Abstract
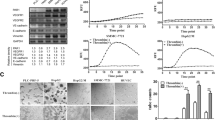
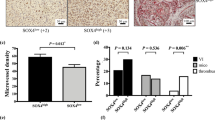
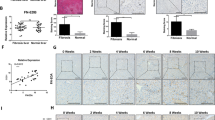
T-cadherin is a unique receptor of adiponectin, which plays a critical role in various angiogenesis. In the present study, T-cadherin expression in tumor vessels of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and, subsequently, the molecular mechanism, which induced T-cadherin expression in sinusoidal endothelial cells were investigated. Sinusoidal endothelium in nontumorous liver, chronic hepatitis, or liver cirrhosis expressed little or no T-cadherin. By contrast, T-cadherin was found in intratumoral capillary endothelial cells of 34 out of 63 HCC specimens. In positive cases, focal T-cadherin expression was found in well-differentiated HCC, whereas diffuse and intense T-cadherin expression was observed in poorly differentiated HCC specimens. T-cadherin was much expressed in intratumoral capillary endothelial cells in a less differentiated HCC region than that in a well-differentiated region in five specimens, in which various differentiated HCC components were coexistent. In a double-cell chamber assay, fibroblast growth factor-2 appeared to have a critical role to induce T-cadherin in cultured liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. The present finding indicated that T-cadherin was selectively expressed in intratumoral capillary endothelial cells of many HCCs, increasingly expressed as tumor progression, and T-cadherin may have a positive role in angiogenesis of HCC. In addition, cross talk between the signal pathways mediated by fibroblast growth factor-2 and adiponectin was suggested.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asada N, Tanaka Y, Hayashido Y, Toratani S, Kan M, Kitamoto M, Nakanishi T, Kajiyama G, Chayama K, Okamoto T (2003) Expression of fibroblast growth factor receptor genes in human hepatoma-derived cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 39:321–328
Bråkenhielm B, Veitonmäki N, Cao R, Kihara S, Matsuzawa Y, Zhivotovsky B, Fukuhashi T, Cao Y (2004) Adiponectin-induced antiangiogenesis and antitumor activity involve caspase-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:2476–2481
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407:249–257
Chen X, Cheung ST, So S, Fan ST, Barry C, Higgins J, Lai KM, Ji J, Dudoit S, Ng IO, Van De Rijn M, Botstein D, Brown PO (2002) Gene expression patterns in human liver cancers. Mol Biol Cell 13:1929–1939
Edmonson HA, Steiner PE (1954) Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 among 489,000 necropsies. Cancer (Phila), 7:462–503
Edwards S, Lalor PF, Nash GB, Rainger GE, Adams DH (2005) Lymphocyte traffic through sinusoidal endothelial cells is regulated by hepatocytes. Hepatology 41:451–459
Gibson JB, Sobin LH (1978) Histological typing of tumors of the liver, biliary tract and pancreas. In: International Histological Classification of Tumors. World Health Organization, Geneva 19–25
Goldstein BJ, Scalia R (2004) Adiponectin: a novel adipokine linking adipocytes and vascular function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2563–2568
Huang ZY, Wu Y, Hedrick N, Gutmann DH (2003) T-cadherin-mediated cell growth regulation involves G2 phase arrest and requires p21(CIP1/WAF1) expression. Mol Cell Biol 23:566–578
Hug C, Wang J, Ahmad NS, Bogan JS, Tsao TS, Lodish HF (2004) T-cadherin is a receptor for hexameric and high-molecular-weight forms of Acrp30/adiponectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:10308–10313
Ivanov D, Philippova M, Allenspach R, Erne P, Resink T (2004) T-cadherin upregulation correlates with cell-cycle progression and promotes proliferation of vascular cells. Cardiovasc Res 64:132–143
