Abstract
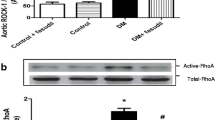
The present study has been designed to investigate the effect of fasudil (Rho-kinase inhibitor) in diabetes mellitus (DM) and hyperhomocyteinemia (HHcy) induced vascular endothelial dysfunction (VED). Streptozotocin (55 mg kg−1, i.v., once only) and methionine (1.7% w/w, p.o., daily for 4 weeks) were administered to rats to produce DM (serum glucose >140 mg dl−1) and HHcy (serum homocysteine >10 μM) respectively. VED was assessed using isolated aortic ring, electron microscopy of thoracic aorta, and serum concentration of nitrite/nitrate. Serum thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) concentration was estimated to assess oxidative stress. Atorvastatin has been employed in the present study as standard agent to improve vascular endothelial dysfunction. Fasudil (15 mg kg−1 and 30 mg kg−1, p.o., daily) and atorvastatin (30 mg kg−1, p.o., daily) treatments significantly attenuated increase in serum glucose and homocysteine but their concentrations remained markedly higher than sham control value. Fasudil and atorvastatin treatments markedly prevented DM and HHcy-induced (i) attenuation of acetylcholine induced endothelium-dependent relaxation, (ii) impairment of vascular endothelial lining, (iii) decrease in serum nitrite/nitrate concentration, and (iv) increase in serum TBARS. It may be concluded that fasudil prevented DM and HHcy-induced VED partially by decreasing serum glucose and homocysteine concentration due to inhibition of Rho-kinase. Moreover, inhibition of Rho-kinase by fasudil and consequent prevention of oxidative stress may have directly improved VED in diabetic and hyperhomocysteinemic rats. The Rho-kinase appears to be a pivotal target site involved in DM and HHcy-induced VED.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luscher TF, Vanhoutte PM: Endothelium dependent vascular response in normotensive and hypertensive Dahl rats. Hypertension 9: 157–163, 1987
Li H, Forstermann U: Nitric oxide in the pathogennesis of vascular disease. J Pathol 190: 244–262, 2000
De Vriese AS, Verbeuren TJ, van de Voorde J, Lameire NH, Vanhoutte PM: Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes. Br J Pharmacol 130: 963–974, 2000
Bonetti PO, Lerman L, Lerman A: Endothelial dysfunction: a marker of atherosclerotic risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23: 168–175, 2003
Lentz SR, Rodionov RN, Dayal S: Hyperhomocysteinemia, endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular risk: the potential role of ADMA. Atheroscler Suppl 4: 61–65, 2003
Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV: Signal transduction by G-proteins, Rho-kinase and protein phosphatase to smooth muscle and non-muscle myosin II. J Physiol 522: 177–185, 2000
Hernandez-Perera O, Perez-Sala D, Soria E, Lamas S: Involvement of Rho GTPases in transcriptional inhibition of preproendothelin-1 gene expression by simvastatin in vascular endothelial cells. Circ Res 87: 616–622, 2000
Laufs U, Liao JK: Post-transcriptional regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA stability by Rho GTPase. J Biol Chem 273: 24266–24271, 1998
Ming XF, Viswambharan H, Barandier C, Ruffieux J, Kaibuchi K, Rusconi S, Yang Z: Rho GTPase/Rho kinase negatively regulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation through the inhibition of protein kinase B/Akt in human endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol 22: 8467–8477, 2002
Shiotani S, Shimada M, Suehiro T, Soejima Y, Yosizumi T, Shimokawa H, Maehara Y: Involvement of Rho-kinase in cold ischemia-reperfusion injury after liver transplantation in rats. Transplantation 78: 375–382, 2004
Higashi M, Shimokawa H, Hattori T, Hiroki J, Mukai Y, Morikawa K, Ichiki T, Takahashi S, Takeshita A: Long term inhibition of Rho-kinase suppresses angiotensin II-induced cardiovascular hypertrophy in rats in vivo: effect on endothelial NAD(P)H oxidase system. Circ Res 93: 767–775, 2003
Kandabashi T, Shimokawa H, Miyata K, Kunihiro I, Kawano Y, Fukata Y, Higo T, Egashira K, Takashi S, Kaibuchi K, Takeshita A: Inhibition of myosin phosphatase by upregulated Rho-kinase plays a key role for coronary artery in a porcine model with interleukin 1-B. Circulation 101: 1319–1323, 2000
Bivalacqua TJ, Champion HC, Usta MF, Cellek S, Chitaley K, Webb RC, Lewis RL, Mills TM, Helstrom WJG, Kadowitz PJ: RhoA/Rho-kinae suppresses endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the penis: a mechanism for diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction. Proct Nat Acad Sci 101: 9121–9126, 2004
Abe K, Shimokawa H, Morikawa K, Uwatoku T, Oi K, Matsumoto Y, Hattori T, Nakashima Y, Kaibuchi K, Sueishi K, Takeshita A: Long-term treatment with a Rho-kinase inhibitor improves monocrotaline-induced fatal pulmonary hypertension in rats. Circ Res 94: 385–393, 2004
