Abstract
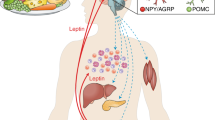
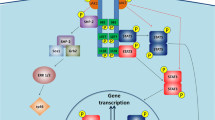
The hormone leptin is secreted by adipose tissue in proportion to fat mass to signal the repletion of body energy stores to the neuroendocrine system. Leptin acts on neurons in the hypothalamus and elsewhere in the brain to decrease appetite and regulate the activity of the thyroid, adrenal, growth, gonadal, and lactational axes. Conversely, absence of leptin signaling initiates the neuroendocrine starvation response. Leptin mediates these effects by activating the long form (LRb) of its receptor. One LRb signal, STAT3, has recently been shown to play a critical role in the regulation of body weight and some elements of neuroendocrine function (thyroid, adrenal, lactation), although the participation of STAT3 in the gonadal and growth axes is negligible. We discuss these findings in the context of the hypothalamic neuroendocrine system as it is presently understood.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AgRP :
-
Agouti-related peptide
- ARC :
-
Arcuate nucleus
- CRH :
-
Corticotropin-releasing hormone
- ERK :
-
Extracellular signal regulated kinase
- GH :
-
Growth hormone
- GHRH :
-
Growth hormone releasing hormone
- GnRH :
-
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
- LR :
-
Leptin receptor
- MCR :
-
Melanocortin receptor
- MSH :
-
Melanocyte stimulating hormone
- NPY :
-
Neuropeptide Y
- POMC :
-
Pro-opiomelanocortin
- PVH :
-
Paraventricular hypothalamus
- SH :
-
Src homology
- SHP :
-
Src homology 2 containing phosphatase
- SOCS :
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling
- STAT :
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription
- TRH :
-
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
- VMH :
-
Ventromedial hypothalamus
References
MacDougald OA, Hwang CS, Fan H, Lane MD (1995) Regulated expression of the obese gene product (leptin) in white adipose tissue and 3T3–L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:9034–9037
Rentsch J, Chiesi M (1996) Regulation of ob gene mRNA levels in cultured adipocytes. FEBS Lett 379:55–59
Slieker LJ, Sloop KW, Surface PL, Kriauciunas A, LaQuier F, Manetta J, Bue-Valleskey J, Stephens TW (1996) Regulation of expression of ob mRNA and protein by glucocorticoids and cAMP. J Biol Chem 271:5301–5304
Maffei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, Pratley RE, Lee GH, Zhang Y, Fei H, Kim S, Lallone R, Ranganathan S, Kern PA, Friedman JM (1995) Leptin levels in human and rodent: measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat Med 1:1155–1161
Frederich RC, Hamann A, Anderson S, Lollmann B, Lowell BB, Flier JS (1995) Leptin levels reflect body lipid content in mice: evidence for diet-induced resistance to leptin action. Nat Med 1:1311–1314
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL, Caro JF (1996) Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 334:292–295
Licinio J, Mantzoros C, Negrao AB, Cizza G, Wong ML, Bongiorno PB, Chrousos GP, Karp B, Allen C, Flier JS, Gold PW (1997) Human leptin levels are pulsatile and inversely related to pituitary-adrenal function. Nat Med 3:575–579
Bornstein SR, Uhlmann K, Haidan A, Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Scherbaum WA (1997) Evidence for a novel peripheral action of leptin as a metabolic signal to the adrenal gland: leptin inhibits cortisol release directly. Diabetes 46:1235–1238
Grunfeld C, Zhao C, Fuller J, Pollack A, Moser A, Friedman J, Feingold KR (1996) Endotoxin and cytokines induce expression of leptin, the ob gene product, in hamsters. J Clin Invest 97:2152–2157
Sarraf P, Frederich RC, Turner EM, Ma G, Jaskowiak NT, Rivet DJ, III, Flier JS, Lowell BB, Fraker DL, Alexander HR (1997) Multiple cytokines and acute inflammation raise mouse leptin levels: potential role in inflammatory anorexia. J Exp Med 185:171–175
Friedman JM, Halaas JL (1998) Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 395:763–770
Elmquist JK, Maratos-Flier E, Saper CB, Flier JS (1998) Unraveling the central nervous system pathways underlying responses to leptin. Nature Neuroscience 1:445–449
