Abstract
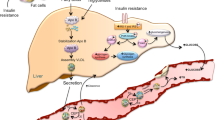
Sedentary life style and high calorie dietary habits are prominent leading cause of metabolic syndrome in modern world. Obesity plays a central role in occurrence of various diseases like hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia, which lead to insulin resistance and metabolic derangements like cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) mediated by oxidative stress. The mortality rate due to CVDs is on the rise in developing countries. Insulin resistance (IR) leads to micro or macro angiopathy, peripheral arterial dysfunction, hampered blood flow, hypertension, as well as the cardiomyocyte and the endothelial cell dysfunctions, thus increasing risk factors for coronary artery blockage, stroke and heart failure suggesting that there is a strong association between IR and CVDs. The plausible linkages between these two pathophysiological conditions are altered levels of insulin signaling proteins such as IR-β, IRS-1, PI3K, Akt, Glut4 and PGC-1α that hamper insulin-mediated glucose uptake as well as other functions of insulin in the cardiomyocytes and the endothelial cells of the heart. Reduced AMPK, PFK-2 and elevated levels of NADP(H)-dependent oxidases produced by activated M1 macrophages of the adipose tissue and elevated levels of circulating angiotensin are also cause of CVD in diabetes mellitus condition. Insulin sensitizers, angiotensin blockers, superoxide scavengers are used as therapeutics in the amelioration of CVD. It evidently becomes important to unravel the mechanisms of the association between IR and CVDs in order to formulate novel efficient drugs to treat patients suffering from insulin resistance-mediated cardiovascular diseases. The possible associations between insulin resistance and cardiovascular diseases are reviewed here.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACE:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme
- ARBs:
-
Angiotensin receptor blockers
- ADA:
-
American Diabetes Association
- AGEs:
-
Advanced glycation end-products
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- AT1R:
-
Angiotensin II type I receptor
- C/EBP:
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein
- CAN:
-
Cardiac autonomic neuropathy
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- CVD:
-
Cardio vascular diseases
- DG:
-
Diacyl glycerol
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- ERR:
-
Estrogen-related nuclear receptors
- ET-1:
-
Endothelin-1
- FAT/CD36:
-
Fatty acid translocase
- FetA:
-
Fetuin-A
- FFA:
-
Free fatty acid
- Glut4:
-
Glucose transporter 4
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- ICAM-1:
-
Intracellular adhesion molecule-1
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IR:
-
Insulin resistance
- IR-β:
-
Insulin receptor β
- IRS-1:
-
Insulin receptor substrate-1
- JNK:
-
Janus kinase
- STAT:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription
- LCFA:
-
Long-chain fatty acid
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- LPL:
-
Lipoprotein lipase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MCP-1:
-
Macrophage chemo attractant protein-1
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- NADP:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NEFA:
-
Non-esterified fatty acid
- NFAT:
-
Nuclear factor of activated T cells
- NFκ-B:
-
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NOXs:
-
NADPH oxidases
- NRF1:
-
Nuclear respiratory factor 1
- OXPHO:
-
Oxidative phosphorylation
- PAI-1:
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
- PFK2:
-
Phosphofructokinase 2
- PGC-1α:
-
PPAR-γ coactivator 1α
- PH:
-
Pleckstrin homology
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PKB/Akt:
-
Protein kinase B
- PPARs:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- PTP1B:
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SHIP:
-
SH2-containing inositol 5′-phosphatase
- SOCS:
-
Suppressors of cytokine signaling
- SREBP:
-
Sterol regulatory element binding protein
- TAG:
-
Triacyl glycerol
- Tfam A:
-
Mitochondrial transcription factor A
- TLRs:
-