Pieper GM, Langenstroer P, Siebeneich W: Diabetic induced endothelial dysfunction in rat aorta: role of hydroxyl radicals. Cardiovasc Res 37: 145–156, 1997
Pieper GM, Siebeneich W: Oral administration of the anioxidant, N-acetylcysteine, abrogates diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 32: 101–105, 1998
Ungvari Z, Sarkadi-Nagy E, Bagi Z, Szollar L, Koller A: Simultaneously increased TXA2 activity in isolated arterioles and platelets of rats with hyperhomocysteinemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20: 1203–1208, 2000
Dimitrova KR, DeGroot KW, Pacquing AM, Suyderhoud JP, Pirovic EA, Munro TJ, Wieneke JA, Myers AK, Kim YD: Estradiol prevents homocysteine-induced endothelial injury in male rats. Cardiovasc Res 53: 589–596, 2002
Mitra S, Singh M: Possible mechanism of captopril induced endothelium-dependet relaxation in isolated rabbit aorta. Mol Cell Biochem 183: 63–67, 1998
Ignarro LJ, Bryns RE, Buga GM, Wood KS, Chaudhari G: Pharmacological evidence that endothelium-derived relaxing factor is NO: use of pyrogallol and superoxide dismutase to study endothelium dependent and NO-elicited vascular smooth muscle relaxation. J Pharmacol Exp Therap 244: 181–188, 1988
Schiller NK, Timothy AM, Chen IL, Rice RC, Akers DL, Kadowitz PJ, McNamaran DB: Endothelial cell regrowth and morphology after balloon catheter injury of alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits. Am J Physiol 277: 240–248, 1999
David GFX, Herbert J, Wright CDS: The ultrastructure of the pineal ganglion in the ferret. J Anat 115: 79–97, 1973
Sastry KVH, Moudgal RP, Mohan J, Tyagi JS, Rao GS: Spectophotometric determination of serum nitrite and nitrate by copper-cadmium alloy. Anal Biochem 306: 79–82, 2002
Ma FA, Liu LY, Xiong XM: Protective effects of lovastatin on vascular endothelium injured by low density lipoprotein. Acta Pharmacol Sin 24: 1027–1032, 2003
Wolfrum, S, Jensen KS, Liao JK: Endothelium-dependent effects of statins. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23: 729–736, 2003
Zhou MS, Jaimes EA, Raij L: Atorvastatin prevents end-organ injury in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension 44: 186–190, 2004
Kohn AD, Summer SA, Birnbaum MJ, Roth RA: Expression of constitutively active Akt Ser/Thr kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocystes stimulates glucose uptake and glucose transporter 4 translocation. J Biol Chem 271: 31372–31378, 1996
Calera MR, Martinez C, Liu H, Jack AKE, Birnbaum MJ, Pilch PF: Insulin increases the association of Akt-2 with Glut4-containing vesicles. J Biol Chem 273: 7201–7204, 1998
Begum N, Sandu OA, Ito M, Lohmann SM, Smolenski A: Active Rho kinase associates with insulin receptor substrate-1 and inhibits insulin signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 22: 6214–6222, 2001
Waly M, Olteanu H, Banerjee R, Choi S-W, Mason JB, Parker BS, Sukumar S, Shim S, Sharma A, Benzecry JM, Power-Charnitsky V-A, Deth RC: Activation of methionine synthase by insulin-like growth factor-1 and dopamine: A target for neurodevelopemental toxins and thimerosal. Mol Psychiatry 1–13, 2004
Fonesca V, Keebler M, Dicker-Brown A, DeSouza C, Poirier LA, Murthy SN, McNamara DB: The effect of troglitazone on plasma homocysteine, hepatic and red blood cell S-adenosyl methionine, and S-adenosyl homocysteine and enzymes in homocysteine metabolism in zucker rats. Metabolism 61: 783–786, 2002
Shimokawa H, Seto M, Katsumata N, Amano M, Kozai T, Yamawaki T, Kuwata K, Kandabashi T, Egashira K, Ikegaki I, Asano T, Kaibuchi K, Takeshita A: Rho-kinase-mediated pathway induces enhanced myosin light chain phosphorylations in a swine model of coronary artery spasm. Cardiovasc Res 43: 1029–1039, 1999
Satoh S, Ikegaki I, Suzuki Y, Asano T, Shibuya M, Hidaka H: Neuroprotective properties of a protein kinase inhibitor against ischaemia-induced neuronal damage in rats and gerbils. Br J Pharmacol 118: 1592–1596, 1996
Kamei S, Oishi M, Takasu T: Evaluation of fasudil hydrochloride treatment for wandering symptoms in cerebrovascular dementia with 31P-magnetic resonance spectroscopy and Xe-computed tomography. Clin Neuropharmacol 19: 428–438, 1996.
Sward K, Dreja K, Susnjar M, Hellstrand P, Hartshorne DJ, Walsh MP: Inhibition of Rho-associated kinase blocks agonist-induced Ca+2 sensitization of myosin phosphorylation and force in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol 522: 33–49, 2000
Hayden MR, Tyagi SC: Homocysteine and reactive oxygen species in metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and atheroscleropathy: The pleotropic effects of folate supplementation. Nutrition J 3: 4–27, 2004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, D.I., Singh, M. Involvement of Rho-kinase in experimental vascular endothelial dysfunction. Mol Cell Biochem 283, 191–199 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-2679-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-2679-6