Abstract
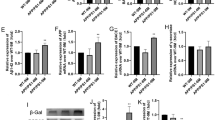
The activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway plays an important role in the neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In this study, we investigated the effects of JC-124, a rationally designed NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor, on AD-related deficits in CRND8 APP transgenic mice (TgCRND8). We first demonstrated increased formation and activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in TgCRND8 mice compared to non-transgenic littermate controls, which was inhibited by the treatment with JC-124. Importantly, JC-124 treatment led to decreased levels of Aβ deposition and decreased levels of soluble and insoluble Aβ1–42 in the brain of CRND8 mice which was accompanied by reduced β-cleavage of APP, reduced activation of microglia but enhanced astrocytosis. Oxidative stress was decreased and synaptophysin was increased in the CRND8 mice after JC-124 treatment, demonstrating a neuroprotective effect. Overall, these data demonstrated beneficial effects of JC-124 as a specific NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor in AD mouse model and supported the further development of NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors as a viable option for AD therapeutics.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81(2):741–766
Selkoe DJ, Hardy J (2016) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol Med 8(6):595–608
Strandberg TE, Tilvis RS (2000) C-reactive protein, cardiovascular risk factors, and mortality in a prospective study in the elderly. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20(4):1057–1060
Swardfager W, Lanctot K, Rothenburg L, Wong A, Cappell J, Herrmann N (2010) A meta-analysis of cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Psychol 68(10):930–941
Lim SL, Rodriguez-Ortiz CJ, Kitazawa M (2015) Infection, systemic inflammation, and Alzheimer’s disease. Microbes Infect 17(8):549–556. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2015.04.004
Weggen S, Eriksen JL, Das P, Sagi SA, Wang R, Pietrzik CU, Findlay KA, Smith TE et al (2001) A subset of NSAIDs lower amyloidogenic Abeta42 independently of cyclooxygenase activity. Nature 414(6860):212–216
Sastre M, Dewachter I, Landreth GE, Willson TM, Klockgether T, van Leuven F, Heneka MT (2003) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists modulate immunostimulated processing of amyloid precursor protein through regulation of beta-secretase. J Neurosci 23(30):9796–9804
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (2013) The amyloid cascade-inflammatory hypothesis of Alzheimer disease: implications for therapy. Acta Neuropathol 126(4):479–497
Heneka MT, O’Banion MK, Terwel D, Kummer MP (2010) Neuroinflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 117(8):919–947
Korvatska O, Leverenz JB, Jayadev S, McMillan P, Kurtz I, Guo X, Rumbaugh M, Matsushita M et al (2015) R47H variant of TREM2 associated with Alzheimer disease in a large late-onset family: clinical, genetic, and neuropathological study. JAMA Neurol 72(8):920–927. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.0979
Jonsson T, Stefansson H, Steinberg S, Jonsdottir I, Jonsson PV, Snaedal J, Bjornsson S, Huttenlocher J et al (2013) Variant of TREM2 associated with the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 368(2):107–116. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1211103
Freeman LC, Ting JP (2016) The pathogenic role of the inflammasome in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem 136(Suppl 1):29–38. doi:10.1111/jnc.13217
Schroder K, Tschopp J (2010) The inflammasomes. Cell 140(6):821–832
Shao BZ, Xu ZQ, Han BZ, Su DF, Liu C (2015) NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: a review. Front Pharmacol 6:262
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Stutz A, Delekate A, Schwartz S, Vieira-Saecker A, Griep A, Axt D et al (2013) NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 493(7434):674–678. doi:10.1038/nature11729
Saresella M, La Rosa F, Piancone F, Zoppis M, Marventano I, Calabrese E, Rainone V, Nemni R et al (2016) The NLRP3 and NLRP1 inflammasomes are activated in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 11:23
Halle A, Hornung V, Petzold GC, Stewart CR, Monks BG, Reinheckel T, Fitzgerald KA, Latz E et al (2008) The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate immune response to amyloid-beta. Nat Immunol 9(8):857–865
Couturier J, Stancu IC, Schakman O, Pierrot N, Huaux F, Kienlen-Campard P, Dewachter I, Octave JN (2016) Activation of phagocytic activity in astrocytes by reduced expression of the inflammasome component ASC and its implication in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Neuroinflammation 13:20
Marchetti C, Toldo S, Chojnacki J, Mezzaroma E, Liu K, Salloum FN, Nordio A, Carbone S et al (2015) Pharmacologic inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome preserves cardiac function after ischemic and nonischemic injury in the mouse. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 66(1):1–8. doi:10.1097/FJC.0000000000000247
Chishti MA, Yang DS, Janus C, Phinney AL, Horne P, Pearson J, Strome R, Zuker N et al (2001) Early-onset amyloid deposition and cognitive deficits in transgenic mice expressing a double mutant form of amyloid precursor protein 695. J Biol Chem 276(24):21562–21570
Ye H, Jalini S, Mylvaganam S, Carlen P (2010) Activation of large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels depresses basal synaptic transmission in the hippocampal CA1 area in APP (swe/ind) TgCRND8 mice. Neurobiol Aging 31(4):591–604. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.05.012
Dudal S, Krzywkowski P, Paquette J, Morissette C, Lacombe D, Tremblay P, Gervais F (2004) Inflammation occurs early during the Abeta deposition process in TgCRND8 mice. Neurobiol Aging 25(7):861–871. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.08.008
Velasco PT, Heffern MC, Sebollela A, Popova IA, Lacor PN, Lee KB, Sun X, Tiano BN et al (2012) Synapse-binding subpopulations of Abeta oligomers sensitive to peptide assembly blockers and scFv antibodies. ACS Chem Neurosci 3(11):972–981. doi:10.1021/cn300122k
Wang C, Zhang F, Jiang S, Siedlak SL, Shen L, Perry G, Wang X, