Abstract
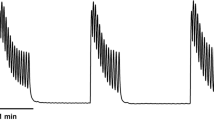
Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) isoenzymes are key proteins regulating intracellular cyclic nucleotide turnover and thus smooth muscle tension. Several in vitro studies have indicated that the cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP-mediated signaling may play a role in the control of human ureteral muscle. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the functional effects of PDE5 inhibitors sildenafil (Sil), vardenafil (Var) and tadalafil (Tad), as well as nitric oxide (NO)-donating agent sodium nitroprusside (SNP) and non-selective muscarinic antagonist butylscopolamine (BSC) on the tension induced by KCl and the turnover of cyclic nucleotides in isolated human ureteral smooth muscle. In vitro relaxant responses of human ureteral smooth muscle to the PDE5 inhibitors mentioned above were investigated using the organ bath technique. Cyclic nucleotides cAMP and cGMP were determined by means of specific radioimmunoassay following incubation of the tissue with Sil, Var, Tad and SNP. The tension induced by KCl of the ureteral tissue was dose dependently reversed by the drugs with the following rank order of efficacy: SNP > Var ≥ Sil > Tad > BSC. R max values ranged from 25 ± 9% (SNP) to 5 ± 3% (BSC). Relaxant responses were paralleled by threefold to fourfold increase in tissue levels of cGMP. Our results indicate that PDE5 inhibitors can reverse the tension of isolated human ureteral smooth muscle via cGMP-mediated pathways. Nevertheless, further studies are indicated in order to evaluate as to whether there might be a use for PDE5 inhibitors in the treatment of ureteral stone disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moe OW (2006) Kidney stones: pathophysiology and medical management. Lancet 367:333–344
Coll DM, Varanelli MJ, Smith RC (2002) Relationship of spontaneous passage of ureteral calculi to stone size and location as revealed by unenhanced helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 178:101–103
Roberts WW, Cadeddu JA, Micali S, Kavoussi LR, Moore RG (1998) Ureteral stricture formation after removal of impacted calculi. J Urol 159:723–726
Porpiglia F, Destefanis P, Fiori C, Fontana D (2000) Effectiveness of nifedipine and deflazacort in the management of distal ureter stones. Urology 56:579–582
Sivrikaya A, Celik OF, Sivrikaya N, Ozgur GK (2003) The effect of diclofenac sodium and papaverine on isolated human ureteric smooth muscle. Int Urol Nephrol 35:479–483
Ahmad M, Chaughtai MN, Khan FA (1991) Role of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors in the passage of ureteric calculus. J Pak Med Assoc 41:268–270
Cervenakov I, Fillo J, Mardiak J, Kopecny M, Smirala J, Lepies P (2002) Speedy elimination of ureterolithiasis in lower part of ureters with the alpha 1-blocker—Tamsulosin. Int Urol Nephrol 34:25–29
Dellabella M, Milanese G, Muzzonigro G (2003) Efficacy of tamsulosin in the medical management of juxtavesical ureteral stones. J Urol 170:2202–2205
Pozzan T, Rizzuto R, Volpe P, Meldolesi J (1994) Molecular and cellular physiology of intracellular calcium stores. Physiol Rev 74:595–636
Schmidt HH, Lohmann SM, Walter U (1993) The nitric oxide and cGMP signal transduction system: regulation and mechanism of action. Biochim Biophys Acta 1178:153–175
Briganti A, Salonia A, Deho’ F, Zanni G, Barbieri L, Rigatti P, Montorsi F (2005) Clinical update on phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction. World J Urol 23:374–384
Sairam K, Kulinskaya E, McNicholas TA, Boustead GB, Hanbury DC (2002) Sildenafil influences lower urinary tract symptoms. BJU Int 90:836–839
McVary T, Roehrborn CG, Kaminetsky JC, Auerbach SM, Wachs B, Young JM, Esler A, Sides GD, Denes B (2006) The efficacy and safety of tadalafil administered once a day for lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol 5(Suppl 2):196
