Abstract
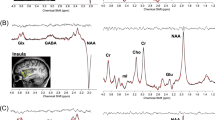
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptors are thought to play an important role in modulating the central nervous system in response to stress. Animal data have shown alterations in the GABAA receptor complex by uncontrollable stressors. SPECT imaging with benzodiazepine ligands showed lower distribution volumes of the benzodiazepine-GABAA receptor in the prefrontal cortex of patients with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in one, but not in another study. The objective of the present study was to assess differences in the benzodiazepine-GABAA receptor complex in veterans with and without PTSD using [11C]flumazenil and positron emission tomography (PET). Nine drug naive male Dutch veterans with deployment related PTSD and seven male Dutch veterans without PTSD were recruited, and matched for age, region and year of deployment. Each subject received a [11C]flumazenil PET scan and a structural magnetic resonance imaging scan. Dynamic 3D PET scans with a total duration of 60 min were acquired, and binding in template based and manually defined regions of interest (ROI) was quantified using validated plasma input and reference tissue models. In addition, parametric binding potential images were compared on a voxel-by-voxel basis using statistical parametric mapping (SPM2). ROI analyses using both template based and manual ROIs showed significantly reduced [11C]flumazenil binding in PTSD subjects throughout the cortex, hippocampus and thalamus. SPM analysis confirmed these results. The observed global reduction of [11C]flumazenil binding in patients with PTSD provides circumstantial evidence for the role of the benzodiazepine-GABAA receptor in the pathophysiology of PTSD and is consistent with previous animal research and clinical psychopharmacological studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vaiva G, Thomas P, Ducrocq F, Fontaine M, Boss V, Devos P et al. Low posttrauma GABA plasma levels as a predictive factor in the development of acute posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 55: 250–254.
Harvey BH, Oosthuizen F, Brand L, Wegener G, Stein DJ . Stress-restress evokes sustained iNOS activity and altered GABA levels and NMDA receptors in rat hippocampus. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2004; 175: 494–502.
Lippa AS, Klepner CA, Yunger L, Sano MC, Smith WV, Beer B . Relationship between benzodiazepine receptors and experimental anxiety in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1978; 9: 853–856.
Medina JH, Novas ML, Wolfman CN, Levi de Stein M, De Robertis E . Benzodiazepine receptors in rat cerebral cortex and hippocampus undergo rapid and reversible changes after acute stress. Neuroscience 1983; 9: 331–335.
Drugan RC, Basile AS, Crawley JN, Paul SM, Skolnick P . Inescapable shock reduces. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1986; 24: 1673–1677.
Adamec R, Strasser K, Blundell J, Burton P, McKay DW . Protein synthesis and the mechanisms of lasting change in anxiety induced by severe stress. Behav Brain Res 2006; 167: 270–286.
Davidson JR . Use of benzodiazepines in social anxiety disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 2004; 65 (Suppl 5): 29–33.
Gelpin E, Bonne O, Peri T, Brandes D, Shalev AY . Treatment of recent trauma survivors with benzodiazepines: a prospective study. J Clin Psychiatry 1996; 57: 390–394.
Viola J, Ditzler T, Batzer W, Harazin J, Adams D, Lettich L et al. Pharmacological management of post-traumatic stress disorder: clinical summary of a five-year retrospective study, 1990--1995. Mil Med 1997; 162: 616–619.
Connor KM, Davidson JR, Weisler RH, Zhang W, Abraham K . Tiagabine for posttraumatic stress disorder: effects of open-label and double-blind discontinuation treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2006; 184: 21–25.
Taylor FB . Tiagabine for posttraumatic stress disorder: a case series of 7 women. J Clin Psychiatry 2003; 64: 1421–1425.
Bremner JD, Innis RB, Southwick SM, Staib L, Zoghbi S, Charney DS . Decreased benzodiazepine receptor binding in prefrontal cortex in combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry 2000; 157: 1120–1126.
Fujita M, Southwick SM, Denucci CC, Zoghbi SS, Dillon MS, Baldwin RM et al. Central type benzodiazepine receptors in Gulf War veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 56: 95–100.
Fedi M, Berkovic SF, Marini C, Mulligan R, Tochon-Danguy H, Reutens DC . A GABAA receptor mutation causing generalized epilepsy reduces benzodiazepine receptor binding. Neuroimage 2006; 32: 995–1000.
Katsifis A, Kassiou M . Development of radioligands for in vivo imaging of GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptors. Mini Rev Med Chem 2004; 4: 909–921.
Juhasz C, Chugani HT . Imaging the epileptic brain with positron emission tomography. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2003; 13: 705–716, viii.
Erritzoe D, Talbot P, Frankle WG, Abi-Dargham A . Positron emission tomography and single photon emission CT molecular imaging in schizophrenia. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2003; 13: 817–832.
Talbot PS, Laruelle M . The role of in vivo molecular imaging with PET and SPECT in the elucidation of psychiatric drug action and new drug development. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2002; 12: 503–511.
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW . Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders. SCID-I/P, 1997.