Toll-like receptors
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- UCP:
-
Uncoupling protein
- VAT:
-
Visceral adipose tissue
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VLDL:
-
Very low-density lipoprotein
References
Ceriello A (2005) Postprandial hyperglycemia and diabetes complications is it time to treat? Diabetes 54(1):1–7
Kannel WB, Hjortland M, Castelli WP (1974) Role of diabetes in congestive heart failure: the Framingham study. Am J Cardiol 34(1):29–34
Garcia M, McNamara P, Gordon T, Kannel W (1972) Cardiovascular complications in diabetics. Adv Metab Disord 2(Suppl 2):493–499
Fowler MJ (2008) Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes 26(2):77–82
Ceriello A (2003) New insights on oxidative stress and diabetic complications may lead to a “causal” antioxidant therapy. Diabetes Care 26(5):1589–1596
Farahmand F, Lou H, Singal PK (2003) Oxidative stress in cardiovascular complications of diabetes. In: Pierce GN, Nagano M, Zahradka P, Dhalla NS (eds) Atherosclerosis, hypertension and diabetes. Kluwer Academic Publications, Boston, pp 427–437
Gyurko R, Siqueira CC, Caldon N, Gao L, Kantarci A, Van Dyke TE (2006) Chronic hyperglycemia predisposes to exaggerated inflammatory response and leukocyte dysfunction in Akita mice. J Immunol 177(10):7250–7256
Lum H, Roebuck KA (2001) Oxidant stress and endothelial cell dysfunction. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280(4):C719–C741
Versari D, Daghini E, Virdis A, Ghiadoni L, Taddei S (2009) Endothelial dysfunction as a target for prevention of cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 32(suppl 2):S314–S321
Schram MT, Chaturvedi N, Schalkwijk C, Giorgino F, Ebeling P, Fuller JH, Stehouwer CD (2003) Vascular risk factors and markers of endothelial function as determinants of inflammatory markers in type 1 diabetes the EURODIAB Prospective complications study. Diabetes Care 26(7):2165–2173
El-Osta A, Brasacchio D, Yao D, Pocai A, Jones PL, Roeder RG, Cooper ME, Brownlee M (2008) Transient high glucose causes persistent epigenetic changes and altered gene expression during subsequent normoglycemia. J Exp Med 205(10):2409–2417
Hink U, Li H, Mollnau H, Oelze M, Matheis E, Hartmann M, Skatchkov M, Thaiss F, Stahl RA, Warnholtz A (2001) Mechanisms underlying endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Circ Res 88(2):e14–e22
Watts G, Playford D (1998) Dyslipoproteinaemia and hyperoxidative stress in the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: an hypothesis. Atherosclerosis 141(1):17–30
Renard CB, Kramer F, Johansson F, Lamharzi N, Tannock LR, von Herrath MG, Chait A, Bornfeldt KE (2004) Diabetes and diabetes-associated lipid abnormalities have distinct effects on initiation and progression of atherosclerotic lesions. J Clin Investig 114(5):659
Poirier P, Giles TD, Bray GA, Hong Y, Stern JS, Pi-Sunyer FX, Eckel RH (2006) Obesity and cardiovascular disease: pathophysiology, evaluation, and effect of weight loss an update of the 1997 American Heart Association Scientific statement on obesity and heart disease from the obesity committee of the council on nutrition, physical activity, and metabolism. Circulation 113(6):898–918
Duncan BB, Schmidt MI, Pankow JS, Ballantyne CM, Couper D, Vigo A, Hoogeveen R, Folsom AR, Heiss G (2003) Low-grade systemic inflammation and the development of type 2 diabetes the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes 52(7):1799–1805
Turner R, Holman R, Matthews D, Bassett P, Coster R, Stratton I, Cull C, Peto R, Frighi V, Kennedy I (1993) Hypertension in diabetes study (Hds). 1. Prevalence of hypertension in newly presenting type-2 diabetic-patients and the association with risk-factors for cardiovascular and diabetic complications. J Hypertens 11(3):309–317
ADA (1993) Treatment of hypertension in diabetes. Diabetes Care 16:1394–1401
Goto A, Arah OA, Goto M, Terauchi Y, Noda M (2013) Severe hypoglycaemia and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis with bias analysis. BMJ 347:F4533
