Summary
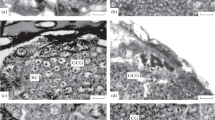
Using immunocytochemistry we find substance P-like material in nerve cells of hydra. These nerve cells are situated in the ectoderm of the basal disk and tentacles. Radioimmunoassay of hydra extracts gives dilution curves parallel to that of synthetic substance P, from which it can be calculated that one animal contains at least 0.6 fmol substance P-like immunoreactivity. After chromatography on Biogel P-100, the substance P-like immunoreactivity elutes as a peak in the void volume and a peak at the position of synthetic substance P.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastasi A, Erspamer V (1963) The isolation and amino-acid sequence of eledoisin, the active undecapeptide of the posterior salivary glands of Eledone. Arch Biochem Biophys 101:56–65
Anastasi A, Erspamer V, Cei JM (1964) Isolation and aminoacid sequence of physalaemin, the main active polypeptide of the skin of Physalaemus fuscumaculatus. Arch Biochem Biophys 108:341–348
Anastasi A, Montecucchi P, Erspamer V, Visser V (1977) Amino-acid composition and sequence of kassinin, a tachykinin dodecapeptide from the skin of the african frog Kassina senegalensis. Experientia 33:857–858
Balfe A, Cannon D, Skrabanek P, Powell D (1980) Substance P heterogeneity in human plasma. Regulat Peptides 1: Suppl. 7
Baumgarten HG, Holstein AF, Owman C (1970) Auerbach's plexus of mammals and man: Electronmicroscopic identification of three different types of neuronal processes in the myenteric ganglia of the large intestine from rhesus monkey, guinea pig and man. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 106:376–397
Brownstein MJ, Mroz EA, Kizer JS, Palkowits M, Leeman SE (1976) Regional distribution of substance P in the brain of the rat. Brain Res 116:299–305
Chang MM, Leeman SE (1970) Isolation of a sialogic peptide from bovine hypothalamic tissue and its characterization as substance P. J Biol Chem 245:4784–4790
Chang MM, Leeman SE, Niall HD (1971) Amino-acid sequence of substance P. Nature [New Biol] 232:86–87
Cannon D, Skrabanek P, Powell D, Harrington MG (1977) Immunological characterization of two substance P antisera with substance P fragments and analogues. Biochem Soc Trans 5:1736–1738
Coons AH, Leduc EH, Connoly JM (1955) Studies on antibody production. I. A method for the histochemical demonstration of specific antibody and its application to the study of the hyperimmune rabbit. J Exp Med 102:49–59
Cuello AE, Emson PC, Del Fiacco M, Gale J, Iversen LL, Jessell TM, Kanasawa I, Paxinos G, Quik M (1978) Distribution and release of substance P in the central nervous system In: Hughes J (ed) Centrally acting peptides. Macmillan, London, pp 135–156
Cuello AC, McQueen DS (1980) Substance P: a carotid body peptide. Neurosci Lett 17:215–219
Creagh T, Skrabanek P, Cannon D, Balfe A, Powell D (1980) Phylogeny of substance P Gen Comp Endocrinol 40:503–506
Davis LE, Burnett AL, Haynes JF (1968) Histological and ultrastructural study on the muscular and nervous systems in Hydra. J Exp Zool 167:295–332
Davis LE, Bursztan S (1973) Histological and ultrastructural studies of the basal disk of Hydra. II. Nerve cells and other epithelial cells. Z Zellforsch 139:29–45
Erspamer V, Falconieri-Erspamer G, Linari G (1977) Occurrence of tachykinins (physalaeminor substance P-like peptides) in the amphibian skin and their actions on smooth muscle preparations. In: von Euler US, Pernow B (eds) Substance P. Raven Press, New York, pp 67–74
El-Salhy M, Abou-El-Ela R, Falkmer S, Grimelius L, Wilander E (1980) Immunohistochemical evidence of gastro-entero-pancreatic neurohormonal peptides of vertebrate type in the nervous system of a dipteran insect, the hoverfly Eristalis aeneus. Regulat Peptides 1:187–204
von Euler US, Gaddum JH (1931) An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J Physiol 72:74–87
Fritsch HAR, van Noorden S, Pearse AGE (1979) Localization of somatostatin-, substance P-and calcitonin-like immunoreactivity in the neural ganglion of Ciona intestinalis L. (Ascidiaceae). Cell Tissue Res 202:263–274
Gaudino G, Fasolo A (1980) Substance P-related peptides in the hypothalamus of amphibia. Cell Tissue Res 211:241–250
