Abstract
Background
Bronchial asthma is an inflammatory disease of the airways. Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) is a carboxypeptidase that besides inhibiting fibrinolysis, also regulates inflammatory processes. The only validated substrate known for TAFI is fibrin. In the present study we evaluated the role of TAFI in bronchial asthma by comparing the development of allergic bronchial asthma between wild-type (WT) and TAFI-deficient mice (KO).
Methods
Asthmatic inflammation was induced by sensitization and challenge with ovalbumin in WT (WT/OVA) and TAFI KO (KO/OVA) mice. WT mice (WT/SAL) and TAFI KO (KO/SAL) were used as controls. Cytokines, markers of inflammation, and coagulation were measured in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF).
Results
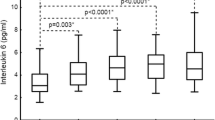
Airway hyperresponsiveness was worse in KO/OVA mice than in WT/OVA mice or control mice. Markers of lung injury were significantly increased in BALF from KO/OVA mice compared to WT/OVA mice. Airway hyperresponsiveness and the BALF concentrations of IL-5 and osteopontin were significantly increased in KO/OVA mice compared to WT/OVA mice. Treatment of WT/OVA and KO/OVA mice with a C5a receptor antagonist significantly decreased hyperresponsiveness along with the BALF concentrations of total protein and C5a compared to untreated asthmatic mice.
Conclusion
The results of this study suggest that TAFI plays a protective role in the pathogenesis of allergic inflammation probably by inhibiting the complement system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Subbarao P, Mandhane PJ, Sears MR (2009) Asthma: epidemiology, etiology and risk factors. CMAJ 181:E181–E190
Robinson DS (2010) The role of the T cell in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126:1081–1091
Bouma BN, Meijers JC (2003) Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI, plasma procarboxypeptidase B, procarboxypeptidase R, procarboxypeptidase U). J Thromb Haemost 1:1566–1574
Morser J, Gabazza EC, Myles T, Leung LL (2010) What has been learnt from the thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor-deficient mouse? J Thromb Haemost 8:868–876
Mosnier LO, Bouma BN (2006) Regulation of fibrinolysis by thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor, an unstable carboxypeptidase B that unites the pathways of coagulation and fibrinolysis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:2445–2453
Bajzar L, Jain N, Wang P, Walker JB (2004) Thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor: not just an inhibitor of fibrinolysis. Crit Care Med 32:S320–S324
Krug N, Tschernig T, Erpenbeck VJ, Hohlfeld JM, Kohl J (2001) Complement factors C3a and C5a are increased in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid after segmental allergen provocation in subjects with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1841–1843
Karp CL, Grupe A, Schadt E, Ewart SL, Keane-Moore M, Cuomo PJ, Kohl J, Wahl L, Kuperman D, Germer S, Aud D, Peltz G, Wills-Karp M (2000) Identification of complement factor 5 as a susceptibility locus for experimental allergic asthma. Nat Immunol 1:221–226
Walters DM, Breysse PN, Schofield B, Wills-Karp M (2002) Complement factor 3 mediates particulate matter-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 27:413–418
Humbles AA, Lu B, Nilsson CA, Lilly C, Israel E, Fujiwara Y, Gerard NP, Gerard C (2000) A role for the C3a anaphylatoxin receptor in the effector phase of asthma. Nature 406:998–1001
Drouin SM, Corry DB, Hollman TJ, Kildsgaard J, Wetsel RA (2002) Absence of the complement anaphylatoxin C3a receptor suppresses Th2 effector functions in a murine model of pulmonary allergy. J Immunol 169:5926–5933
Bautsch W, Hoymann HG, Zhang Q, Meier-Wiedenbach I, Raschke U, Ames RS, Sohns B, Flemme N, Vilsendorf AMZ, Grove M, Klos A, Kohl J (2000) Cutting edge: guinea pigs with a natural C3a-receptor defect exhibit decreased bronchoconstriction in allergic airway disease: evidence for an involvement of the C3a anaphylatoxin in the pathogenesis of asthma. J Immunol 165:5401–5405
Taube C, Rha YH, Takeda K, Park JW, Joetham A, Balhorn A, Dakhama A, Giclas PC, Holers VM, Gelfand EW (2003) Inhibition of complement activation decreases airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:1333–1341
Paczkowski NJ, Finch AM, Whitmore JB, Short AJ, Wong AK, Monk PN, Cain SA, Fairlie DP, Taylor SM (1999) Pharmacological characterization of antagonists of the C5a receptor. Br J Pharmacol 128:1461–1466