Sommerfield AJ, Wilkinson IB, Webb DJ, Frier BM (2007) Vessel wall stiffness in type 1 diabetes and the central hemodynamic effects of acute hypoglycemia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293(5):E1274–E1279
Frier BM, Schernthaner G, Heller SR (2011) Hypoglycemia and cardiovascular risks. Diabetes Care 34(Supplement 2):S132–S137
Desouza CV, Bolli GB, Fonseca V (2010) Hypoglycemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular events. Diabetes Care 33(6):1389–1394
Spallone V, Ziegler D, Freeman R, Bernardi L, Frontoni S, Pop-Busui R, Stevens M, Kempler P, Hilsted J, Tesfaye S (2011) Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in diabetes: clinical impact, assessment, diagnosis, and management. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 27(7):639–653
Witte D, Tesfaye S, Chaturvedi N, Eaton S, Kempler P, Fuller J, Group EPCS (2005) Risk factors for cardiac autonomic neuropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 48(1):164–171
Astrup AS, Tarnow L, Rossing P, Hansen BV, Hilsted J, Parving H-H (2006) Cardiac autonomic neuropathy predicts cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care 29(2):334–339
DeFronzo RA, Tripathy D (2009) Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is the primary defect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(suppl 2):S157–S163
Groop L, Bonadonna R, Del Prato S, Ratheiser K, Zyck K, DeFronzo R (1989) Effect of insulin on oxidative and non-oxidative pathways of glucose and FFA metabolism in NIDDM. Evidence for multiple sites of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 84:205–213
Morino K, Petersen KF, Shulman GI (2006) Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance in humans and their potential links with mitochondrial dysfunction. Diabetes 55(Supplement 2):S9–S15
Langin D, Dicker A, Tavernier G, Hoffstedt J, Mairal A, Rydén M, Arner E, Sicard A, Jenkins CM, Viguerie N (2005) Adipocyte lipases and defect of lipolysis in human obesity. Diabetes 54(11):3190–3197
Kern PA (1997) Potential role of TNFα and lipoprotein lipase as candidate genes for obesity. J Nutr 127(9):1917S–1922S
Bugianesi E, McCullough AJ, Marchesini G (2005) Insulin resistance: a metabolic pathway to chronic liver disease. Hepatology 42(5):987–1000
Dröge W (2002) Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev 82(1):47–95
Brownlee M (2001) Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 414(6865):813–820
Greene DA, Stevens MJ, Obrosova I, Feldman EL (1999) Glucose-induced oxidative stress and programmed cell death in diabetic neuropathy. Eur J Pharmacol 375(1):217–223
Wolff SP, Dean R (1987) Glucose autoxidation and protein modification. The potential role of ‘autoxidative glycosylation’ in diabetes. Biochem J 245:243–250
Yan S, Stern D, Schmidt A (1997) What’s the RAGE? The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and the dark side of glucose. Eur J Clin Invest 27(3):179–181
Stojiljkovic MP, Lopes HF, Zhang D, Morrow JD, Goodfriend TL, Egan BM (2002) Increasing plasma fatty acids elevates F2-isoprostanes in humans: implications for the cardiovascular risk factor cluster. J Hypertens 20(6):1215–1221
S-i Yamagishi, Edelstein D, X-l Du, Kaneda Y, Guzmán M, Brownlee M (2001) Leptin induces mitochondrial superoxide production and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in aortic endothelial cells by increasing fatty acid oxidation via protein kinase A. J Biol Chem 276(27):25096–25100
Paz K, Hemi R, LeRoith D, Karasik A, Elhanany E, Kanety H, Zick Y (1997) A Molecular Basis for Insulin Resistance elevated serine/threonine phosphorylation of irs-1 and irs-2 inhibits their binding to the juxtamembrane region of the insulin receptor and impairs their ability to undergo insulin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 272(47):29911–29918
Potashnik R, Bloch-Damti A, Bashan N, Rudich A (2003) IRS1 degradation and increased serine phosphorylation cannot predict the degree of metabolic insulin resistance induced by oxidative stress. Diabetologia 46(5):639–648
Ogihara T, Asano T, Katagiri H, Sakoda H, Anai M, Shojima N, Ono H, Fujishiro M, Kushiyama A, Fukushima Y (2004) Oxidative stress induces insulin resistance by activating the nuclear factor-κB pathway and disrupting normal subcellular distribution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Diabetologia 47(5):794–805
