Abstract
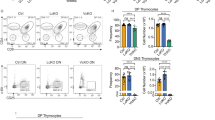
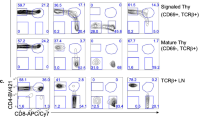
DURING lymphocyte development, cellular proliferation and posi-tive and negative selection events ensure the production of T and B lymphocytes bearing highly diverse, but self-tolerant, repertoires of antigen receptors1,2. These processes are initiated when engage-ment of growth-factor receptors, or the T3,4 and B5 lymphocyte antigen receptors, induces tyrosine phosphorylation of specific SH2- and SH3-domain-containing cytoplasmic proteins, including Vav3,6,7. Here we show that vav-/- embryonic stem cells generate only limited numbers of immature and mature T and B lympho-cytes in the RAG-2 blastocyst complementation assay8. Further-inore, Vav-deficient T lymphocytes showed severely unpaired antigen receptor signalling. Finally, we demonstrate that Vav-dependent signalling pathways regulate maturation, but not CD4/ CD8 lineage commitment, during T-cell-receptor-mediated positive selection of immature CD4 + CD8 + precursors into mature CD4 + CD8- or CD4-CD8+ T cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
von Boehmer, H. Cell 76, 219–228 (1994).
Nossal, G. J. V. Cell 76, 229–239 (1994).
Bustelo, X. R., Ledbetter, J. A. & Barbacid, M. Nature 356, 68–71 (1992).
Margolis, B. et al. Nature 356, 71–74 (1992).
Bustelo, X. R. & Barbacid, M. Science 256, 1196–1199 (1992).
Katzav, S., Martin-Zanca, D. & Barbacid, M. EMBO J. 8, 2283–2290 (1989).
Adams, J. M., Houston, H., Allen, J., Lints, T. & Harvey, R. Oncogene 7, 611–618 (1992).
Chen, J., Lansford, R., Stewart, V., Young, F. & Alt, F. W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 4528–4532 (1993).
Zmuidzinas, A. et al. EMBO J. 14, 1–11 (1995).
Dosil, M., Wang, S. & Lemischka, I. R. Molec. cell. Biol. 13, 6572–6585 (1993).
Godfrey, D., Zlotnik, A. & Suda, T. J. Immun. 149, 2281–2285 (1992).
Rolink, A., Streb, M., Nishikawa, S.-I. & Melchers, F. Eur. J. Immun. 21, 2609–2612 (1991).
Robey, E. & Fowlkes, B. J. A. Rev. Immun. 12, 675–705 (1994).
Guidos, C. J., Danska, J. S., Fathman, C. G. & Weissman, I. L. J. exp. Med. 172, 835–845 (1990).
Davis, C. B., Killeen, N., Crooks, M. E. C., Raulet, D. & Littman, D. R. Cell 73, 237–247 (1993).
Chan, S. H., Cosgrove, D., Waltzinger, C., Benoist, C., & Mathis, D. Cell 73, 225–236 (1993).
van Meerwijk, J. P. M. & Germain, R. N. Science 261, 911–915 (1993).
Guidos, C. J. & Weissman, I. L. in Molecular Mechanisms of Immunological Self-recognition (eds Alt, F. & Vogel, H. J.) 137–147 (Academic, San Diego, 1993).
Bendelac, A., Matzinger, P., Seder, R. A., Paul, W. E. & Schwartz, R. H. J. exp. Med 175, 731–742 (1992).
Ashton-Rickardt, P. G. & Tonegawa, S. Immun. Today 15, 362–365 (1994).
Weiss, A. & Littman, D. R. Cell 76, 263–274 (1994).
Gulbins, E. et al. Science 260, 822–824 (1993).
Boguski, M. S. & McCormick, F. Nature 366, 643–654 (1993).
Molina, T. J. et al. Nature 357, 161–164 (1992).
Mombaerts, P., Anderson, S. J., Perlmutter, R. M., Mak, T. W. & Tonegawa, S. Immunity 1, 261–267 (1994).
Arpaia, E., Shahar, M., Dadi, H., Cohen, A. & Roifman, C. Cell 76, 947–958 (1994).
Chan, A. et al. Science 264, 1599–1601 (1994).
Elder, M. et al. Science 264, 1596–1599 (1994).
Kishihara, K. et al. Cell 74, 143–156 (1993).
Danska, J. S. et al. Science 266, 450–455 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, KD., Zmuidzinas, A., Gardner, S. et al. Defective T-cell receptor signalling and positive selection of Vav-deficient CD4+CDS+thymocytes. Nature 374, 474–476 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/374474a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/374474a0
This article is cited by
-
Opposing roles of hematopoietic-specific small GTPase Rac2 and the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Vav1 in osteoclast differentiation
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) infection alters bone marrow transcriptome in chickens
BMC Genomics (2015)
-
Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors: regulators of Rho GTPase activity in development and disease
Oncogene (2014)
-
The distinct role of guanine nucleotide exchange factor Vav1 in Bcl-2 transcription and apoptosis inhibition in Jurkat leukemia T cells
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2011)
-
Vav1
AfCS-Nature Molecule Pages (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.