Abstract
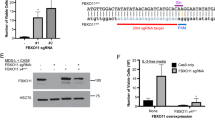
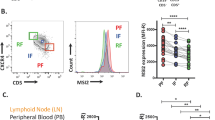
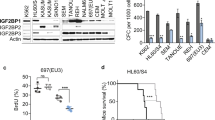
Northern blotting confirmed previous results indicating that the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase Pyst2-L was highly expressed in leukocytes obtained from acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients. High levels of Pyst2-L mRNA were expressed in bone marrow (BM) and peripheral leukocytes from nine AML and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patients. BM from healthy individuals expressed very low levels of Pyst2-L. Whereas high levels of Pyst2-L mRNA and protein were detected in several leukemia cell lines, Pyst2-L mRNA was detected neither in 33/34 samples of normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) nor in leukocyte fractions enriched with CD34+ cells. Certain solid tumor and lymphoblastoid cell lines expressed high levels of Pyst2-L mRNA. In view of the association of Pyst2-L to MAPK signaling cascades, we tested if cell activation, a process involving MAPK signaling, influences Pyst2-L expression. Indeed, activation of T cells and endothelial cells increased Pyst2-L in these cells. Furthermore, TPA, a known MAPK activator, induces the expression of both Pyst2-L mRNA as well as the Pyst2-L protein in leukemia cells. This induction was partially inhibited by PD098059, an Mek1/2-specific inhibitor. Based on the results of this and previous studies, we hypothesize that the high levels of Pyst2-L detected in the active state of AML and ALL diseases and in other types of cancer reflect an altered MAPK signaling pathway in such malignant processes. This alteration may be the result of a failed attempt to counter the constitutive activation of MAPK in transformed cells or alternatively, may represent the activated state of such cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AML:
-
acute myeloid leukemia
- ML:
-
myeloid leukemia
- ALL:
-
acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- MAPK:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinase
- DUSP:
-
dual-specificity phosphatases
- BM:
-
bone marrow
- PBMC:
-
peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- HUVEC:
-
human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells
- TPA:
-
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
- FN:
-
fibronectin
References
Adams PD and Parker PJ . (1991). FEBS Lett., 290, 77–82.
Andersen JN, Elson A, Lammers R, Romer J, Clausen JT, Moller KB and Moller NP . (2001). Biochem. J., 354, 581–590.
Babcock GJ, Hochberg D and Thorley-Lawson AD . (2000). Immunity, 13, 497–506.
Ballif BA and Blenis J . (2001). Cell Growth Differ., 12, 397–408.
Beghini A, Ripamonti CB, Peterlongo P, Roversi G, Cairoli R, Morra E and Larizza L . (2000). Hum. Mol. Genet., 9, 2297–2304.
Berndt N . (1999). Front. Biosci., 4, D22–D42.
Biethahn S, Alves F, Wilde S, Hiddemann W and Spiekermann K . (1999). Exp. Hematol., 27, 885–894.
Chorvath B, Duraj J and Stockbauer P . (1983). Neoplasma, 30, 273–280.
Chu Y, Solski PA, Khosravi-Far R, Der CJ and Kelly K . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 6497–6501.
Dahia PL . (2000). Endocr. Relat. Cancer, 7, 115–129.
Dickinson RJ, Williams DJ, Slack DN, Williamson J, Seternes OM and Keyse SM . (2002). Biochem. J., 364, 145–155.
Dowd S, Sneddon AA and Keyse SM . (1998). J. Cell Sci., 111, 3389–3399.
Dudley DT, Pang L, Decker SJ, Bridges AJ and Saltiel AR . (1995). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 7686–7689.
Eckstein JW . (2000). Invest. New Drugs, 18, 149–156.
Eshel R, Besser M, Zanin A, Sagi-Assif O and Witz IP . (2001). Cell Immunol., 213, 141–148.
Eshel R, Zanin A, Sagi-Assif O, Meshel T, Smorodinsky NI, Dwir O, Alon R, Brakenhoff R, van Dongen G and Witz IP . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 12833–12840.
Frearson JA and Alexander DR . (1996). Immunol. Today, 17, 385–391.
Galaktionov K, Lee AK, Eckstein J, Draetta G, Meckler J, Loda M and Beach D . (1995). Science, 269, 1575–1577.
Geller RB and Bray RA . (1997). Leukemia Res., 21, 387–389.
Gopalakrishna R, Gundimeda U, Fontana JA and Clarke R . (1999). Cancer Lett., 136, 143–151.
Groom LA, Sneddon AA, Alessi DR, Dowd S and Keyse SM . (1996). EMBO J., 15, 3621–3632.
Hantisteanu S, Levy-Nissenbaum O, Sagi-Assif O, Raanani P, Avigdor A, Ben-Bassat I and Witz I . (2002). Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Tumor Microenvironment: Progression, Therapy and Prevention. Baden, Austria, Manduzzi Editore. Witz IP (ed). S.p.A., Bologna, Italy, 95–100.
Hass R, Bartels H, Topley N, Hadam M, Kohler L, Goppelt-Strube M and Resch K . (1989). Eur. J. Cell Biol., 48, 282–293.
He H, Wang X, Gorospe M, Holbrook NJ and Trush MA . (1999). Cell Growth Differ., 10, 307–315.
Hernandez S, Hernandez L, Bea S, Cazorla M, Fernandez PL, Nadal A, Muntane J, Mallofre C, Montserrat E, Cardesa A and Campo E . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 1762–1767.
