Summary
-
1.
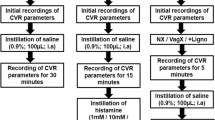
Antidromic vasodilation and neurogenic plasma extravasation were induced by antidromic stimulation of the saphenous nerve in guanethidine-treated rats. Vasodilation was measured by the change of outflow from the femoral vein and plasma extravasation was determined by Evans blue exudation.
-
2.
Antidromic vasodilation was reduced by 85% in adult rats which were pretreated with capsaicin on the second day of life.
-
3.
Antidromic vasodilation was inhibited by 46% after pretreatment with cimetidine plus mepyramine and by 64% after pretreatment with compound 48/80, but was not affected by pretreatment with cimetidine, atropine, methysergide, or indomethacin. Similarly, neurogenic plasma extravasation was reduced by 50% after pretreatment with cimetidine plus mepyramine, and by 88% after pretreatment with compound 48/80, but was not altered after pretreatment with indomethacin.
-
4.
Infusion of substance P into the femoral artery dose-dependently produced vasodilation (threshold: 0.1 pmol min−1) and plasma extravasation (threshold: 0.5 pmol·min−1). Vasodilation induced by substance P was inhibited by 47% after pretreatment with cimetidine plus mepyramine and by 58% after pretreatment with compound 48/80. Plasma extravasation induced by substance P was reduced by 61% after pretreatment with cimetidine plus mepyramine and by 81% after pretreatment with compound 48/80. Pretreatment with indomethacin had no influence on substance P-induced vasodilation and plasma extravasation.
-
5.
It is concluded that vasodilation and plasma extravasation following antidromic stimulation of sensory nerves are initiated by peripheral release of substance P from chemosensitive pain fibres. The actions of substance P include, besides direct effects, release of histamine from mast cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvier, P. T., Chahl, L. A., Ladd, R. J.: Modification by capsaicin and compound 48/80 of dye leakage induced by irritants in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 59, 61–68 (1977)
Ballard, D. R., Abboud, F. M., Mayer, H. E.: Release of a humoral vasodilator substance during neurogenic vasodilatation. Am. J. Physiol. 219, 1451–1457 (1970)
Bayliss, W. M.: On the origin from the spinal cord of the vasodilator fibres of the hind limb, and on the nature of these fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 26, 173–209 (1901)
Bill, A., Stjernschantz, J., Mandahl, A., Brodin, E., Nilsson, G.: Substance P: release on trigeminal nerve stimulation, effects in the eye. Acta Physiol. Scand. (in press, 1979)
Bruce, A. N.: Über die Beziehung der sensiblen Nervenendigungen zum Entzündungsvorgang. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Exp. Path. Pharmakol. 63, 424–433 (1910)
Celander, O., Folkow, B.: The nature and distribution of afferent fibres provided with the axon reflex arrangement. Acta Physiol. Scand. 29, 359–370 (1953)
Chahl, L. A.: Interactions of substance P with putative mediators of inflammation and ATP. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 44, 45–49 (1977)
Cuello, A. C., Del Fiacco, M., Paxinos, G.: The central and peripheral ends of the substance P-containing sensory neurons in the rat trigeminal system. Brain Res. 152, 499–509 (1978)
Cuello, A. C., Polak, J. M., Pearse, A. G. E.: Substance P: a naturally occuring transmitter in human spinal cord. Lancet II, 1054–1056 (1976)
Dale, H. H.: Pharmacology and nerve endings. Proc. R. Soc. London (Biol.) 28, 319–332 (1935)
Gaddum, J. H.: Tryptamine receptors. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 119, 363–368 (1953)
Galeno, T. M., Knuepfer, M. M., Brody, M. J.: Vasodilator response to histamine: dependence upon the site of administration. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 56, 257–260 (1979)
Gamse, R., Holzer, P., Lembeck, F.: Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurones and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin. Br. J. Pharmacol. (in press, 1979)
Garcia Leme, J., Hamamura, L.: Formation of a factor increasing vascular permeability during electrical stimulation of the saphenous nerve in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 51, 383–389 (1974)
Hägermark, Ö., Hökfelt, T., Pernow, B.: Flare and itch induced by substance P in human skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 71, 233–235 (1978)
