Abstract
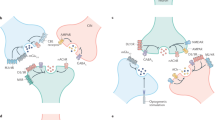
The modulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels at presynaptic nerve terminals is an important factor in the control of neurotransmitter release and synaptic efficacy. Some terminals contain multiple Ca2+-channel subtypes (N and P/Q)1–3, which are differentially regulated by G-protein activation4–8 and by protein kinase C (PKC)-dependent phosphorylation9–11. Regulation of channel activity by crosstalk between second messenger pathways has been reported12,13, although the molecular mechanisms underlying crosstalk have not been described. Here we show that crosstalk occurs at the level of the presynaptic Ca2+-channel complex. The α1 subunit domain I–II linker, which connects the first and second transmembrane domains, contributes to the PKC-dependent upregulation of channel activity, while G-protein-dependent inhibition occurs through binding of Gβλ to two sites in the I–II linker. Crosstalk results from the PKC-dependent phosphorylation of one of the Gβλ binding sites which antagonizes Gβλ-induced inhibition. The results provide a mechanism for the highly regulated and dynamic control of neurotransmitter release that depends on the integration of multiple presynaptic signals.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takahashi, T. & Momiyama, A. Nature 366, 156–158 (1993).
Wheeler, D. B., Randall, A. & Tsien, R. W. Science 264, 107–111 (1994).
Dunlap, K., Luebke, J. I. & Turner, T. J. Trends Neurosci. 18, 89–98 (1995).
Dolphin, A. C., Forda, S. R. & Scott, R. H. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 373, 47–61 (1986).
Bean, B. P. Nature 340, 153–156 (1989).
Mintz, I. M. & Bean, B. P. Neuron 10, 889–898 (1993).
Rhim, H. & Miller, R. J. J. Neurosci. 14, 7608–7615 (1994).
Bourinet, E. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 1486–1491 (1996).
Yang, J. & Tsien, R. W. Neuron 10, 127–136 (1993).
Zhu, Y. & Ikeda, S. R. J. Neurophysiol. 72, 1549–1560 (1994).
Stea, A., Soong, T. W. & Snutch, T. P. Neuron 15, 929–940 (1995).
Swartz, K. J. Neuron 11, 305–320 (1993).
Swartz, K. J. et al. Nature 361, 165–168 (1993).
Campbell, V. et al. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 485, 365–372 (1995).
Pragnell, M. et al. Nature 368, 67–70 (1994).
Ikeda, S. Nature 380, 255–258 (1996).
Herlitze, S. et al. Nature 380, 258–262 (1996).
Hille, B. Trends Neurosci. 17, 531–536 (1994).
Chen, H. et al. Science 268, 1166–1169 (1995).
De Waard, M. et al. Nature (this issue). (Eds to update on page.)
Dolphin, A. C. Exp. Physiol. 80, 1–36 (1995).
Wickman, K. et al. Nature 365, 255–257 (1994).
Krapivinsky, G. B. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 29059–29062 (1995).
Huang, C.-L. et al. Neuron 15, 1133–1143 (1995).
Dascal, N. et al. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 6758–6762 (1995).
Westenbroek, R. E. et al. Neuron 9, 1099–1115 (1992).
Westenbroek, R. E. et al. J. Neurosci. 15, 6403–6418 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamponi, G., Bourinet, E., Nelson, D. et al. Crosstalk between G proteins and protein kinase C mediated by the calcium channel α1 subunit. Nature 385, 442–446 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/385442a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/385442a0
This article is cited by
-
The T-type calcium channelosome
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2024)
-
Regulation of N-type calcium channels by nociceptin receptors and its possible role in neurological disorders
Molecular Brain (2022)
-
Opioid Receptor Regulation of Neuronal Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Differential regulation of Cav2.2 channel exon 37 variants by alternatively spliced μ-opioid receptors
Molecular Brain (2019)
-
5-HT2A receptor-dependent phosphorylation of mGlu2 receptor at Serine 843 promotes mGlu2 receptor-operated Gi/o signaling
Molecular Psychiatry (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.