Abstract
Rationale
Glutamate receptors and their related second messengers in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) are known to play critical roles in the initiation of behavioral sensitization to cocaine.
Objectives
To evaluate the hypothesis that repeated intra-VTA microinjections of the ionotropic glutamate agonist, AMPA, or the metabotropic glutamate agonist, t-ACPD, augment the behavioral hyperactivity induced by a subsequent challenge injection of cocaine. In addition, the dependency of the t-ACPD effect on activation of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinases (CaM-Ks) was assessed.
Methods
Male Sprague–Dawley rats received four once-daily microinjections of saline, AMPA, t-ACPD, or t-ACPD plus the CaM-KII inhibitor KN-93 directly into the VTA; locomotor activity was measured for 120 min after each of the daily treatments. One week after the 4 treatment days, all animals received a challenge injection of cocaine (15 mg/kg, IP) and behavioral activity was monitored for 120 min.
Results
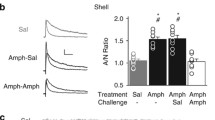
Intra-VTA administration of t-ACPD increased behavioral activity only on the first 2 treatment days, an effect that was blocked by pre-treatment with KN-93. Administration of AMPA into the VTA, in contrast, produced behavioral hyperactivity that sensitized over the 4 treatment days. Following the cocaine challenge injection, there was an augmentation of cocaine-induced behavioral hyperactivity in the groups pretreated with AMPA or t-ACPD but not in the animals administered t-ACPD plus KN-93.
Conclusions
These results indicate that repeated stimulation of AMPA or metabotropic glutamate receptors in the VTA mimics the initiation of behavioral sensitization to cocaine. The present findings also suggest that glutamate agonist-induced activation of CaM-KII in the VTA plays a critical role in the behavioral and neuronal plasticity induced by repeated cocaine injections.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aniksztejn L, Otani S, Ben-Ari Y (1992) Quisqualate metabotropic receptors modulate NMDA currents and facilitate induction of long-term potentiation through protein kinase C. Eur J Neurosci 4:500–505
Carlezon WAJ, Nestler EJ (2002) Elevated levels of GluR1 in the midbrain: a trigger for sensitization to drugs of abuse? Trends Neurosci 25:610–615
Cerne R, Randic M (1992) Modulation of AMPA and NMDA responses in rat spinal dorsal horn neurons by trans-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid. Neurosci Lett 144:180–184
Druhan JP, Deschamps S, Stewart J (1993) d-Amphetamine-like stimulus properties are produce by morphine injections into the ventral tegmental area but not into the nucleus accumbens. Behav Brain Res 59:41–51
Fitzjohn SM, Irving AJ, Palmer MJ, Harvey J, Lodge D, Collingridge GL (1996) Activation of group I mGluRs potentiates NMDA responses in rat hippocampal slices. Neurosci Lett 203:211–213
Fujii S, Sasaki H, Mikoshiba K, Kuroda Y, Yamazaki Y, Mostafa Taufiq A, Kato H (2004) A chemical LTP induced by co-activation of metabotropic and N-methyl-d-aspartate glutamate receptors in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Brain Res 999:20–28
Giorgetti M, Hotsenpiller G, Ward P, Teppen T, Wolf ME (2001) Amphetamine-induced plasticity of AMPA receptors in the ventral tegmental area: effects on extracellular levels of dopamine and glutamate in freely moving rats. J Neurosci 21:6362–6369
Harvey J, Collingridge GL (1993) Signal transduction pathways involved in the acute potentiation of NMDA responses by 1S,3R-ACPD in rat hippocampal slices. Br J Pharmacol 109:1085–1090
Hayashi Y, Shi SH, Esteban JA, Piccini A, Poncer JC, Malinow R (2000) Driving AMPA receptors into synapses by LTP and CaMKII: requirement for GluR1 and PDZ domain interaction. Science 287:2262–2267
Herrero I, Miras-Portugal MT, Sanchez-Prieto J (1992) Positive feedback of glutamate exocytosis by metabotropic presynaptic receptor stimulation. Nature 360:163–166
Kalivas PW, Alesdatter JE (1993) Involvement of NMDA receptor stimulation in the VTA and amygdala in behavioral sensitization to cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:486–495
Kalivas PW, Duffy P (1998) Repeated cocaine administration alters extracellular glutamate in the ventral tegmental area. J Neurochem 70:1497–1502
Karler R, Calder LD, Chaudhry IA, Turkanis SA (1989) Blockade of “reverse tolerance” to cocaine and amphetamine by MK-801. Life Sci 45:599–606
Kim JH, Vezina P (1998) Metabotropic glutamate receptors are necessary for sensitization by amphetamine. Neuroreport 9:403–406
Li Y, Vartanian AJ, White FJ, Xue CJ, Wolf ME (1997) Effects of the AMPA receptor antagonist NBQX on the development and expression of behavioral sensitization to cocaine and amphetamine. Psychopharmacology 134:266–276
