Abstract
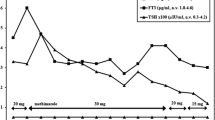
Amiodarone iodine induced thyrotoxicosis occurs frequently in patients residing in areas of mild iodine deficiency and in patients with preexisting goiter. Drug therapy of the hyperthyroidism is often unsuccessful. Twenty-three patients with amiodarone induced thyrotoxicosis were either not treated, treated with 40 mg methimazole daily or with methimazole and 1 gm potassium perchlorate daily for up to 40 days and then with methimazole alone. Thyrotoxicosis was more likely to spontaneously remit in patients without goiter. Therapy with methimazole alone was unsuccessful in inducing euthyroidism in 5 patients with goiter. However, combined therapy with methimazole and potassium perchlorate rapidly alleviated hyperthyroidism in almost all patients with goiter. This drug combination is successful because perchlorate inhibits the active transport of iodine into the thyroid and methimazole blocks the intrathyroidal synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vastesaeger M., Gillot P., Rasson G. Etude clinique d’une nouvelle medication antiangoreuse. Acta Cardiol. 22: 483, 1967.
Singh B.N., Vaughan Williams E.M. The effect of amiodarone, a new anti-anginal drug, on cardiac muscle. Br, J. Pharmacol. 39: 657, 1970.
Rosenbaum M.B., Chiale P.A., Halpern M.S. Clinical efficacy of amiodarone as an antiarrythmic agent. Am. J. Cardiol. 38: 934, 1976.
Touboul P., Huerta R., Porte J., Delahaye J.P. Bases electrophysiologiques de l’action antiarythmique de l’amiodarone chez l’homme. Arch. Mal. Coeur 69: 845, 1976.
Heger J.J., Prystowsky E.N., Jackman W.M., Naccarelli G.V., Warfei K.A., Rinkenberger R.L., Zipes D.P. Amiodarone: clinical efficacy and electrophysiology during long-term therapy for recurrent ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 305: 539, 1981.
Nademanfee K., Singh B., Hendrickson J., Intarachot V., Lopez B., Feld G., Cannon D.S., Weis J.L Amiodarone in refractory, life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias. Ann. Intern. Med. 98: 577, 1983.
Singh B.N. Amiodarone: Historical development and pharmacologic profile. Am. Heart J. 106: 788, 1983.
Pritchard D.A., Singh B.N., Hurley P.J. Effects of amiodarone on thyroid function in patients with ischaemic heart disease. Br. Heart J. 37: 856, 1975.
Burger A., Dinichert D., Nicod P., Jenny M., Lemarchand-Beraud T., Vallotton M.B. Effect of amiodarone on serum triiodothyronine, reverse triiodothyronine, thyroxine and thyrotropin: a drug influencing peripheral metabolism of thyroid hormones. J. Clin. Invest. 58: 255, 1976.
Jonckheer M.H., Blockx P., Broeckaert I., Cornette C., Beckers C. “Low T3 syndrome” in patients chronically treated with an iodine-containing drug, amiodarone. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 9: 27, 1978.
Melmed S., Nademanee K., Reed A.W., Hendrickson J.A., Singh B.N., Hershman J.M. Hyperthyroxinemia with bradycardia and normal thyrotropin secretion after chronic amiodarone administration. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 53: 997, 1981.
Lambert M.J., Burger A.G., Galeazzi R.L., Engler D. Are selective increases in serum thyroxine (T4) due to iodinated inhibitors of T4 monodeiodination indicative of hyperthyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 55: 1058, 1982.
Singh B.N., Nademanee K. Amiodarone and thyroid function: clinical implication during antiarrhythmic therapy. Am. Heart J. 106: 857, 1983.
Chevigne-Brancart M., Vandalem J.L. Thyroid function during and after amiodarone therapy. Program of the 64th Annual Meeting of the Endocrine Society, San Francisco, 1982, p. 111.
Fradkin J.E., Woolf J. Iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 62: 1, 1983.
Baillet J. Amiodarone et dysthyroïde. In: Colloque sur l’amiodarone, Paris 1977, Paris: Documentation Labaz, 1977, p. 238.
Bugugnani M.J., Bailly M., De Soutter P., Fouye H., Haiat R. Surveillance de la fonction thyroïdienne au cours des traitments prolongés par l’amiodarone. Ann. Cardiol. Angeiol. (Paris) 29: 375, 1980.
Martino E., Safran M., Aghini-Lombardi F., Rajatanavin R., Lenziardi M., Fay M., Pacchiarotti A., Aronin N., Macchia E., Haffajee C., Odoguardi L., Love J., Bigalli A., Baschieri L., Pinchera A., Braverman L. Environmental iodine intake and thyroid dysfunction during chronic amiodarone therapy. Ann. Intern. Med.: 28, 101, 1984.
Savoie J.C., Massin J.P., Thomopoulos P., Leger F. Iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis in apparently normal thyroid gland. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 41: 685, 1975.
Wimpfheimer L., Staubli M., Schadelin J., Studer H. Prednisone in amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis. Br. Med. J. 284: 1835, 1982.
Leger A.F., Fragu P., Rouger P., Laurent M.F., Tubiana M., Savoie J.C. Thyroid iodine content measured by X-Ray fluorescence in amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis: concise communication. J. Nucl. Med. 24: 582, 1983.
Jonckheer M.H., Blockx P., Kaivers R., Wyffels G. Hyperthyroidism as a possible complication of the treatment of ischemic heart disease with amiodarone. Acta Cardiol. 28: 192, 1973.
Leger A.F., Massin J.P., Laurent M.F., Vencens M., Auriol M., Helal O.B., Chomette G., Savoie J.C. Iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis: analysis of eighty-five consecutive cases. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 14: 449, 1984.
Benotti J., Benotti N. Protein-bound iodine, total iodine, and butanol-extractable iodine by partial automation. Clin. Chem. 9: 408, 1963.
Siegel S. Nonparametric Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences. McGraw-Hiil, New York, 1956, p. 96.
Morgans M.E., Trotter W.R. Treatment of thyrotoxicosis with potassium perchlorate. Lancet 1: 749, 1954.
Crooks J., Wayne W.E.J. A comparison of potassium perchlorate, methylthiouracil and carbimazole in the treatment of thyrotoxicosis. Lancet 1: 401, 1960.
Cassano C., Baschieri L. La tiroide fisiopatologia e clinica. F. Vallardi Editore, Milano 1964, p. 292.
Editorial Potassium perchlorate and aplastic anemia. Br. Med. J. 1: 1520, 1961.
Barzilai D., Sheinfeld M. Fatal complications following use of potassium perchlorate in thyrotoxicosis. Report of two cases and a review of the literature. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 2: 453, 1966.
Wenzel K.W., Lente J.R. Similar effects of thionamide drugs and perchlorate on thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins in Graves’ disease: evidence against an immunosuppressive action of thionamide drugs. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 58: 62, 1984.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Grant of CNR Rome Italy and by Grant AM-18919 from NIAMDD, NIH, Bethesda, MD.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martino, E., Aghini-Lombardi, F., Mariotti, S. et al. Treatment of amiodarone associated thyrotoxicosis by simultaneous administration of potassium perchlorate and methimazole. J Endocrinol Invest 9, 201–207 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03348098
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03348098