Ahima RS, Prabakaran D, Mantzoros CS, Qu D, Lowell BB, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS (1996) Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature 382:250–252
Rahmouni K, Haynes WG, Morgan DA, Mark AL (2003) Intracellular mechanisms involved in leptin regulation of sympathetic outflow. Hypertension 41:763–767
Montague CT, Farooqi IS, Whitehead JP, Soos MS, Rau H, Wareham NJ, Sewter CP, Digby JE, Mohammed SN, Hurst JA, Cheetham CH, Early AR, Barnett AH, Prins JB, O’Rahilly S (1997) Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early onset obesity in humans. Nature 387:903–908
Clement K, Vaisse C, Lahlou N, Cabrol S, Pelloux V, Cassuto D, Gourmelen M, Dina C, Chambaz J, Lacorte JM, Basdevant A, Bougneres P, leBouc Y, Froguel P, Guy-Grand B (1998) A mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity and pituitary dysfunction. Nature 392:398–401
Farooqi IS, Matarese G, Lord GM, Keogh JM, Lawrence E, Agwu C, Sanna V, Jebb SA, Perna F, Fontana S, Lechler RI, Depaoli AM, O’Rahilly S (2002) Beneficial effects of leptin on obesity, T cell hyporesponsiveness, and neuroendocrine/metabolic dysfunction of human congenital leptin deficiency. J Clin Invest 110:1093–1103
Tartaglia LA, Dembski M, Weng X, Deng N, Culpepper J, Devos R, Richards GJ, Campfield LA, Clark FT, Deeds J, Muir C, Sanker S, Moriarty A, Moore KJ, Smutko JS, Mays GG, Woolf EA, Monroe CA, Tepper RI (1995) Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell 83:1263–1271
Lee GH, Proenca R, Montez JM, Carroll KM, Darvishzadeh JG, Lee JI, Friedman JM (1996) Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature 379:632–635
Wang MY, Zhou YT, Newgard CB, Unger RH (1996) A novel leptin receptor isoform in rat. Growth Regul 392:87–90
Mercer JG, Moar KM, Hoggard N, Strosberg AD, Froguel P, Bailleul B (2000) B219/OB-R 5’-UTR and leptin receptor gene-related protein gene expression in mouse brain and placenta: tissue-specific leptin receptor promoter activity. J Neuroendocrinol 12:649–655
Chua SC Jr, Chung WK, Wu-Peng XS, Zhang Y, Liu SM, Tartaglia LA, Leibel RL (1996) Phenotypes of mouse diabetes and rat fatty due to mutations in the OB (leptin) receptor. Science 271:994–996
Ge H, Huang L, Pourbahrami T, Li C (2002) Generation of soluble leptin receptor by ectodomain shedding of membrane-spanning receptors in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 277:45898–45903
Tartaglia LA (1997) The leptin receptor. J Biol Chem 272:6093–6096
Chua SC Jr, Koutras IK, Han L, Liu SM, Kay J, Young SJ, Chung WK, Leibel RL (1997) Fine structure of the murine leptin receptor gene: splice site suppression is required to form two alternatively spliced transcripts. Genomics 45:264–270
Elmquist JK, Elias CF, Saper CB (1999) From lesions to leptin: hypothalamic control of food intake and body weight. Neuron 22:221–232
Elmquist JK, Bjorbaek C, Ahima RS, Flier JS, Saper CB (1998) Distributions of leptin receptor mRNA isoforms in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 395:535–547
Kowalski TJ, Liu SM, Leibel RL, Chua SC Jr (2001) Transgenic complementation of leptin-receptor deficiency. I. Rescue of the obesity/diabetes phenotype of LEPR-null mice expressing a LEPR-B transgene. Diabetes 50:425–435
Bjorbaek C, Elmquist JK, Michl P, Ahima RS, van Bueren A, McCall AL, Flier JS (1998) Expression of leptin receptor isoforms in rat brain microvessels. Endocrinology 139:3485–3491
Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Huang W, Jaspan JB, Maness LM (1996) Leptin enters the brain by a saturable system independent of insulin. Peptides 17:305–311
Inui A (1999) Feeding and body-weight regulation by hypothalamic neuropeptides-mediation of the actions of leptin. Trends Neurosci 22:62–67
Grill HJ, Schwartz MW, Kaplan JM, Foxhall JS, Breininger J, Baskin DG (2002) Evidence that the caudal brainstem is a target for the inhibitory effect of leptin on food intake. Endocrinology 143:239–246
Elmquist JK, Ahima RS, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS, Saper CB (1997) Leptin activates neurons in ventrobasal hypothalamus and brainstem. Endocrinology 138:839–842
Roth J (1998) Diabetes and obesity. Diabetes Metab Rev 13:1–2