Licata SC, Pierce RC (2003) The roles of calcium/calmodulin-dependent and Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinases in the development of psychostimulant-induced behavioral sensitization. J Neurochem 85:14–22
Licata SC, Freeman AY, Pierce-Bancroft AF, Pierce RC (2000) Repeated stimulation of L-type calcium channels in the rat ventral tegmental area mimics the initiation of behavioral sensitization to cocaine. Psychopharmacology 152:110–118
Licata SC, Schmidt HD, Pierce RC (2004) Suppressing calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in the ventral tegmental area enhances the acute behavioural response to cocaine but attenuates the initiation of cocaine-induced behavioural sensitization in rats. Eur J Neurosci 19:405–414
Moroni F, Cozzi A, Lombardi G, Sourtcheva S, Leonardi P, Carfi M, Pellicciari R (1998) Presynaptic mGlu1 type receptors potentiate transmitter output in the rat cortex. Eur J Pharmacol 347:189–195
Paxinos G, Watson C (1997) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd edn. Academic, San Diego
Pin JP, Duvoisin R (1995) The metabotropic glutamate receptors: structure and functions. Neuropharmacology 34:1–26
Schenk S, Partridge B (1997) Effects of acute and repeated administration of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) into the ventral tegmental area: locomotor activating effects of NMDA and cocaine. Brain Res 769:225–232
Shi SH, Hayashi Y, Petralia RS, Zaman SH, Wenthold RJ, Svoboda K, Malinow R (1999) Rapid spine delivery and redistribution of AMPA receptors after synaptic NMDA receptor activation. Science 284:1811–1816
Skeberdis VA, Lan J, Opitz T, Zheng X, Bennett MV, Zukin RS (2001) mGluR1-mediated potentiation of NMDA receptors involves a rise in intracellular calcium and activation of protein kinase C. Neuropharmacology 40:856–865
Smith TL, Navratilova E (1999) Increased calcium/calmodulin protein kinase activity in astrocytes chronically exposed to ethanol: influences on glutamate transport. Neurosci Lett 269:145–148
Suaud-Chagny MF, Chergui K, Chouvet G, Gonon F (1992) Relationship between dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens and the discharge activity of dopaminergic neurons during local in vivo application of amino acids in the ventral tegmental area. Neuroscience 49:63–72
Swanson CJ, Kalivas PW (2000) Regulation of locomotor activity by metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292:406–414
Testa CM, Standaert DG, Young AB, Penney JBJ (1994) Metabotropic glutamate receptor mRNA expression in the basal ganglia of the rat. J Neurosci 14:3005–3018
Tu JC, Xiao B, Naisbitt S, Yuan JP, Petralia RS, Brakeman P, Doan A, Aakalu VK, Lanahan AA, Sheng M, Worley PF (1999) Coupling of mGluR/Homer and PSD-95 complexes by the Shank family of postsynaptic density proteins. Neuron 23:583–592
Vezina P, Kim JH (1999) Metabotropic glutamate receptors and the generation of locomotor activity: interactions with midbrain dopamine. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:577–589
Vezina P, Queen AL (2000) Induction of locomotor sensitization by amphetamine requires the activation of NMDA receptors in the rat ventral tegmental area. Psychopharmacology 151:184–191
White FJ, Hu X-T, Zhang X-F, Wolf ME (1995) Repeated admnistration of cocaine or amphetamine alters neuronal responses to glutamate in the mesoaccumbens dopamine system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273:445–454
Wolf ME (1998) The role of excitatory amino acids in behavioral sensitization to psychomotor stimulants. Prog Neurobiol 54:679–720
Wolf ME, Jeziorski M (1993) Coadministration of MK-801 with amphetamine, cocaine or morphine prevents rather than transiently masks the development of behavioral sensitization. Brain Res 613:291–294
Xue C-J, Ng JP, Li Y, Wolf ME (1996) Acute and repeated systemic amphetamine administration: effects on extracellular glutamate, aspartate, and serine levels in rat ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 67:352–363
Zhang XF, Hu XT, White FJ, Wolf ME (1997) Increased responsiveness of ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons to glutamate after repeated administration of cocaine or amphetamine is transient and selectively involves AMPA receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:699–706
Zheng F, Johnson SW (2002) Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated enhancement of dopamine cell burst firing in rat ventral tegmental area in vitro. Brain Res 948:171–174
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dunn, J.M., Inderwies, B.R., Licata, S.C. et al. Repeated administration of AMPA or a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist into the rat ventral tegmental area augments the subsequent behavioral hyperactivity induced by cocaine. Psychopharmacology 179, 172–180 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2054-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2054-9