Abstract
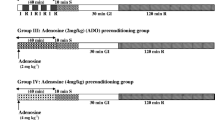
Exogenously administered adenosine agonist will protect myocardium against infarction during ischemia. However, long-term exposure to adenosine agonists is associated with loss of this protection. To determine why this protection is lost, isolated, perfused rabbit hearts were studied after administration of R(-)-N6-(2-phenylisopropyl)adenosine (PIA), 0.25 mg/h IP, for 3-4 days to intact animals. All hearts experienced 30 min of regional ischemia and 120 min of reperfusion. Control groups 1 and 2 were untreated. In group 1 this ischemia/reperfusion was the only intervention, whereas group 2 hearts were preconditioned with a cycle of 5 min global ischemia/10 min reperfusion preceding the 30 min regional ischemia. Groups 3-5 had been chronically exposed to PIA. Group 3 hearts had 1 preconditioning ischemia/reperfusion cycle before the prolonged ischemia. Group 4 received a 5 min infusion of 0.1 μmol/L phenylephrine in lieu of global ischemia, whereas group 5 was instead treated with 1 μmol/L carbachol. Infarct size averaged 32% of the risk zone in group 1, whereas ischemic preconditioning limited infarction to 8.2 in group 2. Prolonged exposure of group 3 hearts to PIA resulted in the inability of preconditioning with 5 min global ischemia to protect (28.7 ± 4.4% infarction). However, protection was restored by either phenylephrine, an agonist of α1-adrenergic receptors which couple to Gq and stimulate PKC, or carbachol, an agonist of M2-muscarinic receptors which couple instead to Gi as do adenosine A1 receptors (5.2 ± 1.7% and 9.2 ± 2.1% infarction, resp.). Therefore, cross tolerance to ischemic preconditioning develops after chronic PIA infusion. Since both the Gi and the PKC components of the preconditioning pathway were shown to be intact, tolerance must have been related to downregulation or desensitization of the A1 adenosine receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu GS, Thorton J, Van Winkle DM, Stanley AWH, Olsson RA, Downey JM: Protection against infarction afforded by preconditioning is mediated by A1 adenosine receptors in rabbit heart. Circulation 84: 350–356, 1991
Tsuchida A, Liu GS, Wilborn WH, Downey JM: Pretreatment with the adenosine A1 selective agonist, 2-chloro-N6-cyclopentyladenosine (CCPA), causes a sustained limitation of infarct size in rabbits. Cardiovasc Res 27: 652–656, 1993
Thornton JD, Liu GS, Olsson RA, Downey JM: Intravenous pretreatment with A1-selective adenosine analogues protects the heart against infarction. Circulation 85: 659–665, 1992
Tsuchida A, Thompson R, Olsson RA, Downey JM: The anti-infarct effect of an adenosine A1-selective agonist is diminished after prolonged infusion as is the cardioprotective effect of ischaemic preconditioning in rabbit heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 26: 303–311, 1994
Cohen MV, Yang X-M, Downey JM: Conscious rabbits become tolerant to multiple episodes of ischemic preconditioning. Circ Res 74: 998–1004, 1994
Green A: Adenosine receptor down-regulation and insulin resistance following prolonged incubation of adipocytes with an A1 adenosine receptor agonist. J Biol Chem 262: 15702–15707, 1987
Ramkumar V, Olah ME, Jacobson KA, Stiles GL: Distinct pathways of desensitization of A1-and A2-adenosine receptors in DDT1 MF-2 cells. Mol Pharmacol 40: 639–647, 1991
Green A, Johnson JL, Milligan G: Down-regulation of Gi sub-types by prolonged incubation of adipocytes with an A1 adenosine receptor agonist. J Biol Chem 265: 5206–5210, 1990
Lohse MJ, Andexinger S, Pitcher J, Trukawinski S, Codina J, Faure J-P, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ: Receptor-specific desensitization with purified proteins: Kinase dependence and receptor specificity of β-arrestin and arrestin in the β2-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin systems. J Biol Chem 267: 8558–8564, 1992
Hausdorff WP, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ: Turning off the signal: Desensitization of β-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J 4: 2881–2889, 1990
Fleming JW, Wisler PL, Watanabe AM: Signal transduction by G proteins in cardiac tissues. Circulation 85: 420–433, 1992
Kohl C, Linck B, Schmitz W, Scholz H, Scholz J, Tóth M: Effects of carbachol and (–)-N6-phenylisopropyladenosine on myocardial inositol phosphate content and force of contraction. Br J Pharmacol 101: 829–834, 1990