Gura T (1999) Obesity research. Leptin not impressive in clinical trial. Science 286:881–882
Taga T, Kishimoto T (1997) gp130 and the interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol 15:797–819
Ihle J N, Kerr IM (1995) Jaks and Stats in signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Genet 11:69–74
Taniguchi T (1995) Cytokine signaling through nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases. Science 268:251–255
Kloek C, Haq AK, Dunn SL, Lavery HJ, Banks AS, Myers MG Jr (2002) Regulation of Jak kinases by intracellular leptin receptor sequences. J Biol Chem 277:41547–41555
Devos R, Guisez Y, Van der Heyden J, White DW, Kalai M, Fountoulakis M, Plaetinck G (1997) Ligand-independent dimerization of the extracellular domain of the leptin receptor and determination of the stoichiometry of leptin binding. J Biol Chem 272:18304–18310
Couturier C, Jockers R (2003) Activation of the leptin receptor by a ligand-induced conformational change of constitutive receptor dimers. J Biol Chem 278:26604–26611
White DW, Kuropatwinski KK, Devos R, Baumann H, Tartaglia LA (1997) Leptin receptor (OB-R) signaling. J Biol Chem 272:4065–4071
Banks AS, Davis SM, Bates SH, Myers MG Jr (2000) Activation of downstream signals by the long form of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem 275:14563–14572
Bjorbaek C, Uotani S, da Silva B, Flier JS (1997) Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem 272:32686–32695
Koch CA, Anderson DJ, Moran MF, Ellis CA, Pawson T (1991) SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science 252:668–674
Songyang Z, Shoelson SE, Chaudhuri M, Gish GD, Pawson T, Haser WG, King F, Roberts T, Ratnofsky S, Lechleider RJ, Neel BG, Birge RB, Fajardo JE, Chou MM, Hanafusa H, Schaffhausen B, Cantley LC (1993) SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell 72:767–778
Haan S, Hemmann U, Hassiepen U, Schaper F, Schneider-Mergener J, Wollmer A, Heinrich PC, Grotzinger J (1999) Characterization and binding specificity of the monomeric STAT3-SH2 domain. J Biol Chem 274:1342–1348
Bjorbaek C, Buchholz RM, Davis SM, Bates SH, Pierroz DD, Gu H, Neel BG, Myers MG Jr, Flier JS (2001) Divergent roles of SHP-2 in ERK activation by leptin receptors. J Biol Chem 276:4747–4755
Bjorbaek C, Elmquist JK, Frantz JD, Shoelson SE, Flier JS (1998) Identification of SOCS-3 as a potential mediator of central leptin resistance. Mol Cell 1:619–625
Bjorbak C, Lavery HJ, Bates SH, Olson RK, Davis SM, Flier JS, Myers MG Jr (2000) SOCS3 mediates feedback inhibition of the leptin receptor via Tyr985. J Biol Chem 275:40649–40657
Niswender KD, Morton GJ, Stearns WH, Rhodes CJ, Myers MG Jr, Schwartz MW (2001) Intracellular signalling. Key enzyme in leptin-induced anorexia. Nature 413:794–795
Niswender KD, Morrison CD, Clegg DJ, Olson R, Baskin DG, Myers MG Jr, Seeley RJ, Schwartz MW (2003) Insulin activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus: a key mediator of insulin-induced anorexia. Diabetes 52:227–231
Schwartz MW, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Seeley RJ, Baskin DG (2000) Central nervous system control of food intake. Nature 404:661–671
Cowley MA, Smart JL, Rubinstein M, Cerdan MG, Diano S, Horvath TL, Cone RD, Low MJ (2001) Leptin activates anorexigenic POMC neurons through a neural network in the arcuate nucleus. Nature 411:480–484
Fan W, Boston BA, Kesterson RA, Hruby VJ, Cone RD (1997) Role of melanocortinergic neurons in feeding and the agouti obesity syndrome. Nature 385:165–168
Seeley RJ, Yagaloff KA, Fisher SL, Burn P, Thiele TE, van Dijk G, Baskin DG, Schwartz MW (1997) Melanocortin receptors in leptin effects. Nature 390:349
Erickson JC, Hollopeter G, Palmiter RD (1996) Attenuation of the obesity syndrome of ob/ob mice by the loss of neuropeptide Y. Science 274:1704–1707
Bates SH, Stearns WH, Schubert M, Tso AWK, Wang Y, Banks AS, Dundon TA, Lavery HJ, Haq AK, Maratos-Flier E, Neel BG, Schwartz MW, Myers MG Jr (2003) STAT3 signaling is required for leptin regulation of energy balance but not reproduction. Nature 421:856–859
Jureus A, Cunningham MJ, McClain ME, Clifton DK, Steiner RA (2000) Galanin-like peptide (GALP) is a target for regulation by leptin in the hypothalamus of the rat. Endocrinology 141:2703–2706