Jin-no K, Tanimizu M, Hyodo I, Kurimoto F, Yamashita T (1997) Plasma level of basic fibroblast growth factor increases with progression of chronic liver disease. J Gastroenterol 32:119–121
Kobayashi H, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Walsh K, Kumada M, Abe Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2004) Selective suppression of endothelial cell apoptosis by the high molecular weight form of adiponectin. Circ Res 94:27–31
Lee SW (1996) H-cadherin, a novel cadherin with growth inhibitory functions and diminished expression in human breast cancer. Nat Med 2:776–782
Li X, Massa PE, Hanidu A, Peet GW, Aro P, Savitt A, Mische S, Li J, Marcu KB (2002) IKKalpha, IKKbeta, and NEMO/IKKgamma are each required for the NF-kappa B-mediated inflammatory response program. J Biol Chem 277:45129–45140
Maret A, Galy B, Arnaud E, Bayard F, Prats H (1995) Inhibition of fibroblast growth factor 2 expression by antisense RNA induced a loss of the transformed phenotype in a human hepatoma cell line. Cancer Res 55:5075–5079
Maruyama R, Toyooka S, Toyooka KO, Harada K, Virmani AK, Zochbauer-Muller S, Farinas AJ, Vakar-Lopez F, Minna JD, Sagalowsky A, Czerniak B, Gazdar AF (2001) Aberrant promoter methylation profile of bladder cancer and its relationship to clinicopathological features. Cancer Res 61:8659–8663
Mise M, Arii S, Higashituji H, Furutani M, Niwano M, Harada T, Ishigami S, Toda Y, Nakayama H, Fukumoto M, Fujita J, Imamura M (1996) Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor gene expression in liver tumor. Hepatology 23:455–464
Motoo Y, Sawabu N, Yamaguchi Y, Terada T, Nakanuma Y (1993) Sinusoidal capillarization of human HCC: possible promotion by fibroblast growth factor. Oncology 50:270–274
Mouta Carreira C, Nasser SM, di Tomaso E, Padera TP, Boucher Y, Tomarev SI, Jain RK (2001) LYVE-1 is not restricted to the lymph vessels: expression in normal liver blood sinusoids and down-regulation in human liver cancer and cirrhosis. Cancer Res 61:8079–8084
Nagafuchi A, Takeichi M (1988) Cell binding function of E-cadherin is regulated by the cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J 7:3679–3684
Nakamura S, Muro H, Suzuki S, Sakaguchi T, Konno H, Baba S, Syed AS (1997) Immunohistochemical studies on endothelial cell phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 26:407–415
El-Assal ON, Yamanoi A, Ono T, Kohno H, Nagasue N (2001) The clinicopathological significance of heparanase and basic fibroblast growth factor expressions in HCC. Clin Cancer Res 7:1299–1305
Oshima RG, Lesperance J, Munoz V, Hebbard L, Ranscht B, Sharan N, Muller WJ, Hauser CA, Cardiff RD (2004) Angiogenic acceleration of Neu induced mammary tumor progression and metastasis. Cancer Res 64:169–179
Ouchi N, Kobayashi H, Kihara S, Kumada M, Sato K, Inoue T, Funahashi T, Walsh K (2004) Adiponectin stimulates angiogenesis by promoting cross-talk between AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt signaling in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 279:1304–1309
Ranscht B, Dours-Zimmermann MT (1991) T-cadherin, a novel cadherin cell adhesion molecule in the nervous system, lacks the conserved cytoplasmic region. Neuron 7:391–402
Riou P, Saffroy R, Comoy J, Gross-Goupil M, Thiery JP, Emile JF, Azoulay D, Piatier-Tonneau D, Lemoine A, Debuire B (2002) Investigation in liver tissues and cell lines of the transcription of 13 genes mapping to the 16q24 region that are frequently deleted in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 8:3178–3186
Roman-Gomez J, Castillejo JA, Jimenez A, Cervantes F, Boque C, Hermosin L, Leon A, Granena A, Colomer D, Heiniger A, Torres A (2003) Cadherin-13, a mediator of calcium-dependent cell–cell adhesion, is silenced by methylation in chronic myeloid leukemia and correlates with pretreatment risk profile and cytogenetic response to interferon alfa. J Clin Oncol 21:1429–1472