Khamaisi M, Potashnik R, Tirosh A, Demshchak E, Rudich A, Trischler H, Wessel K, Bashan N (1997) Lipoic acid reduces glycemia and increases muscle GLUT4 content in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Metabolism 46(7):763–768
Pessler D, Rudich A, Bashan N (2001) Oxidative stress impairs nuclear proteins binding to the insulin responsive element in the GLUT4 promoter. Diabetologia 44(12):2156–2164
Castelló A, Rodríguez-Manzaneque JC, Camps M, Perez-Castillo A, Testar X, Palacin M, Santos A, Zorzano A (1994) Perinatal hypothyroidism impairs the normal transition of GLUT4 and GLUT1 glucose transporters from fetal to neonatal levels in heart and brown adipose tissue. Evidence for tissue-specific regulation of GLUT4 expression by thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem 269(8):5905–5912
Randle PJ, Kerbey AL, Espinal J (1988) Mechanisms decreasing glucose oxidation in diabetes and starvation: role of lipid fuels and hormones. Diabetes Metab Rev 4(7):623–638
Shulman GI (2000) Cellular mechanisms of insulin resistance. J Clin Investig 106(2):171
Stalder M, Pometta D, Suenram A (1981) Relationship between plasma insulin levels and high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in healthy men. Diabetologia 21(6):544–548
Sadur UN, Yost TJ, Eckel RH (1984) Insulin responsiveness of adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase is delayed but preserved in obesity*. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 59(6):1176–1182
Golay A, Zech L, Shi M-Z, Chiou Y-A, Reaven G, Chen Y-D (1987) High density lipoprotein (HDL) metabolism in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: measurement of HDL turnover using tritiated HDL*. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 65(3):512–518
Eriksson P, Nilsson L, Karpe F, Hamsten A (1998) Very-low-density lipoprotein response element in the promoter region of the human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene implicated in the impaired fibrinolysis of hypertriglyceridemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18(1):20–26
Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du XL, S-i Yamagishi, Matsumura T, Kaneda Y, Yorek MA, Beebe D, Oates PJ, Hammes H-P (2000) Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature 404(6779):787–790
Pyörälä K (1979) Relationship of glucose tolerance and plasma insulin to the incidence of coronary heart disease: results from two population studies in Finland. Diabetes Care 2(2):131–141
Després J-P, Lamarche B, Mauriège P, Cantin B, Dagenais GR, Moorjani S, Lupien P-J (1996) Hyperinsulinemia as an independent risk factor for ischemic heart disease. N Engl J Med 334(15):952–958
Suzuki M, Shinozaki K, Kanazawa A, Hara Y, Hattori Y, Tsushima M, Harano Y (1996) Insulin resistance as an independent risk factor for carotid wall thickening. Hypertension 28(4):593–598
Shen D-C, Shieh S-M, Fuh M-T, Wu D-A, Chen Y-D, Reaven G (1988) Resistance to insulin-stimulated-glucose uptake in patients with hypertension*. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 66(3):580–583
Reaven GM, Chang H (1991) Relationship between blood pressure, plasma insulin ana triglyceride concentration, and insulin action in spontaneous hypertensive and Wistar-Kyoto rats. Am J Hypertens 4(1 Pt 1):34–38
Sechi LA, Melis A, Tedde R (1992) Insulin hypersecretion: a distinctive feature between essential and secondary hypertension. Metabolism 41(11):1261–1266
Reaven G (1996) Hypertension and associated metabolic abnormalities—the role of insulin resistance and the sympathoadrenal system. N Engl J Med 334:374–381
Mitchell TH, Nolan B, Henry M, Cronin C, Baker H, Greely G (1997) Microalbuminuria in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus relates to nocturnal systolic blood pressure. Am J Med 102(6):531–535
Laine H, Yki-Jarvinen H, Kirvela O, Tolvanen T, Raitakari M, Solin O, Haaparanta M, Knuuti J, Nuutila P (1998) Insulin resistance of glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cannot be ameliorated by enhancing endothelium-dependent blood flow in obesity. J Clin Investig 101(5):1156
