Abstract
Rationale
The serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, which are found in abundance in the mesolimbocortical dopaminergic system, appear to modulate the behavioral effects of cocaine.
Objectives
The present series of studies set out to investigate the role of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors on brain reward and on the reward-facilitating effect of cocaine and localize the neural substrates within the mesolimbocortical dopaminergic system that are responsible for these effects.
Methods
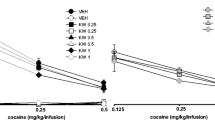
Male Sprague-Dawley rats were implanted with stimulating electrodes and bilateral cannulae for the experiments involving microinjections and were trained to respond to electrical stimulation. In the first study, we examined the effects of systemic administration of selective 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor agonists (TCB-2 and WAY-161503) and antagonists (R-96544 and SB-242084) on intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS). In the second study, we examined the effectiveness of TCB-2, WAY-161503, R-96544, and SB-242084 in blocking the reward-facilitating effect of cocaine. In the third study, we examined the effects of intra-medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), intra-nucleus accumbens (NAC), and intra-ventral tegmental area (VTA) injection of WAY-161503 on the reward-facilitating effect of cocaine.
Results
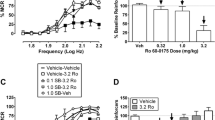
Acute systemic administration of TCB-2 and WAY-161503 increased ICSS threshold. Systemic WAY-161503 attenuated the reward-facilitating effect of cocaine. This effect was reversed by pretreatment with SB-242084. Intracranial microinjections of WAY-161503 into the mPFC and the NAC shell/core, but not the VTA, attenuated the reward-facilitating effect of cocaine.
Conclusion
These data indicate that 5-HT2C receptors within the mPFC and the NAC modulate the reinforcing effects of cocaine and provide evidence that 5-HT2C receptor agonists could be a possible drug discovery target for the treatment of psychostimulant addiction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowski D, Rigo M, Duc D, Hoyer D, Staufenbiel M (1995) Localization of the 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptor protein in human and rat brain using specific antisera. Neuropharmacology 34:1635–1645
Alex KD, Pehek EA (2007) Pharmacologic mechanisms of serotonergic regulation of dopamine neurotransmission. Pharmacol Ther 113:296–320
Benaliouad F, Kapur S, Rompre PP (2007) Blockade of 5-HT2a receptors reduces haloperidol-induced attenuation of reward. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:551–561
Boulougouris V, Robbins TW (2010) Enhancement of spatial reversal learning by 5-HT2C receptor antagonism is neuroanatomically specific. J Neurosci 30:930–938
Boulougouris V, Glennon JC, Robbins TW (2008) Dissociable effects of selective 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor antagonists on serial spatial reversal learning in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2007–2019
Bubar MJ, Cunningham KA (2006) Serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors as potential targets for modulation of psychostimulant use and dependence. Curr Top Med Chem 6:1971–1985
Bubar MJ, Cunningham KA (2007) Distribution of serotonin 5-HT2C receptors in the ventral tegmental area. Neuroscience 146:286–297
Bubar MJ, Cunningham KA (2008) Prospects for serotonin 5-HT2R pharmacotherapy in psychostimulant abuse. Prog Brain Res 172:319–346
Burmeister JJ, Lungren EM, Kirschner KF, Neisewander JL (2004) Differential roles of 5-HT receptor subtypes in cue and cocaine reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:660–668
Campbell KA, Evans G, Gallistel CR (1985) A microcomputer-based method for physiologically interpretable measurement of the rewarding efficacy of brain stimulation. Physiol Behav 35:395–403
Carlezon WA Jr, Chartoff EH (2007) Intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) in rodents to study the neurobiology of motivation. Nat Protoc 2:2987–2995
Coulombe D, Miliaressis E (1987) Fitting intracranial self-stimulation data with growth models. Behav Neurosci 101:209–214
Cryan JF, Lucki I (2000) Antidepressant-like behavioral effects mediated by 5-hydroxytryptamine(2C) receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:1120–1126
De Deurwaerdere P, Navailles S, Berg KA, Clarke WP, Spampinato U (2004) Constitutive activity of the serotonin2C receptor inhibits in vivo dopamine release in the rat striatum and nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 24:3235–3241