Sakai M, Hibi K, Koshikawa K, Inoue S, Takeda S, Kaneko T, Nakao A (2004) Frequent promoter methylation and gene silencing of CDH13 in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci 95:588–591
Sakamoto M, Ino Y, Fujii T, Hirohashi S (1993) Phenotype changes in tumor vessels associated with the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol 23:98–104
Sato M, Mori Y, Sakurada A, Fujimura S, Horii A (1998) The H-cadherin (CDH13) gene is inactivated in human lung cancer. Hum Genet 103:96–101. Erratum in: Hum Genet (1998) 103:532
Takeuchi T, Kobayashi M, Moriki T, Miyoshi I (1988) Application of a monoclonal antibody for the detection of Trichosporon beigelii in paraffin-embedded tissue sections. J Pathol 15:23–27
Takeuchi T, Misaki A, Chen BK, Ohtsuki Y (1999) H-cadherin expression in breast cancer. Histopathology 35:87–88
Takeuchi T, Misaki A, Liang S-B, Tachibana A, Hayashi N, Sonobe H, Ohtsuki Y (2000) Expression of T-cadherin (CDH13, H-cadherin) in human brain and its characteristics as a negative growth regulator of EGF in neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem 74:1489–1497
Takeuchi T, Ohtsuki Y (2001) Recent progress of T-cadherin (CDH13, H-cadherin) research. Histol Histopathol 16:1287–1293
Takeuchi T, Liang SB, Matsuyoshi N, Zhou S, Miyachi Y, Sonobe H, Ohtsuki Y (2002a) Loss of T-cadherin (CDH13, H-cadherin) expression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Lab Invest 82:1023–1029
Takeuchi T, Liang SB, Ohtsuki Y (2002b) Downregulation of expression of a novel cadherin molecule, T-cadherin, in basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Mol Carcinog 35:173–179
Salomon D, Ayalon O, Patel-King R, Hynes RO, Geiger B (1992) Extrajunctional distribution of N-cadherin in cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 102:7–17
Tsao TS, Murrey HE, Hug C, Lee DH, Lodish HF (2002) Oligomerization state-dependent activation of NF-kappa B signaling pathway by adipocyte complement-related protein of 30 kDa (Acrp30). J Biol Chem 277:29359–29362
Toyooka KO, Toyooka S, Virmani AK, Sathyanarayana UG, Euhus DM, Gilcrease M, Minna JD, Gazdar AF (2001) Loss of expression and aberrant methylation of the CDH13 (H-cadherin) gene in breast and lung carcinomas. Cancer Res 61:4556–4560
Toyooka S, Toyooka KO, Harada K, Miyajima K, Makarla P, Sathyanarayana UG, Yin J, Sato F, Shivapurkar N, Meltzer SJ, Gazdar AF (2002) Aberrant methylation of the CDH13 (H-cadherin) promoter region in colorectal cancers and adenomas. Cancer Res 62:3382–3386
Wyder L, Vitaliti A, Schneider H, Hebbard LW, Moritz DR, Wittmer M, Ajimo M, Klemenz R (2000) Increased expression of H/T-cadherin in tumor penetrating blood vessels. Cancer Res 60:4682–4688
Zhou S, Matsuyoshi N, Liang SB, Takeuchi T, Ohtsuki Y, Miyachi Y (2002) Expression of T-cadherin in basal keratinocytes of skin. J Invest Dermatol 118:1080–1084
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. Yamaguchi, Takuya, Ms. Nakamura, Naoyo (Department of Pathology, Kochi Medical School), and Ms. Matumura, Rumi (Division of Molecular Biology, Kochi Medical School) for skillful technique. This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education of Japan (KAKEN 12670165, 13670177, and 17590270) and the Medical Research Fund of Kochi Medical School.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adachi, Y., Takeuchi, T., Sonobe, H. et al. An adiponectin receptor, T-cadherin, was selectively expressed in intratumoral capillary endothelial cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: possible cross talk between T-cadherin and FGF-2 pathways. Virchows Arch 448, 311–318 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-0098-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-005-0098-9