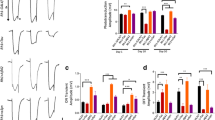
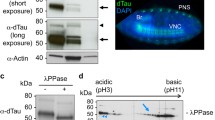
Abstract
The microtubule-binding protein tau has been investigated for its contribution to various neurodegenerative disorders. However, the findings from transgenic studies, using the same tau transgene, vary widely among different laboratories. Here, we have investigated the potential mechanisms underlying tauopathies by comparing Drosophila (d-tau) and human (h-tau) tau in a Drosophila model. Overexpression of a single copy of either tau isoform in the retina results in a similar rough eye phenotype. However, co-expression of Par-1 with d-tau leads to lethality, whereas co-expression of Par-1 with h-tau has little effect on the rough eye phenotype. We have found analogous results by comparing larval proteomes. Through genetic screening and proteomic analysis, we have identified some important potential modifiers and tau-associated proteins. These results suggest that the two tau genes differ significantly. This comparison between species-specific isoforms may help to clarify whether the homologous tau genes are conserved.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker M, Kwok JB, Kucera S, Crook R, Farrer M, Houlden H, Isaacs A, Lincoln S, Onstead L, Hardy J, Wittenberg L, Dodd P, Webb S, Hayward N, Tannenberg T, Andreadis A, Hallupp M, Schofield P, Dark F, Hutton M (1997) Localization of frontotemporal dementia with Parkinsonism in an Australian kindred to chromosome 17q21-22. Ann Neurol 42:794–798
Bertram L, McQueen M, Mullin K, Blacker D, Tanzi R (2006) The AlzGene database, Alzheimer research forum. Available at: http://www.alzgene.org. Accessed July 13, 2006
Chau KW, Chan WY, Shaw PC, Chan HY (2006) Biochemical investigation of tau protein phosphorylation status and its solubility properties in Drosophila. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346:150–159
Chee F, Mudher A, Newman TA, Cuttle M, Lovestone S, Shepherd D (2006) Overexpression of tau results in defective synaptic transmission in Drosophila neuromuscular junctions. Biochem Soc Trans 34:88–90
Delacourte A, Buee L (2000) Tau pathology: a marker of neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 13:371–376
Delobel P, Flament S, Hamdane M, Mailliot C, Sambo AV, Begard S, Sergeant N, Delacourte A, Vilain JP, Buee L (2002) Abnormal tau phosphorylation of the Alzheimer-type also occurs during mitosis. J Neurochem 83:412–420
Doerflinger H, Benton R, Shulman JM, St Johnston D (2003) The role of PAR-1 in regulating the polarised microtubule cytoskeleton in the Drosophila follicular epithelium. Development 130:3965–3975
Götz J, Probst A, Spillantini MG, Schäfer T, Jakes R, Bürki K, Goedert M (1995) Somatodendritic localization and hyperphosphorylation of tau protein in transgenic mice expressing the longest human brain tau isoform. EMBO J 14:1304–1313
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Quinlan M, Tung YC, Zaidi MS, Wisniewski HM (1986a) Microtubule-associated protein tau. A component of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem 261:6084–6089
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung YC, Quinlan M, Wisniewski HM, Binder LI (1986b) Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4913–4917
Guo A, Liu L, Xia SZ, Feng CH, Wolf R, Heisenberg M (1996) Conditioned visual flight orientation in Drosophila: dependence on age, practice, and diet. Learn Mem 3:49–59
Hall GF, Yao J, Lee G (1997) Human tau becomes phosphorylated and forms filamentous deposits when overexpressed in lamprey central neurons in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:4733–4738
Hannus M, Feiguin F, Heisenberg CP, Eaton S (2002) Planar cell polarization requires Widerborst, a B’ regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. Development 129:3493–3503