Di Chiara G, Bassareo V (2007) Reward system and addiction: what dopamine does and doesn’t do. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7:69–76
Di Matteo V, De Blasi A, Di Giulio C, Esposito E (2001) Role of 5-HT(2C) receptors in the control of central dopamine function. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:229–232
Di Matteo V, Cacchio M, Di Giulio C, Esposito E (2002) Role of serotonin(2C) receptors in the control of brain dopaminergic function. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:727–734
Edmonds DE, Gallistel CR (1974) Parametric analysis of brain stimulation reward in the rat: III. Effect of performance variables on the reward summation function. J Comp Physiol Psychol 87:876–883
Filip M (2005) Role of serotonin (5-HT)2 receptors in cocaine self-administration and seeking behavior in rats. Pharmacol Rep 57:35–46
Filip M, Cunningham KA (2002) Serotonin 5-HT(2C) receptors in nucleus accumbens regulate expression of the hyperlocomotive and discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:745–756
Filip M, Cunningham KA (2003) Hyperlocomotive and discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine are under the control of serotonin(2C) (5-HT(2C)) receptors in rat prefrontal cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:734–743
Filip M, Bubar MJ, Cunningham KA (2004) Contribution of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) 5-HT2 receptor subtypes to the hyperlocomotor effects of cocaine: acute and chronic pharmacological analyses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:1246–1254
Filip M, Frankowska M, Zaniewska M, Golda A, Przegalinski E (2005) The serotonergic system and its role in cocaine addiction. Pharmacol Rep 57:685–700
Filip M, Bubar MJ, Cunningham KA (2006) Contribution of serotonin (5-HT) 5-HT2 receptor subtypes to the discriminative stimulus effects of cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 183:482–489
Fink KB, Gothert M (2007) 5-HT receptor regulation of neurotransmitter release. Pharmacol Rev 59:360–417
Flaisher-Grinberg S, Klavir O, Joel D (2008) The role of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors in the signal attenuation rat model of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:811–825
Fletcher PJ, Grottick AJ, Higgins GA (2002a) Differential effects of the 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonist M100907 and the 5-HT(2C) receptor antagonist SB242084 on cocaine-induced locomotor activity, cocaine self-administration and cocaine-induced reinstatement of responding. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:576–586
Fletcher PJ, Korth KM, Robinson SR, Baker GB (2002b) Multiple 5-HT receptors are involved in the effects of acute MDMA treatment: studies on locomotor activity and responding for conditioned reinforcement. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 162:282–291
Fletcher PJ, Chintoh AF, Sinyard J, Higgins GA (2004) Injection of the 5-HT2C receptor agonist Ro60-0175 into the ventral tegmental area reduces cocaine-induced locomotor activity and cocaine self-administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:308–318
Fox MA, French HT, Laporte JL, Blackler AR, Murphy DL (2009) The serotonin 5-HT(2A) receptor agonist TCB-2: a behavioral and neurophysiological analysis. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Gallo A, Lapointe S, Stip E, Potvin S, Rompre PP (2010) Quetiapine blocks cocaine-induced enhancement of brain stimulation reward. Behav Brain Res 208:163–168
Grottick AJ, Fletcher PJ, Higgins GA (2000) Studies to investigate the role of 5-HT(2C) receptors on cocaine- and food-maintained behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:1183–1191
Grottick AJ, Corrigall WA, Higgins GA (2001) Activation of 5-HT(2C) receptors reduces the locomotor and rewarding effects of nicotine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 157:292–298
Halliday GM, Tork I (1989) Serotonin-like immunoreactive cells and fibres in the rat ventromedial mesencephalic tegmentum. Brain Res Bull 22:725–735
Hayes DJ, Clements R, Greenshaw AJ (2009a) Effects of systemic and intra-nucleus accumbens 5-HT2C receptor compounds on ventral tegmental area self-stimulation thresholds in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 203:579–588
Hayes DJ, Mosher TM, Greenshaw AJ (2009b) Differential effects of 5-HT2C receptor activation by WAY 161503 on nicotine-induced place conditioning and locomotor activity in rats. Behav Brain Res 197:323–330
Howell LL, Byrd LD (1995) Serotonergic modulation of the behavioral effects of cocaine in the squirrel monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:1551–1559