Ginsberg HN (2000) Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Investig 106(4):453
Seidell JC, Pérusse L, Després J-P, Bouchard C (2001) Waist and hip circumferences have independent and opposite effects on cardiovascular disease risk factors: the Quebec Family Study. Am J Clin Nutr 74(3):315–321
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH (1997) Inflammation, aspirin, and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men. N Engl J Med 336(14):973–979
Brown NJ, Kim K-S, Chen Y-Q, Blevins LS, Nadeau JH, Meranze SG, Vaughan DE (2000) Synergistic effect of adrenal steroids and angiotensin II on plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 production 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(1):336–344
Sowers JR, Sowers PS, Peuler JD (1994) Role of insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia in development of hypertension and atherosclerosis. J Lab Clin Med 123(5):647–652
Chen Y-Q, Su M, Walia RR, Hao Q, Covington JW, Vaughan DE (1998) Sp1 sites mediate activation of the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promoter by glucose in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 273(14):8225–8231
Westerbacka J, Vehkavaara S, Bergholm R, Wilkinson I, Cockcroft J, Yki-Järvinen H (1999) Marked resistance of the ability of insulin to decrease arterial stiffness characterizes human obesity. Diabetes 48(4):821–827
Steinberg HO, Chaker H, Leaming R, Johnson A, Brechtel G, Baron AD (1996) Obesity/insulin resistance is associated with endothelial dysfunction. Implications for the syndrome of insulin resistance. J Clin Investig 97(11):2601
Després J-P (2006) Abdominal obesity: the most prevalent cause of the metabolic syndrome and related cardiometabolic risk. Eur Heart J Suppl 8(suppl B):B4–B12
Steinberger J, Daniels SR (2003) Obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk in children an American Heart Association scientific statement from the atherosclerosis, hypertension, and obesity in the Young Committee (Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young) and the Diabetes Committee (Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism). Circulation 107(10):1448–1453
Van Gaal LF, Mertens IL, Christophe E (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity with cardiovascular disease. Nature 444(7121):875–880
Turer AT, Hill JA, Elmquist JK, Scherer PE (2012) Adipose tissue biology and cardiomyopathy translational implications. Circ Res 111(12):1565–1577
Ramkhelawon B, Hennessy EJ, Ménager M, Ray TD, Sheedy FJ, Hutchison S, Wanschel A, Oldebeken S, Geoffrion M, Spiro W (2014) Netrin-1 promotes adipose tissue macrophage retention and insulin resistance in obesity. Nat Med 20(4):377–384
Sell H, Habich C, Eckel J (2012) Adaptive immunity in obesity and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8(12):709–716
De Marchi E, Faldassari B, Bononi A, Wieckowski M, Pinton P (2013) Oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases and obesity: role of p66Shc and protein kinase C. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:564961. doi:10.1155/2013/564961
Borén J, Taskinen MR, Olofsson SO, Levin M (2013) Ectopic lipid storage and insulin resistance: a harmful relationship. J Intern Med 274(1):25–40
Yang R, Barouch LA (2007) Leptin signaling and obesity cardiovascular consequences. Circ Res 101(6):545–559
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR (2007) Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Investig 117(1):175
Ruan H, Hacohen N, Golub TR, Van Parijs L, Lodish HF (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-α suppresses adipocyte-specific genes and activates expression of preadipocyte genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes nuclear factor-κB activation by TNF-α is obligatory. Diabetes 51(5):1319–1336
Permana PA, Menge C, Reaven PD (2006) Macrophage-secreted factors induce adipocyte inflammation and insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341(2):507–514