Finch AM, Wong AK, Paczkowski NJ, Wadi SK, Craik DJ, Fairlie DP, Taylor SM (1999) Low-molecular-weight peptidic and cyclic antagonists of the receptor for the complement factor C5a. J Med Chem 42:1965–1974
Nagashima M, Yin ZF, Zhao L, White K, Zhu Y, Lasky N, Halks-Miller M, Broze GJ Jr, Fay WP, Morser J (2002) Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) deficiency is compatible with murine life. J Clin Invest 109:101–110
Yuda H, Adachi Y, Taguchi O, Gabazza EC, Hataji O, Fujimoto H, Tamaki S, Nishikubo K, Fukudome K, D’Alessandro-Gabazza CN, Maruyama J, Izumizaki M, Iwase M, Homma I, Inoue R, Kamada H, Hayashi T, Kasper M, Lambrecht BN, Barnes PJ, Suzuki K (2004) Activated protein C inhibits bronchial hyperresponsiveness and Th2 cytokine expression in mice. Blood 103:2196–2204
Murphy DM, O’Byrne PM (2010) Recent advances in the pathophysiology of asthma. Chest 137:1417–1426
Ma Z, Paek D, Oh CK (2009) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and asthma: role in the pathogenesis and molecular regulation. Clin Exp Allergy 39:1136–1144
Samitas K, Zervas E, Vittorakis S, Semitekolou M, Alissafi T, Bossios A, Gogos H, Economidou E, Lotvall J, Xanthou G, Panoutsakopoulou V, Gaga M (2011) Osteopontin expression and relation to disease severity in human asthma. Eur Respir J 37:331–341
Halwani R, Al-Muhsen S, Al-Jahdali H, Hamid Q (2011) Role of transforming growth factor-beta in airway remodeling in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 44:127–133
Ali H (2010) Regulation of human mast cell and basophil function by anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a. Immunol Lett 128:36–45
Thorburn AN, Hansbro PM (2010) Harnessing regulatory T cells to suppress asthma: from potential to therapy. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 43:511–519
Matthay MA, Clements JA (2004) Coagulation-dependent mechanisms and asthma. J Clin Invest 114:20–23
Gabazza EC, Taguchi O, Tamaki S, Takeya H, Kobayashi H, Yasui H, Kobayashi T, Hataji O, Urano H, Zhou H, Suzuki K, Adachi Y (1999) Thrombin in the airways of asthmatic patients. Lung 177:253–262
Shinagawa K, Martin JA, Ploplis VA, Castellino FJ (2007) Coagulation factor Xa modulates airway remodeling in a murine model of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 175:136–143
Shimizu S, Shimizu T, Morser J, Kobayashi T, Yamaguchi A, Qin L, Toda M, D’Alessandro-Gabazza C, Maruyama T, Takagi T, Yano Y, Sumida Y, Hayashi T, Takei Y, Taguchi O, Suzuki K, Gabazza EC (2008) Role of the coagulation system in allergic inflammation in the upper airways. Clin Immunol 129:365–371
Cho SH, Ryu CH, Oh CK (2004) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in the pathogenesis of asthma. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 229:138–146
Schneider DJ, Chen Y, Sobel BE (2008) The effect of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 on apoptosis. Thromb Haemost 100:1037–1040
Balsara RD, Ploplis VA (2008) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: the double-edged sword in apoptosis. Thromb Haemost 100:1029–1036
Nemeth K, Keane-Myers A, Brown JM, Metcalfe DD, Gorham JD, Bundoc VG, Hodges MG, Jelinek I, Madala S, Karpati S, Mezey E (2010) Bone marrow stromal cells use TGF-beta to suppress allergic responses in a mouse model of ragweed-induced asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:5652–5657
Alcorn JF, Rinaldi LM, Jaffe EF, van Loon M, Bates JH, Janssen-Heininger YM, Irvin CG (2007) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 suppresses airway hyperresponsiveness in allergic airway disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 176:974–982
Wills-Karp M (2007) Complement activation pathways: a bridge between innate and adaptive immune responses in asthma. Proc Am Thorac Soc 4:247–251
Acknowledgment
The present investigation was supported by Grants-in-Aid (Nos. 18590846 and 17590788) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. JM was supported by JSPS scholarship L8020.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, A., Taguchi, O., Takagi, T. et al. Role of Thrombin-Activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor in Allergic Bronchial Asthma. Lung 190, 189–198 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-011-9337-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-011-9337-9