Blake D, Weathers F, Nagy L, Kaloupek D, Klauminzer G, Charney D . A Clinican Rating Scale for Assessing Current and Lifetime PTSD: The CAPS-1. Behav Ther 1990; 13: 187–188.
Brix G, Zaers J, Adam LE, Bellemann ME, Ostertag H, Trojan H et al. Performance evaluation of a whole-body PET scanner using the NEMA protocol. National Electrical Manufacturers Association. J Nucl Med 1997; 38: 1614–1623.
Adam LE, Jears J, Ostertag H, Trojan H, Bellemann ME, Brix G . Performance of the whole-body PET scanner ECAT EXACT HR+ following the IEC standard. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1997; 44: 1172–1179.
Boellaard R, van Lingen A, van Balen SC, Hoving BG, Lammertsma AA . Characteristics of a new fully programmable blood sampling device for monitoring blood radioactivity during PET. Eur J Nucl Med 2001; 28: 81–89.
Maes F, Collignon A, Vandermeulen D, Marchal G, Suetens P . Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1997; 16: 187–198.
West J, Fitzpatrick JM, Wang MY, Dawant BM, Maurer Jr CR, Kessler RM et al. Comparison and evaluation of retrospective intermodality brain image registration techniques. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1997; 21: 554–566.
Svarer C, Madsen K, Hasselbalch SG, Pinborg LH, Haugbol S, Frokjaer VG et al. MR-based automatic delineation of volumes of interest in human brain PET images using probability maps. Neuroimage 2005; 24: 969–979.
Watson C, Andermann F, Gloor P, Jones-Gotman M, Peters T, Evans A et al. Anatomic basis of amygdaloid and hippocampal volume measurement by magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology 1992; 42: 1743–1750.
Duvernoy HM, Bourgouin P . The Human Brain: Surface, Three-Dimensional Sectional Anatomy and MRI, and Blood Supply. Springer Verlag: Vienna, 1999.
Greuter HN, van Ophemert PL, Luurtsema G, Franssen EJ, Boellaard R, Lammertsma AA . Validation of a multiwell gamma-counter for measuring high-pressure liquid chromatography metabolite profiles. J Nucl Med Technol 2004; 32: 28–32.
Koeppe RA, Holthoff VA, Frey KA, Kilbourn MR, Kuhl DE . Compartmental analysis of flumazenil kinetics for the estimation of ligand transport rate and receptor distribution using positron emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1991; 11: 735–744.
Lammertsma AA, Hume SP . Simplified reference tissue model for PET receptor studies. Neuroimage 1996; 4: 153–158.
Klumpers UMH, Veltman DJ, Comans EFI, Kropholler MA, Boellaard R, Hoogendijk WGJ et al. Comparison of various models for analysing [11C] flumazenil studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2005; 25: S660.
Ichise M, Fujita M, Seibyl JP, Verhoeff NP, Baldwin RM, Zoghbi SS et al. Graphical analysis and simplified quantification of striatal and extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptor binding with epidepride SPECT. J Nucl Med 1999; 40: 1902–1912.
Friston KJ, Frith CD, Liddle PF, Frackowiak RS . Comparing functional (PET) images: the assessment of significant change. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1991; 11: 690–699.
Genovese CR, Lazar NA, Nichols T . Thresholding of statistical maps in functional neuroimaging using the false discovery rate. Neuroimage 2002; 15: 870–878.
Caldji C, Francis D, Sharma S, Plotsky PM, Meaney MJ . The effects of early rearing environment on the development of GABAA and central benzodiazepine receptor levels and novelty-induced fearfulness in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000; 22: 219–229.
Weizman R, Weizman A, Kook KA, Vocci F, Deutsch SI, Paul SM . Repeated swim stress alters brain benzodiazepine receptors measured in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1989; 249: 701–707.
Drugan RC, Morrow AL, Weizman R, Weizman A, Deutsch SI, Crawley JN et al. Stress-induced behavioral depression in the rat is associated with a decrease in GABA receptor-mediated chloride ion flux and brain benzodiazepine receptor occupancy. Brain Res 1989; 487: 45–51.
Malizia AL, Cunningham VJ, Bell CJ, Liddle PF, Jones T, Nutt DJ . Decreased brain GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptor binding in panic disorder: preliminary results from a quantitative PET study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1998; 55: 715–720.
Bremner JD, Vermetten E, Vythilingam M, Afzal N, Schmahl C, Elzinga B et al. Neural correlates of the classic color and emotional stroop in women with abuse-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 55: 612–620.
Bremner JD, Staib LH, Kaloupek D, Southwick SM, Soufer R, Charney DS . Neural correlates of exposure to traumatic pictures and sound in Vietnam combat veterans with and without posttraumatic stress disorder: a positron emission tomography study. Biol Psychiatry 1999; 45: 806–816.
Bremner JD, Innis RB, Ng CK, Staib LH, Salomon RM, Bronen RA et al. Positron emission tomography measurement of cerebral metabolic correlates of yohimbine administration in combat-related posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1997; 54: 246–254.
