Abstract.
Abstract.
Background/Purpose:
The peroxidation of membranous phospholipids induced by ischemia reperfusion was inhibited in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD) overexpressing mice, suggesting a detrimental role for intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in reoxygenated cell injury. To ascertain the in-vitro relevance of this hypothesis, the present study examined the participation of intracellular ROS in reoxygenation injury.
Methods:
This examination was done in two experimental models: Cu/Zn-SOD transgenic (Tg) mice that underwent hypoxia-reoxygenation in vitro and normal mice pretreated with a specific inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, BOF-4272, followed by in vitro hypoxia-reoxygenation.
Results:
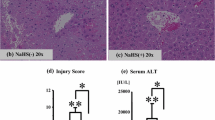
The release of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and the peroxidation of phospholipids were both ameliorated in hepatocytes from the Tg mice compared with findings in hepatocytes from normal mice. Similar findings were seen in the BOF-4272-pretreated cells, in which there was a decrease in AST and phospholipid peroxides.
Conclusions:
These results support the pivotal role of intracellular ROS generated by xanthine oxidase in reoxygenated cell injury, and suggest the viability of using an intracellular antioxidative therapy for reperfusion injury of the liver.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: September 21, 2001 / Accepted: February 6, 2002
About this article
Cite this article
Kakita, T., Suzuki, M., Takeuchi, H. et al. Significance of xanthine oxidase in the production of intracellular oxygen radicals in an in-vitro hypoxia-reoxygenation model. J Hep Bil Pancr Surg 9, 249–255 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005340200027
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005340200027