Grimmelikhuijzen CJP, Schaller HC (1979) Hydra as a model organism for the study of morphogenesis. Trends Biochem Sci 4:265–267
Grimmelikhuijzen CJP, Sundler F, Rehfeld JF (1980) Gastrin/CCK-like immunoreactivity in the nervous system of coelenterates. Histochemistry 69:61–68
Grimmelikhuijzen CJP, Carraway R, Rökaeus Å, Sundler F (1981) Neurotensin-like peptides in the nervous system of hydra. Histochemistry (in press)
Hadži J (1909) Über das Nervensystem von Hydra. Arb Zool Inst Univ Wien 17:225–268
Hökfelt T, Kellerth JO, Nilsson G, Pernow B (1975) Substance P: Localization in the central nervous system and in some primary sensory neurons. Science 190:889–890
Hökfelt T, Elfvin LG, Schultzberg M, Goldstein M, Nilsson G (1977) On the occurrence of substance P containing fibers in sympathic ganglia. Immunohistochemical evidence. Brain Res 132:29–41
Hökfelt T, Johansson O, Ljungdahl A, Lundberg JM, Schultzberg M (1980) Peptidergic neurons. Nature 284:515–521
Karten HJ, Brecha N (1980) Localisation of substance P immunoreactivity in amacrine cells of the retina. Nature 283:87–88
Konishi S, Otsuka M (1974) Excitatory action of hypothalamic substance P on spinal motorneurons of newborn rats. Nature 252:734–735
Langer M, van Noorden S, Polak JM, Pearse AGE (1979) Peptide hormone-like immunoreactivity in the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine pancreas of eleven teleost species. Cell Tissue Res 199:493–508
Lazarus LH, Linnoila RI, Hernandez O, DiAugustine RP (1980) A neuropeptide in mammalian tissue with physalaemin-like immunoreactivity. Nature 287:555–558
Lentz T, Barrnett J (1965) Fine structure of the nervous system of Hydra. Am Zool 5:341–356
Morita K, North RA, Katayama Y (1980) Evidence that substance P is a neurotransmitter in the myenteric plexus. Nature 287:151–152
Nilsson G, Larsson LI, Håkanson R, Brodin E, Pernow B, Sundler F (1975) Localization of substance P-like immunoreactivity in mouse gut. Histochemistry 43:97–99
van Noorden S, Falkmer S (1980) Gut-islet endocrinology — some evolutionary aspects. Invest Cell Pathol 3:21–36
van Noorden S, Fritsch HAR, Grillo TAI, Polak JM, Pearse AGE (1981) Immunocytochemical staining for vertebrate peptides in the nervous system of a gastropod mollusc. Gen Comp Endocrinol (in press)
O'Connell RO, Skrabanek P, Cannon D, Powell P (1976) High-sensitivity radioimmunoassay for substance P. Ir J Med Sci 145:392–398
Reinecke M, Weihe E, Forssmann WG (1980) Substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the heart. Neurosci Lett 20:265–269
Schultzberg M, Hökfelt T, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Rehfeld JF, Brown M, Elde R, Goldstein M, Said S (1980) Distribution of peptide and catecholamine-containing neurons in the gastrointestinal tract of rat and guinea pig: Immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance P, vaso-active intestinal polypeptide, enkephalins, somatostatin, gastrin/cholecystokinin, neurotensin and dopamine β-hydroxylase. Neuroscience 5:689–744
Scrutton CT (1979) Early fossil Cnidarians. In: House MR (ed) The origin of major invertebrate groups. Academic Press, New York, pp 161–209
Sundler F, Alumets J, Brodin E, Dahlberg K, Nilsson G (1977) Perivascular substance P immunoreactive nerves in tracheobronchial tissue. In: von Euler US, Pernow B (eds) Substance P. Raven Press, New York, pp 271–273
Taban CH, Cathieni M (1979) Localisation of substance P-like immunoreactivity in Hydra. Experientia 35:811–812
Westfall JA, Yamataka S, Enos PD (1971) Ultrastructural evidence of polarized synapses in the nervous net of Hydra. J Cell Biol 51:318–323
Westfall JA (1973a) Ultrastructural evidence for neuromuscular systems in coelenterates. Am Zool 13:237–246
Westfall JA (1973b) Ultrastructural evidence for a granule-containing sensory-motor-interneuron in Hydra littoralis. J Ultrastruct Res 42:268–282
Westfall JA, Kinnamon JC (1978) A second sensory-motor-interneuron with neurosecretory granules in Hydra. J Neurocytol 7:365–379
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.P., Balfe, A., Emson, P.C. et al. Substance P-like immunoreactivity in the nervous system of hydra. Histochemistry 71, 325–333 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00495879
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00495879