Abstract
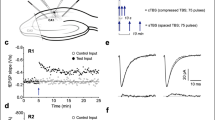
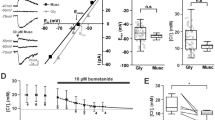
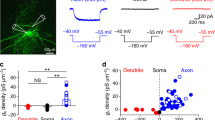
γ-Amlnobutyric acid (GABA) can have a biphasic effect on membrane potential when applied to certain central nervous system neurones1–3. Typically with iontophoresis, this effect is a negative–positive sequence of deflections and both phases are associated with an increase in conductance. However, iontophoretic application of neurotransmitter substances can produce effects even in cases where ordinary synaptic transmitter release is impossible; for example, on dorsal root ganglion cells. Thus, it is important in assessing the physiological relevance of the depolarising GABA response to determine if similar actions are produced synaptically. In addition, although the depolarising aspect of the GABA response has been attributed to activation of dendritic receptors, this identification has remained uncertain. Here, we have used the hippocampal slice preparation to demonstrate that a biphasic inhibitory response results from orthodromic, but not antidromic electrical stimulation in the presence of anaesthetic concentrations of pentobarbital. (For the sake of brevity, we use the term ‘biphasic inhibitory postynaptic potential (i.p.s.p.)’ to describe the response complex, although it seems likely that a combination of two distinct events, rather than two parts of a single event, occurs.) GABA antagonists and tetrodotoxin (TTX) were used to show that the depolarising phase is due to synaptically released GABA acting on dendritic sites in the CA1 region. Both negative and positive phases are associated with a large conductance increase, and both block cell firing, indicating their inhibitory nature. The ionic mechanism of the depolarising phase is not fully understood but seems to involve a chloride conductance increase. Although the functional significance of the depolarising sign of the i.p.s.p. is not clear, the dendritic location would provide very effective control over dendritic excitability.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicoll, R. A., Padjen, A. & Barker, J. L. Neuropharmacology 15, 45–63 (1976).
Langmoen, I. A., Andersen, P., Gjerstad, L., Mosfeldt-Laursen, A. & Ganes, T. Acta physiol. scand. 102, C27 (1978).
Barker, J. L. & Ransom, B. R. J. Physiol., Lond. 280, 331–354 (1978).
Alger, B. E. & Teyler, T. J. Brain Res. 110, 463–480 (1976).
Harvey, J. A., Scholfield, C. N. & Brown, D. A. Brain Res. 76, 235–245 (1974).
Alger, B. E. & Teyler, T. J. Brain Res. Bull. 2, 355–365 (1977).
Andersen, P., Eccles, J. C. & Løyning, Y. J. Neurophysiol. 27, 592–607, 608–619 (1974).
Scholfield, C. N. J. Physiol., Lond. 275, 547–557, 559–566 (1978).
Dudel, J. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 376, 151–157 (1978).
Wong, R. K. S. & Prince, D. A. Science 204, 1228–1231 (1979).
Lorente de Nó, R. J. Psychol. Neurol. 46, 113–177 (1934).
Schwartzkroin, P. A. & Mathers, L. H. Brain Res. 157, 1–10 (1978).
Andersen, P., Gross, G. N., Lømo, T. & Sveen, O. in The Interneuron (ed. Brazier, M. A. B.) 415–467 (UCLA Forum Med. Sci. No. 11, University of California Press, 1969).
Purpura, D. P., Prelevic, S. & Santini, M. Expl Neurol. 22, 408–422 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alger, B., Nicoll, R. GABA-mediated biphasic inhibitory responses in hippocampus. Nature 281, 315–317 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/281315a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/281315a0
This article is cited by
-
Gβγ SNARE Interactions and Their Behavioral Effects
Neurochemical Research (2019)
-
Parvalbumin-expressing interneurons can act solo while somatostatin-expressing interneurons act in chorus in most cases on cortical pyramidal cells
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Impaired Motor Coordination and Learning in Mice Lacking Anoctamin 2 Calcium-Gated Chloride Channels
The Cerebellum (2017)
-
Cation-chloride cotransporters in neuronal development, plasticity and disease
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2014)
-
GABAA receptor-mediated modulation of neuronal activity propagation upon tetanic stimulation in rat hippocampal slices
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.