Hay BA, Wolff T, Rubin GM (1994) Expression of baculovirus P35 prevents cell death in Drosophila. Development 120:2121–2129
Heidary G, Fortini ME (2001) Identification and characterization of the Drosophila tau homolog. Mech Dev 108:171–178
Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, Pickering-Brown S, Chakraverty S, Isaacs A, Grover A, Hackett J, Adamson J, Lincoln S, Dickson D, Davies P, Petersen RC, Stevens M, de Graaff E, Wauters E, van Baren J, Hillebrand M, Joosse M, Kwon JM, Nowotny P, Che LK, Norton J, Morris JC, Reed LA, Trojanowski J, Basun H, Lannfelt L, Neystat M, Fahn S, Dark F, Tannenberg T, Dodd PR, Hayward N, Kwok JB, Schofield PR, Andreadis A, Snowden J, Craufurd D, Neary D, Owen F, Oostra BA, Hardy J, Goate A, van Swieten J, Mann D, Lynch T, Heutink P (1998) Association of missense and 5'-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 393:702–705
Jackson GR, Wiedau-Pazos M, Sang TK, Wagle N, Brown CA, Massachi S, Geschwind DH (2002) Human wild-type tau interacts with wingless pathway components and produces neurofibrillary pathology in Drosophila. Neuron 34:509–519
Karsten SL, Sang TK, Gehman LT, Chatterjee S, Liu J, Lawless GM, Sengupta S, Berry RW, Pomakian J, Oh HS, Schulz C, Hui KS, Wiedau-Pazos M, Vinters HV, Binder LI, Geschwind DH, Jackson GR (2006) A genomic screen for modifiers of tauopathy identifies puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase as an inhibitor of tau-induced neurodegeneration. Neuron 51:549–560
Khurana V, Lu Y, Steinhilb ML, Oldham S, Shulman JM, Feany MB (2006) TOR-mediated cell-cycle activation causes neurodegeneration in a Drosophila tauopathy model. Curr Biol 16:230–241
Kosik KS, Joachim CL, Selkoe DJ (1986) Microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4044–4048
Kraemer BC, Zhang B, Leverenz JB, Thomas JH, Trojanowski JQ, Schellenberg GD (2003) Neurodegeneration and defective neurotransmission in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of tauopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:980–9985
Lemaitre B, Meister M, Govind S, Georgel P, Steward R, Reichhart JM, Hoffmann JA (1995) Functional analysis and regulation of nuclear import of dorsal during the immune response in Drosophila. EMBO J 14:536–545
Li Y, Liu T, Peng Y, Yuan C, Guo A (2004) Specific functions of Drosophila amyloid precursor-like protein in the development of nervous system and nonneural tissues. J Neurobiol 61:343–358
Li C, Tan YX, Zhou H, Ding SJ, Li SJ, Ma DJ, Man XB, Hong Y, Zhang L, Li L, Xia QC, Wu JR, Wang HY, Zeng R (2005) Proteomic analysis of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: identification of potential tumor markers. Proteomics 5:1125–1139
Mershin A, Pavlopoulos E, Fitch O, Braden BC, Nanopoulos DV, Skoulakis EM (2004) Learning and memory deficits upon tau accumulation in Drosophila mushroom body neurons. Learn Mem 11:277–287
Nishimura I, Yang Y, Lu B (2004) PAR-1 kinase plays an initiator role in a temporally ordered phosphorylation process that confers tau toxicity in Drosophila. Cell 116:671–682
Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Wijsman E, Nemens E, Garruto RM, Anderson L, Andreadis A, Wiederholt WC, Raskind M, Schellenberg GD (1998) Tau is a candidate gene for chromosome 17 frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 43:815–825
Probst A, Gotz J, Wiederhold KH, Tolnay M, Mistl C, Jaton AL, Hong M, Ishihara T, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Crowther RA, Spillantini MG, Burki K, Goedert M (2000) Axonopathy and amyotrophy in mice transgenic for human four-repeat tau protein. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 99:469–481
Robertson J, Loviny TL, Goedert M, Jakes R, Murray KJ, Anderton BH, Hanger DP (1993) Phosphorylation of tau by cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase. Dementia 4:256–263
