Summary
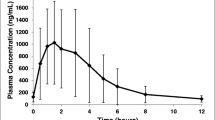
Five healthy male volunteers received 500 mg Aldactone® orally together with 100 μCi 3H-20-21-spironolactone; one elderly patient received 1 mCi 3H-spironolactone without additional ‘cold’ drug. For 6 days the disposition kinetics of the drug were studied in plasma, urine and feces. The tritium concentrations in plasma reached a peak between 25–40 min after administration amounting to 2–3% of the dose/1. Up to the 12th h, they fell rapidly and showed a monoexponential decline (t 1/2 : 2.57±0.27 days) between the 36th and 96th h. Later, a striking increase in the speed of elimination of radioactivity from plasma (t 1/2 : 1.66±0.21 days) was observed. The biological half-life of labeled material in plasma was longer than that of fluorigenic compounds. 47–57% of the dose were excreted in urine and the remaining amount culd be detected in feces (total recovery 90%). The half-life of the urinary excretion rate was distinctly shorter (t 1/2 : 0.9±0.11 days) than that of total radioactivity in plasma. This, together with an observed increase of the polar fraction in urine from 35 up to 85%, which was accompanied by a decrease in plasma from 55 to 35%, suggests either tubular reabsorption or enterohepatic recirculation of lipophilic compounds. TLC-separation of the lipophilic fraction in urine revealed two previously unknown compounds of which the main congener was identified as 3-(3-oxo-7α-methylsulfonyl-6β, 17β-dihydroxy-4-androsten-17α-yl) propionic acid γ-lactone, as well as canrenone and the metabolites which have already been described (Karim and Brown, 1972; Karim et al., 1975). This metabolite represents the main lipophilic degradation product in urine within the first hours, whereas the 6β-OH-7α-methylsulfinylspirolactone leveled off and seemed to be an endexcretion product. For further characterisation, the polar fraction was subjected to acidic hydrolysis. The known metabolic pathways of spironolactone degradation are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abshagen, U.: Effects of pretreatment with spironolactone on pharmacokinetics of 4‴-methyldigoxin in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 278, 91–100 (1973)
Abshagen, U., Rennekamp, H., Kuhlmann, J.: Effects of pretreatment with spironolactone on pharmacokinetics of 4‴-methyldigoxin in man. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 292, 87–92 (1976b)
Abshagen, U., Rennekamp, H., Koch, K., Senn, M., Steingross, W.: Isolation and identification of a further sulfur-containing metabolite of spironolactone from human urine. Steroids (in press, 1976a)
Abshagen, U., Rennekamp, H., Luszpinski, G.: Disposition kinetics of spironolactone in hepatic failure after single dose and after long-term treatment. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol. (in press, 1977)
Baethmann, A., Land, W., Koczorek, K., Stass, P., Brendel, W.: The effect of mineralotropic steroids and antilymphocyte serum (ALS) on the survival of skin grafts in rats. Europ. surg. Res. 1, 212 (1969)
Bjondahl, K., Isomaa, B., Nieminen, L.: Effect of treatment with phenobarbital and spironolactone on 144Ce levels in blood, liver, urine and feces at various time periods. Biochem. Pharmacol. 23, 1509–1517 (1974)
Freerksen, E.: Eine neue Therapie der Sarkoidose und Lungen-fibrose. Internist. Prax. 13, 589–596 (1973)
Garg, B., Solymoss, B., Tuchweber, B.: Effect of spironolactone on the distribution and excretion of 203HgCl2 in the rat. Arzneimittel-Forsch. (Drug Res.) 21, 815–816 (1971)
Gochman, N., Gantt, C.: A fluorimetric method for the determination of a major spironolactone (aldactone®) metabolite in human plasma. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 135, 312–316 (1962)
Haddow, J., Fish, C., Marshall, P., Lester, R.: Biliary excretion of mercury enhanced by spironolactone. Gastroenterology 63, 1053–1058 (1972)
Herken, H., in: Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol. XXIV, pp. 436–493. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1969
ICRP Publication 2: ‘Zulässige Dosis bei Inkorporation von Radionukliden.’ Empfehlungen der Internationalen Kommission für Strahlenschutz (1959). Hrsg. Der Bundesminister für Wissenschaftliche Forschung. Bad Godesberg-München: Gersbach & Sohn 1966