Hoyer D, Pazos A, Probst A, Palacios JM (1986) Serotonin receptors in the human brain. II. Characterization and autoradiographic localization of 5-HT1C and 5-HT2 recognition sites. Brain Res 376:97–107
Karila L, Gorelick D, Weinstein A, Noble F, Benyamina A, Coscas S, Blecha L, Lowenstein W, Martinot JL, Reynaud M, Lepine JP (2008) New treatments for cocaine dependence: a focused review. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:425–438
Kornetsky C (1985) Brain-stimulation reward: a model for the neuronal bases for drug-induced euphoria. NIDA Res Monogr 62:30–50
Liu S, Cunningham KA (2006) Serotonin2C receptors (5-HT2C R) control expression of cocaine-induced conditioned hyperactivity. Drug Alcohol Depend 81:275–282
Liu S, Bubar MJ, Lanfranco MF, Hillman GR, Cunningham KA (2007) Serotonin2C receptor localization in GABA neurons of the rat medial prefrontal cortex: implications for understanding the neurobiology of addiction. Neuroscience 146:1677–1688
Lopez-Gimenez JF, Mengod G, Palacios JM, Vilaro MT (1997) Selective visualization of rat brain 5-HT2A receptors by autoradiography with [3H]MDL 100,907. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 356:446–454
Maldonado-Irizarry CS, Stellar JR, Kelley AE (1994) Effects of cocaine and GBR-12909 on brain stimulation reward. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 48:915–920
Markou A, Koob GF (1991) Postcocaine anhedonia. An animal model of cocaine withdrawal. Neuropsychopharmacology 4:17–26
Matthews K, Baldo BA, Markou A, Lown O, Overstreet DH, Koob GF (1996) Rewarding electrical brain stimulation: similar thresholds for Flinders Sensitive Line Hypercholinergic and Flinders Resistant Line Hypocholinergic rats. Physiol Behav 59:1155–1162
McCreary AC, Cunningham KA (1999) Effects of the 5-HT2C/2B antagonist SB 206553 on hyperactivity induced by cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:556–564
McMahon LR, Cunningham KA (2001) Role of 5-HT(2a) and 5-HT(2B/2C) receptors in the behavioral interactions between serotonin and catecholamine reuptake inhibitors. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:319–329
Miliaressis E, Rompre PP (1987) Effects of concomitant motor reactions on the measurement of rewarding efficacy of brain stimulation. Behav Neurosci 101:827–831
Miliaressis E, Rompre PP, Laviolette P, Philippe L, Coulombe D (1986) The curve-shift paradigm in self-stimulation. Physiol Behav 37:85–91
Morissette MC, Boye SM (2008) Electrolytic lesions of the habenula attenuate brain stimulation reward. Behav Brain Res 187:17–26
Muller CP, Huston JP (2006) Determining the region-specific contributions of 5-HT receptors to the psychostimulant effects of cocaine. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:105–112
Muller CP, Carey RJ, Huston JP, De Souza Silva MA (2007) Serotonin and psychostimulant addiction: focus on 5-HT1A-receptors. Prog Neurobiol 81:133–178
Navailles S, De Deurwaerdere P, Porras G, Spampinato U (2004) In vivo evidence that 5-HT2C receptor antagonist but not agonist modulates cocaine-induced dopamine outflow in the rat nucleus accumbens and striatum. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:319–326
Navailles S, Moison D, Cunningham KA, Spampinato U (2008) Differential regulation of the mesoaccumbens dopamine circuit by serotonin2C receptors in the ventral tegmental area and the nucleus accumbens: an in vivo microdialysis study with cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:237–246
Neisewander JL, Acosta JI (2007) Stimulation of 5-HT2C receptors attenuates cue and cocaine-primed reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Behav Pharmacol 18:791–800
Nocjar C, Roth BL, Pehek EA (2002) Localization of 5-HT(2A) receptors on dopamine cells in subnuclei of the midbrain A10 cell group. Neuroscience 111:163–176
Olds J, Milner P (1954) Positive reinforcement produced by electrical stimulation of septal area and other regions of rat brain. J Comp Physiol Psychol 47:419–427
Panagis G, Spyraki C (1996) Neuropharmacological evidence for the role of dopamine in ventral pallidum self-stimulation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 123:280–288
Panagis G, Kastellakis A, Spyraki C, Nomikos G (2000) Effects of methyllycaconitine (MLA), an alpha 7 nicotinic receptor antagonist, on nicotine- and cocaine-induced potentiation of brain stimulation reward. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 149:388–396
Paterson NE, Myers C, Markou A (2000) Effects of repeated withdrawal from continuous amphetamine administration on brain reward function in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 152:440–446