Truss MC, Stief CG, Uckert S, Becker AJ, Wefer J, Schultheiss D, Jonas U (2001) Phosphodiesterase 1 inhibition in the treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunction: from bench to bedside. World J Urol 19:344–350
Berman JR, Berman LA, Lin H, Flaherty E, Lahey N, Goldstein I, Cantey-Kiser J (2001) Effect of sildenafil on subjective and physiologic parameters of the female sexual response in women with sexual arousal disorder. J Sex Marital Ther 27:411–420
Taher A, Schulz-Knappe P, Meyer M, Truss M, Forssmann WG, Stief CG, Jonas U (1994) Characterization of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes in the human ureter and their functional role in vitro. World J Urol 12:286–291
Kuhn R, Uckert S, Stief CG, Truss MC, Lietz B, Bischoff E, Schramm M, Jonas U (2000) Relaxation of human ureteral smooth muscle in vitro by modulation of cyclic nucleotide-dependent pathways. Urol Res 28:110–115
Saighi D, Zerbib M, Thiounn N, Flam T, Conquy S, Jacob L, l’Ava-Santucci J, Debre B, nh-Xuan AT (2000) In vitro study of the modulation of human ureteral tonus by nitric oxide and zaprinast, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Prog Urol 10:1161–1168
Becker AJ, Stief CG, Meyer M, Truss MC, Forssmann WG, Jonas U (1998) The effect of the specific phosphodiesterase-IV-inhibitor rolipram on the ureteral peristalsis of the rabbit in vitro and in vivo. J Urol 160:920–925
Nicholson CD, Challiss RA, Shahid M (1991) Differential modulation of tissue function and therapeutic potential of selective inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes. Trends Pharmacol Sci 12:19–27
Jeremy JY, Ballard SA, Naylor AM, Miller MA, Angelini GD (1997) Effects of sildenafil, a type-5 cGMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor, and papaverine on cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP levels in the rabbit corpus cavernosum in vitro. Br J Urol 79:958–963
Chuang AT, Strauss JD, Murphy RA, Steers WD (1998) Sildenafil, a type-5 CGMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor, specifically amplifies endogenous cGMP-dependent relaxation in rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle in vitro. J Urol 160:257–261
Stief CG, Uckert S, Truss MC, Becker AJ, Machtens S, Jonas U (1996) A possible role for nitric oxide in the regulation of human ureteral smooth muscle tone in vitro. Urol Res 24:333–337
Lau LC, Adaikan PG (2006) Mechanisms of direct relaxant effect of sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil on corpus cavernosum. Eur J Pharmacol 541(3):184–190
Nies AT, Spring H, Thon WF, Keppler D, Jedlitschky G (2002) Immunolocalization of multidrug resistance protein 5 in the human genitourinary system. J Urol 167(5):2271–2275
Dosda R, Marti-Bonmati L, Ronchera-Oms CL, Molla E, Arana E. (2003) Effect of subcutaneous butylscopolamine administration in the reduction of peristaltic artifacts in 1.5-T MR fast abdominal examinations. Eur Radiol 13(2):294–298
Fuessl HS (2006) Emergency checklist: renal and ureteral colic. MMW Fortschr Med 41:31–32
Wanajo I, Tomiyama Y, Tadachi M, Kobayashi M, Yamazaki Y, Kojima M, Shibata N (2005) The potency of KUL-7211, a selective ureteral relaxant, in isolated canine ureter: comparison with various spasmolytics. Urol Res 33(6):409–414
Holdgate A, Oh CM (2005) Is there a role for antimuscarinics in renal colic? A randomized controlled trial. J Urol 174(2):572–575, discussion 575
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gratzke, C., Ückert, S., Kedia, G. et al. In vitro effects of PDE5 inhibitors sildenafil, vardenafil and tadalafil on isolated human ureteral smooth muscle: a basic research approach. Urol Res 35, 49–54 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-006-0073-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-006-0073-1