Schächinger V, Britten MB, Zeiher AM (2000) Prognostic impact of coronary vasodilator dysfunction on adverse long-term outcome of coronary heart disease. Circulation 101(16):1899–1906
Bugiardini R, Manfrini O, Pizzi C, Fontana F, Morgagni G (2004) Endothelial function predicts future development of coronary artery disease a study of women with chest pain and normal coronary angiograms. Circulation 109(21):2518–2523
Han S, Liang C-P, DeVries-Seimon T, Ranalletta M, Welch CL, Collins-Fletcher K, Accili D, Tabas I, Tall AR (2006) Macrophage insulin receptor deficiency increases ER stress-induced apoptosis and necrotic core formation in advanced atherosclerotic lesions. Cell Metab 3(4):257–266
Kuboki K, Jiang ZY, Takahara N, Ha SW, Igarashi M, Yamauchi T, Feener EP, Herbert TP, Rhodes CJ, King GL (2000) Regulation of endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase gene expression in endothelial cells and in vivo a specific vascular action of insulin. Circulation 101(6):676–681
Hamsten A, Wiman B, de Faire U, Blombäck M (1985) Increased plasma levels of a rapid inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator in young survivors of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 313(25):1557–1563
Wiman B, Andersson T, Hallqvist J, Reuterwall C, Ahlbom A (2000) Plasma levels of tissue plasminogen activator/plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 complex and von Willebrand factor are significant risk markers for recurrent myocardial infarction in the Stockholm Heart Epidemiology Program (SHEEP) study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(8):2019–2023
Calles-Escandon J, Mirza SA, Sobel BE, Schneider DJ (1998) Induction of hyperinsulinemia combined with hyperglycemia and hypertriglyceridemia increases plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 in blood in normal human subjects. Diabetes 47(2):290–293
Bertrand L, Horman S, Beauloye C, Vanoverschelde J-L (2008) Insulin signalling in the heart. Cardiovasc Res 79(2):238–248
Randle P, Garland P, Hales C, Newsholme E (1963) The glucose fatty-acid cycle its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet 281(7285):785–789
Proud C (2007) Signalling to translation: how signal transduction pathways control the protein synthetic machinery. Biochem J 403:217–234
Heineke J, Molkentin JD (2006) Regulation of cardiac hypertrophy by intracellular signalling pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(8):589–600
Dimmeler S, Fleming I, Fisslthaler B, Hermann C, Busse R, Zeiher AM (1999) Activation of nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells by Akt-dependent phosphorylation. Nature 399(6736):601–605
McFarlane SI, Banerji M, Sowers JR (2001) Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(2):713–718
Mehta PK, Griendling KK (2007) Angiotensin II cell signaling: physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292(1):C82–C97
Lowell BB, Shulman GI (2005) Mitochondrial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Science 307(5708):384–387
Kim YJ, Park T (2008) Genes are differentially expressed in the epididymal fat of rats rendered obese by a high-fat diet. Nutr Res 28(6):414–422
Dong F, Li Q, Sreejayan N, Nunn JM, Ren J (2007) Metallothionein prevents high-fat diet-induced cardiac contractile dysfunction role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α and mitochondrial biogenesis. Diabetes 56(9):2201–2212
Garcia-Roves P, Huss JM, Han D-H, Hancock CR, Iglesias-Gutierrez E, Chen M, Holloszy JO (2007) Raising plasma fatty acid concentration induces increased biogenesis of mitochondria in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(25):10709–10713
Hancock CR, Han D-H, Chen M, Terada S, Yasuda T, Wright DC, Holloszy JO (2008) High-fat diets cause insulin resistance despite an increase in muscle mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(22):7815–7820
Petersen KF, Dufour S, Befroy D, Garcia R, Shulman GI (2004) Impaired mitochondrial activity in the insulin-resistant offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 350(7):664–671