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Pierce RC, Kumaresan V (2006) The mesolimbic dopamine system: the final common pathway for the reinforcing effect of drugs of abuse? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:215–238
Platt DM, Rowlett JK, Spealman RD (2002) Behavioral effects of cocaine and dopaminergic strategies for preclinical medication development. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 163:265–282
Pompeiano M, Palacios JM, Mengod G (1994) Distribution of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptor family mRNAs: comparison between 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 23:163–178
Ranaldi R, Bauco P, Wise RA (1997) Synergistic effects of cocaine and dizocilpine (MK-801) on brain stimulation reward. Brain Res 760:231–237
Robinson ES, Dalley JW, Theobald DE, Glennon JC, Pezze MA, Murphy ER, Robbins TW (2008) Opposing roles for 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors in the nucleus accumbens on inhibitory response control in the 5-choice serial reaction time task. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2398–2406
Rocha BA, Goulding EH, O’Dell LE, Mead AN, Coufal NG, Parsons LH, Tecott LH (2002) Enhanced locomotor, reinforcing, and neurochemical effects of cocaine in serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine 2C receptor mutant mice. J Neurosci 22:10039–10045
Romeas T, Morissette MC, Mnie-Filali O, Pineyro G, Boye SM (2009) Simultaneous anhedonia and exaggerated locomotor activation in an animal model of depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 205:293–303
Sharma A, Punhani T, Fone KC (1997) Distribution of the 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptor protein in adult rat brain and spinal cord determined using a receptor-directed antibody: effect of 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine. Synapse 27:45–56
Shioda K, Nisijima K, Yoshino T, Kuboshima K, Iwamura T, Yui K, Kato S (2008) Risperidone attenuates and reverses hyperthermia induced by 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in rats. Neurotoxicology 29:1030–1036
Singh J, Desiraju T, Raju TR (1996) Comparison of intracranial self-stimulation evoked from lateral hypothalamus and ventral tegmentum: analysis based on stimulation parameters and behavioural response characteristics. Brain Res Bull 41:399–408
Slattery DA, Markou A, Cryan JF (2007) Evaluation of reward processes in an animal model of depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 190:555–568
Thomas MJ, Kalivas PW, Shaham Y (2008) Neuroplasticity in the mesolimbic dopamine system and cocaine addiction. Br J Pharmacol 154:327–342
Tomkins DM, Joharchi N, Tampakeras M, Martin JR, Wichmann J, Higgins GA (2002) An investigation of the role of 5-HT(2C) receptors in modifying ethanol self-administration behaviour. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:735–744
Vlachou S, Nomikos GG, Panagis G (2003) WIN 55, 212-2 decreases the reinforcing actions of cocaine through CB1 cannabinoid receptor stimulation. Behav Brain Res 141:215–222
Vlachou S, Stamatopoulou F, Nomikos GG, Panagis G (2008) Enhancement of endocannabinoid neurotransmission through CB1 cannabinoid receptors counteracts the reinforcing and psychostimulant effects of cocaine. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:905–923
Willins DL, Meltzer HY (1998) Serotonin 5-HT2C agonists selectively inhibit morphine-induced dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens. Brain Res 781:291–299
Wise RA (1996) Addictive drugs and brain stimulation reward. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:319–340
Wise RA (1998) Drug-activation of brain reward pathways. Drug Alcohol Depend 51:13–22
Xi ZX, Gardner EL (2008) Hypothesis-driven medication discovery for the treatment of psychostimulant addiction. Curr Drug Abuse Rev 1:303–327
Zaniewska M, McCreary AC, Filip M (2009) Interactions of serotonin (5-HT)2 receptor-targeting ligands and nicotine: locomotor activity studies in rats. Synapse 63:653–661
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Research Committee (KA 2581) and the Department of Psychology of the University of Crete. The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katsidoni, V., Apazoglou, K. & Panagis, G. Role of serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors on brain stimulation reward and the reward-facilitating effect of cocaine. Psychopharmacology 213, 337–354 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1887-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1887-7