Karim, A., Brown, E.: Isolation and identification of novel sulfurcontaining metabolites of spironolactone (aldactone®). Steroids 20, 41–62 (1972)
Karim, A., Hribar, J., Aksamit, W., Doherty, M., Chinn, L.: Spironolactone metabolism in man studied by gas chromatography —mass spectrometry. Drug Metab. Dis. 3, 467–478 (1975)
Karim, A., Ranney, R., Maibach, H.: Pharmacokinetic and metabolic fate of potassium canrenoate (SC-14266) in man. J. pharm. Sci. 60, 708–715 (1971)
Karim, A., Zagarella, J., Hribar, J., Dooley, M.: Spironolactone. I. Disposition and metabolism. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 19, 158–169 (1976)
Koczorek, K.: Dermatologisch-venerologisches Kolloquium über immunosuppressive Therapie von Autoimmunerkrankungen. Med. Klin. 66, 1583–1584 (1971)
Kovács, K., Somogyi, A.: Prevention by spironolactone of 7,12-dimethylbenz-(α)-anthracene-induced adrenal necrosis (34103). Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 131, 1350–1352 (1969)
Marshek, W., Karim, A.: Preparation of spironolactone by microbial oxygenation. Appl. Microbiol. 25, 647–649 (1973)
Sadée, W., Abshagen, U., Finn, C., Rietbrock, N.: Conversion of spironolactone to canrenone and disposition kinetics of spironolactone and canrenoate-potassium in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 283, 303–318 (1974a)
Sadée, W., Dagcioglu, M., Riegelman, S.: Fluorimetric microassay for spironolactone and its metabolites in biological fluids. J. pharm. Sci. 61, 1126–1129 (1972a)
Sadée, W., Dagcioglu, M., Schröder, R.: Pharmacokinetics of spironolactone, canrenone and canrenoate-K in humans. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 185, 686–695 (1973)
Sadée, W., Riegelman, S., Jones, S.: Plasma levels of spironolactone in the dog. J. pharm. Sci. 61, 1129–1132 (1972b)
Sadée, W., Schröder, R., v. Leitner, E., Dagcioglu, M.: Multiple dose kinetics of spironolactone and canrenoate-potassium in cardiac and hepatic failure. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol. 7, 195–200 (1974b)
Schröder, R., Ramdohr, B., Hüttemann, U., Schüren, K.: Direkt positiv-ionotrope Herzwirkung von Spironolakton und Canrenoat-Kalium. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 97, 1535–1538 (1972)
Selye, H., Jelinek, J., Krajny, M.: Prevention of digitoxin poisoning by various steroids. Pharmacol. Sci. 58, 1055–1059 (1969)
Solymoss, B., Classen, H., Varga, S.: Increased hepatic microsomal activity induced by spironolactone and other steroids. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 132, 940–942 (1969)
Solymoss, B., Somogyi, A., Kovács, K.: Effect of spironolactone and proadifen on 7,12-dimethylbenz-(α)-anthracene-induced haematologic changes. Haematologia 5, 87–96 (1971a)
Solymoss, B., Tóth, S., Varga, S., Krajny, M.: The influence of spironolactone on its own biotransformation. Steroids 16, 263–275 (1970a)
Solymoss, B., Tóth, S., Varga, S., Selye, H.: Protection by spironolactone and oxandrolone against chronic digitoxin or indomethacin intoxication. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 18, 586–592 (1971b)
Solymoss, B., Varga, S., Krajny, M., Werringloer, J.: Influence of spironolactone and other steroids on the enzymatic decay and anticoagulant activity of bishydroxycoumarin. Thrombes Diathes. haemorrh. (Stuttg.) 23, 562–568 (1970b)
Stripp, B., Hamrick, M., Zampaglione, N., Gillette, J.: The effect of spironolactone on drug metabolism by hepatic microsomes. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 176, 766–771 (1971)
Taylor, S., Rawlins, M., Smith, S.: Spironolactone—a weak enzyme inducer in man. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 24, 578–579 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The paper includes parts of the thesis of G. Luszpinski
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abshagen, U., Rennekamp, H. & Luszpinski, G. Pharmacokinetics of spironolactone in man. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 296, 37–45 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498838
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00498838