosis and the atherogenicity of antioxidants. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 34:599–608
Aviram M, Rosenblat M, Bisgaier CL, Newton RS (1998) Atorvastatin and gemfibrozil metabolites, but not parent drugs, are potent antioxidants against lipoprotein oxidation. Atherosclerosis 138:271–280
Hoffman R, Brook GJ, Aviram M (1992) Hypolipidemic drugs reduce lipoprotein susceptibility to undergo lipid peroxidation: in vitro and ex vivo studies. Atherosclerosis 93:105–113
Raslova K, Dobiasova M, Nagyova A, Fabry R, Rauchova H, Dusinska M (1998) Ciprofibrate treatment in patients with atherogenic lipoprotein phenotype: effects on HDL quality, LDL susceptibility to oxidation and DNA damage. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 54:697–699
Imaeda A, Tanigawa T, Aoki T, Kondo Y, Nakamura N, Yoshikawa T (2001) Antioxidative effects of fluvastatin and its metabolites against oxidative DNA damage in mammalian cultured cells. Free Radic Res 35:789–801
Griess P (1879) Bemerkungen zu der Abhandlung der HH. Wesley and Benedikt Ueber einige Azoverbindungen. Berl Deutsch Chem Gen 12:426
Boyum A (1968) Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. J Clin Lab Invest Suppl 97:77–108
Guerin M, Lassel TS, Le-Goff W, Farnier M, Chapman MJ (2000) Action of atorvastatin in combined hyperlipidemia: preferential reduction of cholesteryl ester transfer from HDL to VLDL1 particles. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:189–197
Noseda G, Darioli R, Keller U, Mordasini R, Shokry A, Schaffhauser B, Riesen W (2000) Evaluating the efficacy and tolerance of atorvastatin in hyperlipidemia in general practice (SWITCH Study). Schweiz Med Wochenschr 130:889–895
Schrott HG, Knapp H, Davila M, Shurzinske L, Black D (2000) Effect of atorvastatin on blood lipid levels in the first 2 weeks of treatment: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am Heart J 140:249–252
Le NA, Innis-Whitehouse W, Li X, Bakker-Arkema R, Black D, Brown WV (2000) Lipid and apolipoprotein levels and distribution in patients with hypertriglyceridemia: effect of triglyceride reductions with atorvastatin. Metabolism 49:167–177
Zhu Q, McMaster J, Mymin D, Dembinski T, Hatch G, Choy PC, Kroeger EA (2000) Effects of atorvastatin treatment on the oxidatively modified low density lipoprotein in hyperlipidemic patients. Mol Cell Biochem 207:9–17
Wierzbicki AS, Lumb PJ, Chik G, Crook MA (1999) Comparison of therapy with simvastatin 80 mg and atorvastatin 80 mg in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Int J Clin Pract 53:609–611
Insull W, Kafonek S, Goldner D, Zieve F (2001) Comparison of efficiency and safety of atorvastatin (10 mg) with simvastatin (10 mg) at six weeks. Am J Cardiol 87:554–559
Gentile S, Turco S, Guarino G, Sasso CF, Amodio M, Magliano P, Salvatore T, Corigliano G, Agrusta M, De Simone G, Gaeta I, Oliviero N, Torella R (2000) Comparative efficiency study of atorvastatin vs. simvastatin, pravastatin, lovastatin and placebo in type 2 diabetic patients with hypercholesterolaemia. Diab Obes Metab 2:355–362
Shishehbor MH, Brennan ML, Aviles RJ, Fu X, Penn MS, Sprecher DL, Hazen SL (2003) Statins promote potent antioxidant effects through specific inflammatory pathways. Circulation 108:426–431
Tomás M, Sentí M, García-Faria F, Vila J, Torrents A, Covas M, Marrugat J (2000) Effect of simvastatin therapy on paraoxonase activity and related lipoproteins in familial hypercholesterolemic patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:2113–2119
Sorenson RC, Bisgaier CL, Aviram M, Hsu C, Billecke S, La Du BN (1999) Human serum paraoxonase/arylesterase’s retained hydrophobic N-terminal leader sequence associates with HDLs by binding phospholipids: apolipoprotein A-I stabilizes activity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:2214–2225
O’Donnell VB, Chumley PH, Hogg N, Bloodsworth A, Darley-Usmar VM, Freeman BA (1997) Nitric oxide inhibition of lipid peroxidation: kinetics of reaction with lipid peroxyl radicals and comparison with alpha-tocopherol. Biochemistry 36:15216–15223
Wagner AH, Kohler T, Ruckschloss U, Just I, Hecker M (2000) Improvement of nitric oxide-dependent vasodilatation by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors through attenuation of endothelial superoxide anion formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:61–69
Bonneau C, Couderc R, Tissot M, Athias A, Roch-Arveiller M, Giroud JP (1997) Effects of human low-density lipoproteins on superoxide production by formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine activated polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Eur J Chem Clin Biochem 35:73–80
Paragh G, Kovacs E, Seres I, Keresztes T, Balogh Z, Szabo J, Teichmann F, Foris G (1999) Altered signal pathway in granulocytes from patients with hypercholesterolemia. J Lipid Res 40:1728–1733
Bartsch H, Nair J (2000) Ultrasensitive and specific detection methods for exocyclic DNA adducts: markers for lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress. Toxicology 153:105–114
Harangi M, Remenyik E, Seres I, Varga Z, Katona E, Paragh G (2002) Determination of DNA damage induced by oxidative stress in hyperlipidemic patients. Mutat Res 513:17–25
Franzoni F, Quinones-Galvan A, Regoli F, Ferrannini E, Galetta F (2003) A comparative study of the in vitro antioxidant activity of statins. Int J Cardiol 90:317–321
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from OTKA (Hungarian Scientific Research Fund) (T032674), and ETT (Medical Research Council) (107/2001), Hungary.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harangi, M., Seres, I., Varga, Z. et al. Atorvastatin effect on high-density lipoprotein-associated paraoxonase activity and oxidative DNA damage. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 60, 685–691 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-004-0820-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-004-0820-6