Abstract
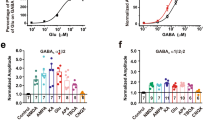
The major excitatory amino acids, glutamate (Glu) and aspartate (Asp), are thought to act at three receptor subtypes1 in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). These are termed quisqualate (QA), N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and kainate (KA) receptors according to the specific agonist properties of these compounds revealed by electrophysiological studies1,2. Although Glu has been shown to stimulate cyclic GMP formation in brain slices3, direct regulation of second messenger systems (cyclic AMP, Ca2+ or inositol phosphates) subsequent to activation of excitatory amino-acid receptors, has not been extensively studied. Here we demonstrate that in striatal neurones, excitatory amino acids, but not inhibitory or non-neuroactive amino acids, induce a three- to fourfold increase in inositol mono-, di- and triphosphate (IP1, IP2, IP3) formation with the relative potency QA > Glu > NMDA, KA. The Glu-evoked formation of inositol phosphates appears to result principally from actions at QA as well as NMDA receptors on striatal neurones. Our results suggest that excitatory amino acids stimulate inositol phosphate formation directly, rather than indirectly by the evoked release and subsequent actions of adenosine4 or acetylcholine5.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watkins, J. C. & Evans, R. H. A. Rev. Pharmac. 21, 165–205 (1981).
Evans, R. H. & Watkins, J. C. Life Sci. 28, 1301–1308 (1981).
Garthwaite, J. & Balazs, R. in Glutamate as a Neurotransmitter (eds Di Chiara, G. & Gessa, G. L.) 317–326 (Raven, New York, 1981).
Bruns, R. F., Pons, F. & Daly, J. W. Brain Res. 189, 550–555 (1980).
Scatton, B. & Lehmann, J. Nature 297, 422–424 (1982).
Weiss, S., Sebben, M., Garcia-Sainz, A. & Bockaert, J. Molec. Pharmac. 27, 595–599 (1985).
Berridge, M. J. & Irvine, R. F. Nature 312, 315–321 (1984).
Berridge, M. J., Dawson, R. M. C., Downes, C. P., Heslop, J. P. & Irvine, R. F. Biochem. J. 212, 473–483 (1983).
Fagg, G. E. & Matus, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 6876–6880 (1984).
Nishizuka, Y. Science 225, 1365–1370 (1984).
Lehmann, J. & Scatton, B. Brain Res. 252, 77–89 (1982).
Shimizu, H., Ichishita, H. & Odagiri, H. J. biol. Chem. 249, 5955–5962 (1974).
Berridge, M. Biochem. J. 220, 345–360 (1984).
Kendall, D. A. & Nahorski, S. R. J. Neurochem. 42, 1388–1394 (1984).
Retz, K. C. & Coyle, J. T. Neuropharmacology 23, 89–94 (1984).
Salpeter, M., Leonard, J. P. & Kasporak, H. Neurosci. Comment. 1, 73–82 (1982).
Leonard, J. P. & Salpeter, M. M. J. Cell Biol. 82, 811–819 (1979).
Bone, E. A., Fretten, P., Palmer, S., Kirk, C. J. & Michell, R. H. Biochem. J. 221, 803–811 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sladeczek, F., Pin, JP., Récasens, M. et al. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurones. Nature 317, 717–719 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/317717a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/317717a0
This article is cited by
-
Inter-individual differences in serotonin and glutamate co-transmission reflect differentiation in context-induced conditioned 50-kHz USVs response after morphine withdrawal
Brain Structure and Function (2018)
-
Mutual activation of glutamatergic mGlu4 and muscarinic M4 receptors reverses schizophrenia-related changes in rodents
Psychopharmacology (2018)
-
Control of neuronal excitability by Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors
Biophysical Reviews (2017)
-
Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors regulates the excitability of rat retinal ganglion cells by suppressing Kir and I h
Brain Structure and Function (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.