Abstract
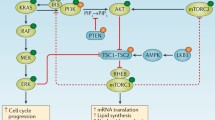
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is commonly amplified and mutated in glioblastoma, making it a compelling therapeutic target. Recent reports have demonstrated clinical activity of the EGFR inhibitors gefitinib and erlotinib in a subset of glioblastoma patients. Co-expression of EGFRvIII, a constitutively active mutant receptor expressed in 50% of tumours, and PTEN, an inhibitor of PI3K activity, by glioblastoma cells is associated with clinical response to these EGFR kinase inhibitors. PTEN loss and resulting increased PI3K pathway activity appears to act as a resistance factor. A critical therapeutic challenge is to identify agents that enhance the anti-cancer effects of these agents and promote responsiveness to EGFR kinase inhibitors in a broader spectrum of glioblastoma patients. For example, combining gefitinib with inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT pathway show enhanced cytotoxicity in glioblastoma derived cell lines. Here, we show that targeting HMG-CoA reductase with lovastatin, that can affect the activity of multiple cell signaling pathways, significantly enhanced the sensitivity of glioblastoma cells to the EGFR kinase inhibitor gefitinib in the five cell lines tested. In an isogenic model system, U87MG glioblastoma cells expressing EGFRvIII and PTEN in relevant combinations, we show that combined gefitinib and lovastatin treatments induce potent synergistic cytotoxicity irrespective of EGFRvIII and PTEN status. These studies demonstrate the potential of lovastatin to augment the cytotoxic effects of gefitinib and provide a rationale for combined statin/EGFR targeted therapies in glioblastoma patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gschwind A, Zwick E, Prenzel N, Leserer M, Ullrich A (2001) Cell communication networks: epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation as the paradigm for interreceptor signal transmission. Oncogene 20:1594–1600
Pawson T (2002) Regulation and targets of receptor tyrosine kinases. Eur J Cancer 38(Suppl 5):S3–10
Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2000) The EGF receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene 19:6550–6565
Threadgill DW, Dlugosz AA, Hansen LA, Tennenbaum T, Lichti U, Yee D, LaMantia C, Mourton T, Herrup K, Harris RC et al (1995) Targeted disruption of mouse EGF receptor: effect of genetic background on mutant phenotype. Science 269:230–234
Jorissen RN, Walker F, Pouliot N, Garrett TP, Ward CW, Burgess AW (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptor: mechanisms of activation and signalling. Exp Cell Res 284:31–53
Stern DF, Kamps MP (1988) EGF-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of p185neu: a potential model for receptor interactions. Embo J 7:995–1001
Tan PB, Kim SK (1999) Signaling specificity: the RTK/RAS/MAP kinase pathway in metazoans. Trends Genet 15:145–149
Boulougouris P, Elder J (2001) Epidermal growth factor receptor structure, regulation, mitogenic signalling and effects of activation. Anticancer Res 21:2769–2775
Herbst RS (2002) ZD1839: targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 11:837–849
Herbst RS (2003) Erlotinib (Tarceva): an update on the clinical trial program. Semin Oncol 30:34–46
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, Gurubhagavatula S, Okimoto RA, Brannigan BW, Harris PL, Haserlat SM, Supko JG, Haluska FG, Louis DN, Christiani DC, Settleman J, Haber DA (2004) Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med 350:2129–2139
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, Naoki K, Sasaki H, Fujii Y, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Johnson BE, Meyerson M (2004) EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 304:1497–1500
Schwartzbaum JA, Fisher JL, Aldape KD, Wrensch M (2006) Epidemiology and molecular pathology of glioma. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2:494–503
Rich JN, Reardon DA, Peery T, Dowell JM, Quinn JA, Penne KL, Wikstrand CJ, Van Duyn LB, Dancey JE, McLendon RE, Kao JC, Stenzel TT, Ahmed Rasheed BK, Tourt-Uhlig SE, Herndon JE 2nd, Vredenburgh JJ, Sampson JH, Friedman AH, Bigner DD, Friedman HS (2004) Phase II trial of gefitinib in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 22:133–142
Barber TD, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW, Velculescu VE (2004) Somatic mutations of EGFR in colorectal cancers and glioblastomas. N Engl J Med 351:2883
Frederick L, Wang XY, Eley G, James CD (2000) Diversity and frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in human glioblastomas. Cancer Res 60:1383–1387
Li B, Yuan M, Kim IA, Chang CM, Bernhard EJ, Shu HK (2004) Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor displays increased signaling through the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/AKT pathway and promotes radioresistance in cells of astrocytic origin. Oncogene 23:4594–4602
Smith JS, Tachibana I, Passe SM, Huntley BK, Borell TJ, Iturria N, O’Fallon JR, Schaefer PL, Scheithauer BW, James CD, Buckner JC, Jenkins RB (2001) PTEN mutation, EGFR amplification, and outcome in patients with anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma multiforme. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:1246–1256