Hallberg, D., Pernow, B.: Effect of substance P on various vascular beds in the dog. Acta Physiol. Scand. 93, 277–285 (1975)
Henry, J. L.: Effects of substance P on functionally identified units in cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 114, 439–452 (1976)
Hinsey, J. C., Gasser, H. S.: The component of the dorsal root mediating vasodilatation and the Sherrington contracture. Am. J. Physiol. 92, 679–689 (1930)
Hökfelt, T., Kellerth, J. O., Nilsson, G., Pernow, B.: Experimental immunohistochemical studies on the localization and distribution of substance P in cat primary sensory neurones. Brain Res. 100, 235–252 (1975)
Holton, F. A., Holton, P.: The capillary dilator substance in dry powders of spinal roots; a possible role of adenosine triphosphate in chemical transmission from nerve endings. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 126, 124–140 (1954)
Holton, P., Perry, W. L. M.: On the transmitter responsible for antidromic vasodilatation in the rabbit's ear. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 114, 240–251 (1951)
Jancsó, G., Kiraly, E., Jancsó-Gábor, A.: Pharmacologically induced selective degeneration of chemosensitive primary sensory neurones. Nature 270, 741–743 (1977)
Jancsó, N., Jancsó-Gábor, A., Szolcsányi, J.: Direct evidence for neurogenic inflammation and its prevention by denervation and by pretreatment with capsaicin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 31, 138–151 (1967)
Johnson, A. R., Erdös, E. G.: Release of histamine from mast cells by vasoactive peptides. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 142, 1253–1256 (1973)
Joó, F., Szolcsányi, J., Jancsó-Gábor, A.: Mitochondrial alterations in the spinal ganglion cells of the rat accompanying the long-lasting sensory disturbance induced by capsaicin. Life Sci. 8, 621–626 (1969)
Kiernan, J. A.: A pharmacological and histological investigation of the involvement of mast cells in cutaneous axon reflex vasodilatation. Quart. J. Exp. Physiol. 60, 123–130 (1975)
Langley, J. N.: Antidromic action. J. Physiol. (Lond.), 57, 428–446 (1923)
Lembeck, F.: Zur Frage der zentralen Übertragung afferenter Impulse. III. Mitteilung. Das Vorkommen und die Bedeutung der. Substanz P in den dorsalen Wurzeln des Rückenmarks. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Exp. Path. Pharmakol. 219, 197–213 (1953)
Lembeck, F., Fischer, G.: Crossed tachyphylaxis of peptides. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmakol. Exp. Path. 258, 452–456 (1967)
Lembeck, F., Gamse, R.: Lack of algesic effect of substance P on paravascular pain receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 299, 295–303 (1977)
Lembeck, F., Gamse, R., Juan, H.: Substance P and sensory nerve endings. In: Substance P (U.S. von Euler, B. Pernow, eds.), pp. 169–181. New York: Raven Press 1977
Lewis, T., Marvin, H. M.: Observations relating to vasodilatation arising from antidromic impulses, to herpes zoster and trophic effects. Heart 14, 27–46 (1927)
Olgart, L., Gazelius, B., Brodin, E., Nilsson, G.: Release of substance P-like immunoreactivity from the dental pulp. Acta Physiol. Scand. 101, 510–512 (1977)
Otsuka, M., Konishi, S.: Substance P and excitatory transmitter of primary sensory neurons. Cold Spring. Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 40, 135–143 (1976)
Randić, M., Miletić, V.: Effect of substance P in cat dorsal horn neurones activated by noxious stimuli. Brain Res 128, 164–169 (1977)
Stricker, S.: Untersuchungen über die Gefäßwurzeln des Ischiadicus. Sitz.-Ber. Kaiserl. Akad. Wiss. (Wien) 3, 173–185 (1876)
Szolcsányi, J.: A pharmacological approach to elucidation of the role of different nerve fibres and receptor endings in mediation of pain. J. Physiol. (Paris) 73, 251–259 (1977)
Uvnäs-Wallensten, K.: Release of substance P-like immunoreactivity into the antral lumen of cats. Acta Physiol. Scand. 104, 464–468 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lembeck, F., Holzer, P. Substance P as neurogenic mediator of antidromic vasodilation and neurogenic plasma extravasation. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 310, 175–183 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500282
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500282