Horn S, Meyer J, Heukeshoven J, Fehse B, Schulze C, Li S, Frey J, Poll S, Stocking C and Jucker M . (2001). Leukemia, 15, 112–120.
Hwang PH, Yi HK, Kim DS, Nam SY, Kim JS and Lee DY . (2001). Cancer Lett., 172, 83–91.
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG and Minick CR . (1973). J. Clin. Invest., 52, 2745–2756.
Johnson TR, Biggs JR, Winbourn SE and Kraft AS . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 31755–31762.
Keyse SM and Ginsburg M . (1993). Trends Biochem. Sci., 18, 377–378.
Klint P, Kanda S, Kloog Y and Claesson-Welsh L . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 3354–3364.
Koeffler HP, Bar-Eli M and Territo MC . (1981). Cancer Res., 41, 919–926.
Lee Jr JT and McCubrey JA . (2002). Leukemia, 16, 486–507.
Levy-Nissenbaum O, Sagi-Assif O, Hantisteanu S, Raanani P, Avigdor A, Ben-Bassat I and Witz I . (2002). Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Tumor Microenvironment: Progression, Therapy and Prevention. Baden, Austria. Manduzzi Editore. Witz IP (ed). S.p.A., Bologna, Italy, pp. 11–17.
Levy-Nissenbaum O, Sagi-Assif O, Raanani P, Avigdor A, Ben-Bassat I and Witz I . (2003a). Methods Enzymol. (in press).
Levy-Nissenbaum O, Sagi-Assif O, Raanani P, Avigdor A, Ben-Bassat I and Witz I . (2003b). Cancer Lett. (in press).
Levy-Nissenbaum O, Sagi-Assif O and Witz I . (2003c). Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer. (submitted for publication).
Marshall CJ . (1994a). Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 4, 82–89.
Marshall CJ . (1994b). Nature, 367, 686.
Mercurius KO and Morla AO . (2001). BMC Cell. Biol., 2, 18.
Molla A and Block MR . (2000). Cell Growth Differ., 11, 83–90.
Moore S, McDiarmid LA and Hughes TP . (2000). Leukemia Lymphoma, 38, 211–220.
Muda M, Boschert U, Smith A, Antonsson B, Gillieron C, Chabert C, Camps M, Martinou I, Ashworth A and Arkinstall S . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 5141–5151.
Nilsson I and Hoffmann I . (2000). Prog. Cell. Cycle Res., 4, 107–114.
Ofek P, Ben-Meir D, Kariv-Inbal Z, Oren M and Lavi S . (2003). J. Biol. Chem., 278 (16), 14299–14305.
Parsons R . (1998). Curr. Opin. Oncol., 10, 88–91.
Pestell KE, Ducruet AP, Wipf P and Lazo JS . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 6607–6612.
Poetsch M, Dittberner T and Woenckhaus C . (2001). Cancer Genet. Cytogenet., 125, 21–26.
Rivedal E and Opsahl H . (2001). Carcinogenesis, 22, 1543–1550.
Romagnani S . (1995). J. Clin. Immunol., 15, 121–129.
Sambrook J, Fritsch E and Maniatis T . (1989). Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Sano K, Hayakawa A, Piao JH, Kosaka Y and Nakamura H . (2000). Blood, 95, 1066–1068.
Saxena M and Mustelin T . (2000). Semin. Immunol., 12, 387–396.
Sebolt-Leopold JS . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 6594–6599.
Seger R and Krebs EG . (1995). FASEB J., 9, 726–735.
Shi G, Weh HJ, Martensen S, Seeger D and Hossfeld DK . (1996). Cytogenet. Cell Genet., 74, 295–299.
Shin DY, Ishibashi T, Choi TS, Chung E, Chung IY, Aaronson SA and Bottaro DP . (1997). Oncogene, 14, 2633–2639.
Steinitz M, Klein G, Koskimies S and Makel O . (1977). Nature, 269, 420–422.
Tanuma N, Nakamura K, Shima H and Kikuchi K . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 28216–28221.
Theodosiou A and Ashworth A . (2002). Genome Biol., 3 (Reviews3009), 350–351.
Wagers AJ, Waters CM, Stoolman LM and Kansas GS . (1998). J. Exp. Med., 188, 2225–2231.
Weinstein R, Riordan MA, Wenc K, Kreczko S, Zhou M and Dainiak N . (1989). Blood, 73, 111–116.
Wilkinson MG and Millar JB . (2000). FASEB J., 14, 2147–2157.
Wu W, Fan YH, Kemp BL, Walsh G and Mao L . (1998). Cancer Res., 58, 4082–4085.
Yamamoto M, Suzuki Y, Kihira H, Miwa H, Kita K, Nagao M, Tamura S, Shiku H and Nishikawa M . (1999). Leukemia, 13, 595–600.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Gabrielle Rich Leukemia Research Foundation Lucerne, Switzerland and by the James J Leibman and Rita S Leibman Endowment Fund for Cancer Research. IP Witz is the incumbent of the David Furman Chair in Immunobiology of Cancer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Levy-Nissenbaum, O., Sagi-Assif, O., Kapon, D. et al. Dual-specificity phosphatase Pyst2-L is constitutively highly expressed in myeloid leukemia and other malignant cells. Oncogene 22, 7649–7660 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206971
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206971
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatases: promising targets in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2019)
-
Inside the human cancer tyrosine phosphatome
Nature Reviews Cancer (2011)
-
MKP-X
AfCS-Nature Molecule Pages (2010)
-
Dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases (MKPs) and cancer
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2008)
-
Targeting dual-specificity phosphatases: manipulating MAP kinase signalling and immune responses
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2007)