Ytrehus K, Liu Y, Downey JM: Preconditioning protects ischemic rabbit heart by protein kinase C activation. Am J Physiol 266: H1145–H1152, 1994
Tsuchida A, Liu Y, Liu GS, Cohen MV, Downey JM: α1-Adrenergic agonists precondition rabbit ischemic myocardium independent of adenosine by direct activation of protein kinase C. Circ Res 75: 576–585, 1994
Speechly-Dick ME, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM: Protein kinase C: Its role in ischemic preconditioning in the rat. Circ Res 75: 586–590, 1994
Huang K-P, Huang FL, Nakabayashi H, Mahoney CW, Chen K-H: Mechanism of protein kinase C-mediated signal transduction. In: S Papa, A Azzi, JM Tager (eds). Adenosine Nucleotides in Cellular Energy Transfer and Signal Transduction. Birkhaüser Verlag, Basel, 1992, pp 219–230
Savart M, Letard P, Bultel S, Ducastaing A: Induction of protein kinase C down-regulation by the phorbol ester TPA in a calpain/protein kinase C complex. Int J Cancer 52: 399–403, 1992
Liu G-S, Downey JM, Cohen MV: Adenosine, ischemia, and preconditioning. In: KA Jacobson, MF Jarvis (eds). Purinergic Approaches in Experimental Therapeutics. Wiley-Liss, New York, 1997, pp 153–172
Thornton JD, Liu GS, Downey JM: Pretreatment with pertussis toxin blocks the protective effects of preconditioning: Evidence for a Gprotein mechanism. J Mol Cell Cardiol 25: 311–320, 1993
Thornton JD, Daly JF, Cohen MV, Yang X-M, Downey JM: Catecholamines can induce adenosine receptor-mediated protection of the myocardium but do not participate in ischemic preconditioning in the rabbit. Circ Res 73: 649–655, 1993
Exton JH: Phosphoinositide phospholipases and G proteins in hormone action. Annu Rev Physiol 56: 349–369, 1994
LaMorte VJ, Thornburn J, Absher D, Spiegel A, Brown JH, Chien KR, Feramisco JR, Knowlton KU: Gq-and ras-dependent pathways mediate hypertrophy of neonatal rat ventricular myocytes following α1-adrenergic stimulation. J Biol Chem 269: 13490–13496, 1994
Van Winkle DM, Thornton JD, Downey DM, Downey JM: The natural history of preconditioning: cardioprotection depends on duration of transient ischemia and time to subsequent ischemia. Coron Artery Dis 2: 613–619, 1991
Baxter GF, Marber MS, Patel VC, Yellon DM: Adenosine receptor involvement in a delayed phase of myocardial protection 24 hours after ischemic preconditioning. Circulation 90: 2993–3000, 1994
Dana A, Baxter GF, Walker JM, Yellon DM: Prolonging the delayed phase of myocardial protection: Anti-infarct effects of adenosine A1 receptor activation are maintained despite repetitive dosing. Heart 77(Suppl 1): P23, 1997 (abstr)
Salvatore CA, Jacobson MA, Taylor HE, Linden J, Johnson RG: Molecular cloning and characterization of the human A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 10365–10369, 1993
Lee HT, Thompson CI, Hernandez A, Lewy JL, Belloni FL: Cardiac desensitization to adenosine analogues after prolonged R-PIA infusion in vivo. Am J Physiol 265: H1916–H1927, 1993
Milligan G: Agonist regulation of cellular G protein levels and distribution: Mechanisms and functional implications. Trends Pharmacol Sci 14: 413–418, 1993
Parsons WJ, Stiles GL: Heterologous desensitization of the inhibitory A1 adenosine receptor – adenylate cyclase system in rat adipocytes: Regulation of both Ns and Ni. J Biol Chem 262: 841–847, 1987
Minneman KP: α1-Adrenergic receptor subtypes, inositol phosphates, and sources of cell Ca2+. Pharmacol Rev 40: 87–119, 1988
Fedida D, Braun AP, Giles WR: α1-Adrenoceptors in myocardium: Functional aspects and transmembrane signaling mechanisms. Physiol Rev 73: 469–487, 1993
Collins S, Caron MG, Lefkowtiz RJ: Regulation of adrenergic receptor responsiveness through modulation of receptor gene expression. Annu Rev Physiol 53: 497–508, 1991
Moalic J-M, Bourgeois F, Mansier P, Machida CA, Carré F, Chevalier B, Pitarque P, Swynghedauw B: β1 Adrenergic receptor and Gαs mRNAs in rat heart as a function of mechanical load and thyroxine intoxication. Cardiovasc Res 27: 231–237, 1993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashimi, M.W., Thornton, J.D., Downey, J.M. et al. Loss of myocardial protection from ischemic preconditioning following chronic exposure to R(-)-N6-(2-phenylisopropyl)adenosine is related to defect at the adenosine A1 receptor. Mol Cell Biochem 186, 19–25 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006876627227
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006876627227