Summary
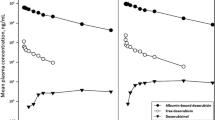
DMDR, a daunorubicin derivative with a higher therapeutic index and lower cardiotoxicity than either the parent drug or doxorubicin, is active when given PO in experimental animals. We studied its pharmacokinetics in ten patients receiving DMDR IV or PO or IV and PO sequentially at 10–12.5 mg/m2. DMDR and its metabolites were quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography and fluorometry. In nine patients who received DMDR IV the unchanged drug disappeared from the plasma biphasically with a mean terminal half-life of 27.0±5.5 h, an apparent volume of distribution of 63.9±12.61 kg-1, and a total clearance of 1.9±0.41 kg-1 h-1. In 24 h only 5.1%±1.1% of the dose was excreted in the urine. In comparison, in 19 studies the plasma half-life of DMDR given PO was 34.8±6.7 h, 2.3%±1.3% was excreted in the urine in 24 h, and the maximum plasma drug concentration was reached in about 1 h. The bioavailability of DMDR given PO was about 39% according to comparison of the areas under the plasma DMDR concentration versus time curves for the two routes, but 45% according to comparison of the 24-h cumulative urinary excretion rates. In one patient with severe liver dysfunction following oral administration, the plasma DMDR half-life was 56.8 h, more than twice the average length. By either route, the drug was quickly metabolized to one major metabolite, DMDR-ol. The plasma half-life of DMDR-ol was 72.5±24.7 h, or 35.7±7.4 when DMDR was administered IV or PO. In the plasma, DMDR-ol always exceeded DMDR in concentration. Moreover, the 24 h cumulative urinary excretion of DMDR-ol as a percentage of the dose of DMDR administered was 7.8 following IV and 7.4 following PO administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aracamone F, Bernardi L, Giardino P, DiMarco A, Casazza AM, Pratesi G (1976) Synthesis and antitumor activity of 4-demethoxy-daunorubicin, 4-demethoxy-7,9-diepidaunorubicin and their β-anomes. Cancer Treat Rep 60:829–834
Benjamin RS, Riggs CE, Bachur VR (1973) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of adriamycin in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 14:592–600
Berman E, Witters R, Leyland Jones B, Casper ES, Gralla RJ, Howard J, Williams L, Baratz R, Young CW (1983) Phase I and clinical pharmacology studies of intravenous and oral administration of 4-demethoxydaunorubicin in patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Res 43:6096–6101
Casazza AM (1979) Experimental evaluation of anthracycline analogues. Cancer Treat Rep 63:835–844
Casazza AM, DiMarco A, Bonadonna G, Bonfante V, Bertazzali C, Bellini O, Pratesi G, Sala L, Ballerini L (1979a) Effects of modifications in position 4 of the chromphore is position 4 of the amino sugar in the antitumor activity and toxicity of daunorubicin and doxorubicin. In: Crooke ST, Reich SD (eds) Anthracyclines: current status and new developments. Academic, New York, pp 403–430
Casazza AM, Bertazzoli C, Pratesi G, Bellini O, DiMarco A (1979b) Antileukemic activity and cardiac toxicity of 4-demethoxydaunorubicin. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 20:16
Casazza AM, Pratesi G, Giuliani F, DiMarco A (1980) Antileukemic activity of 4-demethoxydaunorubicin in mice. Tumori 66:549–564
Daghestani AN, Arlin ZA, Leyland-James B, Gee TS, Kempin SJ, Mertelsmann R, Budman D, Schulman P, Baratz R, Williams L, Clarkson BD, Young CW (1985) Phase I and II clinical and pharmacological studies of 4-demethoxydaunorubicin (idoroubicin) in adult patients with acute leukemia. Cancer Res 45:1408–1412
DiMarco, Zuenio A, Casazza AM (1978) Comparison of biochemical and biological methods in the evaluation of new anthracycline drugs. Antibiot Chemother 23:12–20
Pacciarini MA, Martini A, Moro E, Tamassia V (1982) Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of 4-demethoxydaunorubicin in cancer patients. Proceedings of the 13th International Cancer Congress, Abstr 2319
Rahmann A, Goodman A, Foo W, Harvey J, Smith FP, Schein PS (1984) Clinical pharmacology of daunorubicin in phase I patients with solid tumors: development of an analytical methodology for daunorubicin and its metabolites. Semin Oncol 11:36–44
Riggs CE Jr (1984) Clinical pharmacology of daunorubicin in patients with acute leukemia. Semin Oncol 11:2–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by ADRIA Laboratory
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, K., Savaraj, N., Kavanagh, J. et al. Clinical pharmacology of 4-demethoxydaunorubicin (DMDR). Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 17, 143–148 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306743
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306743