Abstract
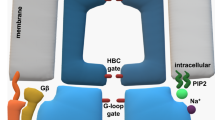
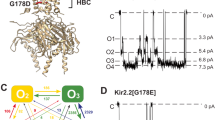
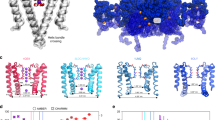
INWARD-RECTIFIER potassium channels conduct K+across the cell membrane more efficiently in the inward than outward direction. This unusual conduction property is directly related to the biological action of these channels1–6. One basis for inward rectification is voltage-dependent blockade by intracellular Mg2+ (refs 1, 7–9): strong inward-rectifier channels are so sensitive to intracellular Mg2+ that no outward K+ current is measurable under physiological conditions; weak inward rectifiers are less sensitive and allow some K+ to flow outwards. Background Kl channels and acetylcholine-regulated K+ channels from the heart are examples of strong inward rectifiers and ATP-sensitive K+ channels are weak rectifiers1,7a–10. Here we show that mutations at one position in the second transmembrane segment can alter the Mg2+affinity and convert a weakly rectifying channel (ROMK1) into a strong rectifier. The amino acid at this position exposes its side chain to the aqueous pore and affects Mg2+ blockade as well as K+ conduction through an electrostatic mechanism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hille, B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes (Sinauer, Sunderland, MA, 1991).
Trautwein, W. & Dudel, J. Pflügers Arch. 266, 324–334 (1958).
Noma, A., Peper, K. & Trautwein, W. Pflügers Arch. 400, 424–431 (1983).
Sakmann, B., Noma, A. & Trautwein, W. Nature 303, 250–253 (1983).
Seojima, M. & Noma, A. Pflügers Arch. 400, 424–431 (1984).
Ashcroft, F. M. & Rorsman, P. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 18, 109–111 (1990).
Horie, M., Isisawa, H. & Noma, A. J. Physiol. 387, 251–272 (1987).
Matsuda, H., Saigusa, A. & Isisawa, H. Nature 325, 156–159 (1987).
Vandenberg, C. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 2560–2564 (1987).
Matsuda, H. J. Physiol. 435, 83–99 (1991).
Ho, K. et al. Nature 362, 31–38 (1993).
Nichols, C. G., Ho, K. & Hebert, S. J. Physiol. 476, 399–409 (1994).
Kubo, Y., Baldwin, T. J., Yan, Y. N. & Jan, L. Y. Nature 362, 127–132 (1993).
Miller, C. Science 252, 1092–1096 (1991).
Choi, K. L., Mossman, C., Aube, J. & Yellen, G. Neuron 10, 533–541 (1993).
Kirsch, G. E., Shieh, C. C., Drewe, J. A., Vener, D. F. & Brown, A. M. Neuron 11, 503–512 (1993).
Slesinger, P. A., Jan, Y. N. & Jan, L. Y. Neuron 11, 739–749 (1993).
Lopez, G. A., Jan, Y. N. & Jan, L. Y. Nature 367, 179–182 (1994).
Kubo, Y., Reuveny, E., Slesinger, P. A., Jan, Y. N. & Jan, L. Y. Nature 364, 802–806 (1993).
Dascal, N. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 10235–10239 (1993).
Stanfield, P. R. et al. J. Physiol. 475, 1–7 (1994).
Kurachi, Y. J. Physiol. 366, 365–385 (1985).
Ishihara, K., Mitsuiye, T., Noma, A. & Takano, T. J. Physiol. 419, 297–320 (1989).
Silver, M. R. & DeCoursey, T. E. J. gen. Physiol. 96, 109–133 (1990).
Taglialatela, M., Wibb, B. A., Caporaso, R. & Brown, A. M. Science 264, 844–847 (1994).
Creighton, T. E. Proteins: Structures and Molecular Properties 2nd edn (Freeman, New York, 1993).
MacKinnon, R., Reinhart, P. H. & White, M. M. Neuron 1, 997–1001 (1988).
Goldman, D. E. J. gen. Physiol. 27, 37–60 (1943).
Grahame, D. Chem. Rev. 41, 441–501 (1947).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Z., MacKinnon, R. Electrostatic tuning of Mg2+ affinity in an inward-rectifier K+channel. Nature 371, 243–246 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/371243a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/371243a0
This article is cited by
-
Hydrocinnamic Acid Inhibits the Currents of WT and SQT3 Syndrome-Related Mutants of Kir2.1 Channel
The Journal of Membrane Biology (2017)
-
A synergistic blocking effect of Mg2+ and spermine on the inward rectifier K+ (Kir2.1) channel pore
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Unique patterns of transcript and miRNA expression in the South American strong voltage electric eel (Electrophorus electricus)
BMC Genomics (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.