Hisano S, Fukui Y, Chikamori-Aoyama M, Aizawa T, Shibasaki T (1993) Reciprocal synaptic relations between CRF-immunoreactive- and TRH-immunoreactive neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res 620:343–346
Burton KA, Kabigting EB, Clifton DK, Steiner RA (1992) Growth hormone receptor messenger ribonucleic acid distribution in the adult male rat brain and its colocalization in hypothalamic somatostatin neurons. Endocrinology 131:958–963
LaPaglia N, Steiner J, Kirsteins L, Emanuele M, Emanuele N (1998) Leptin alters the response of the growth hormone releasing factor-growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor-I axis to fasting. J Endocrinol 159:79–83
Tannenbaum GS, Gurd W, Lapointe M (1998) Leptin is a potent stimulator of spontaneous pulsatile growth hormone (GH) secretion and the GH response to GH-releasing hormone. Endocrinology 139:3871–3875
Yu WH, Kimura M, Walczewska A, Karanth S, McCann SM (1997) Role of leptin in hypothalamic-pituitary function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:1023–1028
Mounzih K, Qiu J, Ewart-Toland A, Chehab FF (1998) Leptin is not necessary for gestation and parturition but regulates maternal nutrition via a leptin resistance state. Endocrinology 139:5259–5262
Malik NM, Carter ND, Murray JF, Scaramuzzi RJ, Wilson CA, Stock MJ (2001) Leptin requirement for conception, implantation, and gestation in the mouse. Endocrinology 142:5198–5202
Chan YY, Clifton DK, Steiner RA (1996) Role of NPY neurones in GH-dependent feedback signalling to the brain. Horm Res 45 [Suppl 1]:12–14
Pinkney JH, Goodrick SJ, Katz J, Johnson AB, Lightman SL, Coppack SW, Mohamed-Ali V (1998) Leptin and the pituitary-thyroid axis: a comparative study in lean, obese, hypothyroid and hyperthyroid subjects. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 49:583–588
Smith MS, Grove KL (2002) Integration of the regulation of reproductive function and energy balance: lactation as a model. Front Neuroendocrinol 23:225–256
Erickson JC, Hollopeter G, Palmiter RD (1996) Attenuation of the obesity syndrome of ob/ob mice by the loss of neuropeptide Y. Science 274:1704–1707
Huszar D, Lynch CA, Fairchild-Huntress V, Dunmore JH, Fang Q, Berkemeier LR, Gu W, Kesterson RA, Boston BA, Cone RD, Smith FJ, Campfield LA, Burn P, Lee F (1997) Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell 88:131–141
Legradi G, Emerson CH, Ahima RS, Flier JS, Lechan RM (1997) Leptin prevents fasting-induced suppression of prothyrotropin-releasing hormone messenger ribonucleic acid in neurons of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Endocrinology 138:2569–2576
Harris M, Aschkenasi C, Elias CF, Chandrankunnel A, Nillni EA, Bjoorbaek C, Elmquist JK, Flier JS, Hollenberg AN (2001) Transcriptional regulation of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone gene by leptin and melanocortin signaling. J Clin Invest 107:111–120
Mantzoros CS, Rosen HN, Greenspan SL, Flier JS, Moses AC (1997) Short-term hyperthyroidism has no effect on leptin levels in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:497–499
Schwartz MW, Baskin DG, Bukowski TR, Kuijper JL, Foster D, Lasser G, Prunkard DE, Porte D Jr, Woods SC, Seeley RJ, Weigle DS (1996) Specificity of leptin action on elevated blood glucose levels and hypothalamic neuropeptide Y gene expression in ob/ob mice. Diabetes 45:531–535
Butler AA, Cone RD (2002) The melanocortin receptors: lessons from knockout models. Neuropeptides 36:77–84
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by NIH DK56731 and DK 57768 and grants from the American Diabetes Association (to M.G.M.) and an American Diabetes Association/European Association for the Study of Diabetes Transatlantic Fellowship (to S.H.B.). We thank Michael Schwartz, M.D. for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bates, S.H., Myers, M.G. The role of leptin→STAT3 signaling in neuroendocrine function: an integrative perspective. J Mol Med 82, 12–20 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-003-0494-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-003-0494-z