Huo L, Scarpulla RC (2001) Mitochondrial DNA instability and peri-implantation lethality associated with targeted disruption of nuclear respiratory factor 1 in mice. Mol Cell Biol 21(2):644–654
Patti ME, Butte AJ, Crunkhorn S, Cusi K, Berria R, Kashyap S, Miyazaki Y, Kohane I, Costello M, Saccone R (2003) Coordinated reduction of genes of oxidative metabolism in humans with insulin resistance and diabetes: potential role of PGC1 and NRF1. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(14):8466–8471
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson K-F, Subramanian A, Sihag S, Lehar J, Puigserver P, Carlsson E, Ridderstråle M, Laurila E (2003) PGC-1α-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet 34(3):267–273
Russell LK, Mansfield CM, Lehman JJ, Kovacs A, Courtois M, Saffitz JE, Medeiros DM, Valencik ML, McDonald JA, Kelly DP (2004) Cardiac-specific induction of the transcriptional coactivator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and reversible cardiomyopathy in a developmental stage-dependent manner. Circ Res 94(4):525–533
Lehman JJ, Barger PM, Kovacs A, Saffitz JE, Medeiros DM, Kelly DP (2000) Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor γ coactivator-1 promotes cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis. J Clin Investig 106(7):847
Huss JM, Kelly DP (2004) Nuclear receptor signaling and cardiac energetics. Circ Res 95(6):568–578
Kelly DP, Scarpulla RC (2004) Transcriptional regulatory circuits controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Genes Dev 18(4):357–368
Garnier A, Fortin D, Delomenie C, Momken I, Veksler V, Ventura-Clapier R (2003) Depressed mitochondrial transcription factors and oxidative capacity in rat failing cardiac and skeletal muscles. J Physiol 551(2):491–501
Ritz P, Berrut G (2005) Mitochondrial function, energy expenditure, aging and insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab 31:5S67–65S73
Savage DB, Petersen KF, Shulman GI (2005) Mechanisms of insulin resistance in humans and possible links with inflammation. Hypertension 45(5):828–833
J-a Kim, Wei Y, Sowers JR (2008) Role of mitochondrial dysfunction in insulin resistance. Circ Res 102(4):401–414
Zick Y (2005) Ser/Thr phosphorylation of IRS proteins: a molecular basis for insulin resistance. Sci STKE 2005(268):pe4. doi:10.1126/stke.2682005pe4
Mather KJ, Lteif A, Steinberg HO, Baron AD (2004) Interactions between endothelin and nitric oxide in the regulation of vascular tone in obesity and diabetes. Diabetes 53(8):2060–2066
Ting HH, Timimi FK, Boles KS, Creager SJ, Ganz P, Creager MA (1996) Vitamin C improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Investig 97(1):22
Chen H, Montagnani M, Funahashi T, Shimomura I, Quon MJ (2003) Adiponectin stimulates production of nitric oxide in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 278(45):45021–45026
Whaley-Connell A, Govindarajan G, Habibi J, Hayden MR, Cooper SA, Wei Y, Ma L, Qazi M, Link D, Karuparthi PR (2007) Angiotensin II-mediated oxidative stress promotes myocardial tissue remodeling in the transgenic (mRen2) 27 Ren2 rat. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293(1):E355–E363
Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, Chung W-J, Ahn JY, Seo Y-H, Choi IS, Shin EK (2005) Additive beneficial effects of fenofibrate combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of combined hyperlipidemia. J Am Coll Cardiol 45(10):1649–1653
Acknowledgments
Prof. Sarita Gupta was a visiting scientist in Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences. Nathalia Bernardes and Danielle da Silva Dias were exchange students, under the Canada-Brazil Training program. Dr. Pawan Singal is the holder of the Dr. Naranjan S. Dhalla Chair in Cardiovascular Research supported by St. Boniface Hospital and Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, T.P., Rawal, K., Bagchi, A.K. et al. Insulin resistance: an additional risk factor in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. Heart Fail Rev 21, 11–23 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-015-9515-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-015-9515-6