Bianco R, Shin I, Ritter CA, Yakes FM, Basso A, Rosen N, Tsurutani J, Dennis PA, Mills GB, Arteaga CL (2003) Loss of PTEN/MMAC1/TEP in EGF receptor-expressing tumor cells counteracts the antitumor action of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene 22:2812–2822
Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I, Haas-Kogan DA, Zhu S, Dia EQ, Lu KV, Yoshimoto K, Huang JH, Chute DJ, Riggs BL, Horvath S, Liau LM, Cavenee WK, Rao PN, Beroukhim R, Peck TC, Lee JC, Sellers WR, Stokoe D, Prados M, Cloughesy TF, Sawyers CL, Mischel PS (2005) Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med 353:2012–2024
Wang MY, Lu KV, Zhu S, Dia EQ, Vivanco I, Shackleford GM, Cavenee WK, Mellinghoff IK, Cloughesy TF, Sawyers CL, Mischel PS (2006) Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition promotes response to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors in PTEN-deficient and PTEN-intact glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 66:7864–7869
Mantha AJ, Hanson JE, Goss G, Lagarde AE, Lorimer IA, Dimitroulakos J (2005) Targeting the mevalonate pathway inhibits the function of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin Cancer Res 11:2398–2407
Mishima K, Johns TG, Luwor RB, Scott AM, Stockert E, Jungbluth AA, Ji XD, Suvarna P, Voland JR, Old LJ, Huang HJ, Cavenee WK (2001) Growth suppression of intracranial xenografted glioblastomas overexpressing mutant epidermal growth factor receptors by systemic administration of monoclonal antibody (mAb) 806, a novel monoclonal antibody directed to the receptor. Cancer Res 61:5349–5354
Soneoka Y, Cannon PM, Ramsdale EE, Griffiths JC, Romano G, Kingsman SM, Kingsman AJ (1995) A transient three-plasmid expression system for the production of high titer retroviral vectors. Nucleic Acids Res 23:628–633
Dimitroulakos J, Yeger H (1996) HMG-CoA reductase mediates the biological effects of retinoic acid on human neuroblastoma cells: lovastatin specifically targets P-glycoprotein-expressing cells. Nat Med 2:326–333
Dimitroulakos J, Ye LY, Benzaquen M, Moore MJ, Kamel-Reid S, Freedman MH, Yeger H, Penn LZ (2001) Differential sensitivity of various pediatric cancers and squamous cell carcinomas to lovastatin-induced apoptosis: therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer Res 7:158–167
Jiang Z, Zheng X, Lytle RA, Higashikubo R, Rich KM (2004) Lovastatin-induced up-regulation of the BH3-only protein, Bim, and cell death in glioblastoma cells. J Neurochem 89:168–178
Piacentini M, Fesus L, Melino G (1993) Multiple cell cycle access to the apoptotic death programme in human neuroblastoma cells. FEBS Lett 320:150–154
Thibault A, Samid D, Tompkins AC, Figg WD, Cooper MR, Hohl RJ, Trepel J, Liang B, Patronas N, Venzon DJ, Reed E, Myers CE (1996) Phase 1 study of lovastatin, an inhibitor of the mevalonate pathway, in patients with cancer. Clinical Cancer Res 2:483–491
Dancey JE, Freidlin B (2003) Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor—are we missing the mark? Lancet 362:62–64
Mamane Y, Petroulakis E, LeBacquer O, Sonenberg N (2006) mTOR, translation initiation and cancer. Oncogene 25:6416–6422
Corsini A, Maggi FM, Catapano AL (1995) Pharmacology of competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. Pharmacol Res 31:9–27
Chan KK, Oza AM, Siu LL (2003) The statins as anticancer agents. Clin Cancer Res 9:10–19
Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1990) Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature 343:425–430
Gibbs JB, Oliff A, Kohl NE (1994) Farnesyltransferase inhibitors: Ras research yields a potential cancer therapeutic. Cell 77:175–178
Sebti S, Hamilton AD (1997) Inhibitors of prenyl transferases. Curr Opin Oncol 9:557–561
Keyomarsi K, Sandoval L, Band V, Pardee AB (1991) Synchronization of tumor and normal cells from G1 to multiple cell cycles by lovastatin. Cancer Res 51:3602–3609
Dimitroulakos J, Nohynek D, Backway KL, Hedley DW, Yeger H, Freedman MH, Minden MD, Penn LZ (1999) Increased sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemias to lovastatin-induced apoptosis: a potential therapeutic approach. Blood 93:1308–1318
Macaulay RJ, Wang W, Dimitroulakos J, Becker LE, Yeger H (1999) Lovastatin-induced apoptosis of human medulloblastoma cell lines in vitro. J Neurooncol 42:1–11
Knox JJ, Siu LL, Chen E, Dimitroulakos J, Kamel-Reid S, Moore MJ, Chin S, Irish J, LaFramboise S, Oza AM (2005) A Phase I trial of prolonged administration of lovastatin in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck or of the cervix. Eur J Cancer 41:523–530
Acknowledgments
Research support from the Canadian Institute of Health Research (J. D.), the Canadian Foundation for Innovation/Ontario Innovation Trust (J.D.) and the Ottawa Regional Cancer Foundation (J. D.). We wish to thank Apotex Canada and AstraZeneca UK for generously providing reagents used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cemeus, C., Zhao, T.T., Barrett, G.M. et al. Lovastatin enhances gefitinib activity in glioblastoma cells irrespective of EGFRvIII and PTEN status. J Neurooncol 90, 9–17 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9627-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9627-0