Roks G, Dermaut B, Heutink P, Julliams A, Backhovens H, Van de Broeck M, Serneels S, Hofman A, Van Broeckhoven C, Duijn CM van, Cruts M (1999) Mutation screening of the tau gene in patients with early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 277:137–139
Russ C, Powell JF, Zhao J, Baker M, Hutton M, Crawford F, Mullan M, Roks G, Cruts M, Lovestone S (2001) The microtubule associated protein Tau gene and Alzheimer’s disease-an association study and meta-analysis. Neurosci Lett 314:92–96
Sang TK, Jackson GR (2005) Drosophila models of neurodegenerative disease. NeuroRx 2:438–446
Scherzer CR, Jensen RV, Gullans SR, Feany MB (2003) Gene expression changes presage neurodegeneration in a Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 12:2457–2466
Shahani N, Brandt R (2002) Functions and malfunctions of the tau proteins. Cell Mol Life Sci 59:1668–1680
Shulman JM, Feany MB (2003) Genetic modifiers of tauopathy in Drosophila. Genetics 165:1233–1242
Spillantini MG, Murrell JR, Goedert M, Farlow MR, Klug A, Ghetti B (1998) Mutation in the tau gene in familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7737–7741
Spittaels K, Van den Haute C, Van Dorpe J, Bruynseels K, Vandezande K, Laenen I, Geerts H, Mercken M, Sciot R, Van Lommel A, Loos R, Van Leuven F (1999) Prominent axonopathy in the brain and spinal cord of transgenic mice overexpressing four-repeat human tau protein. Am J Pathol 155:2153–2165
Spittaels K, Van den Haute C, Van Dorpe J, Geerts H, Mercken M, Bruynseels K, Lasrado R, Vandezande K, Laenen I, Boon T, Van Lint J, Vandenheede J, Moechars D, Loos R, Van Leuven F (2000) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta phosphorylates protein tau and rescues the axonopathy in the central nervous system of human four-repeat tau transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 275:41340–41349
Sullivan W, Ashburner M, Hawley RS (2000) Drosophila protocols. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Tomasiewicz HG, Flaherty DB, Soria JP, Wood JG (2002) Transgenic zebrafish model of neurodegeneration. J Neurosci Res 70:734–745
Torroja L, Chu H, Kotovsky I, White K (1999) Neuronal overexpression of APPL, the Drosophila homologue of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), disrupts axonal transport. Curr Biol 9:489–492
Weingarten MD, Lockwood AH, Hwo SY, Kirschner MW (1975) A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:1858–1862
Wittmann CW, Wszolek MF, Shulman JM, Salvaterra PM, Lewis J, Hutton M, Feany MB (2001) Tauopathy in Drosophila: neurodegeneration without neurofibrillary tangles. Science 293:711–714
Yancopoulou D, Spillantini MG (2003) Tau protein in familial and sporadic diseases. Neuromol Med 4:37–48
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Prof. Rongqiao He for his manuscript annotation, to Prof. Kejing Deng (Fudan University, China), Mel B. Feany, Efthimios M.C. Skoulakis, Bingwei Lu, and Suzanne Eaton for kindly donating valuable fly lines, and to Dr. Jianzheng Guo, Shiyu Xu, and Ziyou Cui for their constructive advice regarding our work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (30270341; 30630028), the Multidisciplinary Program (Brain and Mind) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Major State Basic Research Program (“973 program”; G2000077800; G2006CB806600; 2006CB911003), the Precedent Project of Important Intersectional Disciplines in the Knowledge Innovation Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KJCX1-09-03).
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Data
(DOC 3.38 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Li, Y., Huang, J. et al. Study of tauopathies by comparing Drosophila and human tau in Drosophila . Cell Tissue Res 329, 169–178 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0401-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-007-0401-y