Britton JC, Phan KL, Taylor SF, Fig LM, Liberzon I . Corticolimbic blood flow in posttraumatic stress disorder during script-driven imagery. Biol Psychiatry 2005; 57: 832–840.
Shin LM, Wright CI, Cannistraro PA, Wedig MM, McMullin K, Martis B et al. functional magnetic resonance imaging study of amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex responses to overtly presented fearful faces in posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2005; 62: 273–281.
Weber DL, Clark CR, McFarlane AC, Moores KA, Morris P, Egan GF . Abnormal frontal and parietal activity during working memory updating in post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Res 2005; 140: 27–44.
Lewis DA, Volk DW, Hashimoto T . Selective alterations in prefrontal cortical GABA neurotransmission in schizophrenia: a novel target for the treatment of working memory dysfunction. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2004; 174: 143–150.
Nazar M, Siemiatkowski M, Czlonkowska A, Sienkiewicz-Jarosz H, Plaznik A . The role of the hippocampus and 5-HT/GABA interaction in the central effects of benzodiazepine receptor ligands. J Neural Transm 1999; 106: 369–381.
Geuze E, Vermetten E, Bremner JD . MR-based in vivo hippocampal volumetrics: 2. Findings in neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 160–184.
Nemeroff CB, Bremner JD, Foa EB, Mayberg HS, North CS, Stein MB . Posttraumatic stress disorder: a state-of-the-science review. J Psychiatr Res 2006; 40: 1–21.
Bremner JD, Vythilingam M, Vermetten E, Southwick SM, McGlashan T, Staib LH et al. Neural correlates of declarative memory for emotionally valenced words in women with posttraumatic stress disorder related to early childhood sexual abuse. Biol Psychiatry 2003; 53: 879–889.
Sakamoto H, Fukuda R, Okuaki T, Rogers M, Kasai K, Machida T et al. Parahippocampal activation evoked by masked traumatic images in posttraumatic stress disorder: a functional MRI study. Neuroimage 2005; 26: 813–821.
Seabrook GR, Easter A, Dawson GR, Bowery BJ . Modulation of long-term potentiation in CA1 region of mouse hippocampal brain slices by GABAA receptor benzodiazepine site ligands. Neuropharmacology 1997; 36: 823–830.
Bremner JD, Innis RB, White T, Fujita M, Silbersweig D, Goddard AW et al. SPECT. Biol Psychiatry 2000; 47: 96–106.
Debiec J, LeDoux JE . Oradrenergic signaling in the amygdala contributes to the reconsolidation of fear memory: treatment implications for PTSD. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2006; 1071: 521–524.
Shin LM, Rauch SL, Pitman RK . Mygdala, medial prefrontal cortex, and hippocampal function in PTSD. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2006; 1071: 67–79.
Liberzon I, Martis B . Euroimaging studies of emotional responses in PTSD. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2006; 1071: 87–109.
Geuze E, Westenberg HGM, Jochims A, de Kloet CS, Vermetten E, Schmahl C . Altered pain processing in veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2007; 64: 76–85.
David D, De Faria L, Lapeyra O, Mellman TA . Adjunctive risperidone treatment in combat veterans with chronic PTSD. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2004; 24: 556–559.
Robert S, Hamner MB, Kose S, Ulmer HG, Deitsch SE, Lorberbaum JP . Quetiapine improves sleep disturbances in combat veterans with PTSD: sleep data from a prospective, open-label study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2005; 25: 387–388.
Ichise M, Meyer JH, Yonekura Y . An introduction to PET and SPECT neuroreceptor quantification models. J Nucl Med 2001; 42: 755–763.
Watabe H, Matsumoto K, Senda M, Iida H . Performance of list mode data acquisition with ECAT EXACT HR and ECAT EXACT HR+ positron emission scanners. Ann Nucl Med 2006; 20: 189–194.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Dutch Ministry of Defence. We thank the staff of the Radiology Department of Utrecht University Medical Centre for acquisition of MRI scans, the staff of the Department of Nuclear Medicine & PET Research of the VU University Medical Center for acquisition of PET scans, Arthur Rademaker, MSc, for clinical assessments, Reina Kloet, MSc, for help with data analysis, and the production chemists and the BV Cyclotron VU for providing 11CO2 and [11C]flumazenil for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geuze, E., van Berckel, B., Lammertsma, A. et al. Reduced GABAA benzodiazepine receptor binding in veterans with post-traumatic stress disorder. Mol Psychiatry 13, 74–83 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4002054
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4002054
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification of potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets related to post-traumatic stress disorder due to traumatic brain injury
European Journal of Medical Research (2024)
-
Modeling gene × environment interactions in PTSD using human neurons reveals diagnosis-specific glucocorticoid-induced gene expression
Nature Neuroscience (2022)
-
Transcriptomic organization of the human brain in post-traumatic stress disorder
Nature Neuroscience (2021)
-
Combat-Related Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: From “Irritable Heart Syndrome” to “Psychoorganic Disorder.” Biological Aspects
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2021)
-
The role of the GABAA receptor Alpha 1 subunit in the ventral hippocampus in stress resilience
Scientific Reports (2019)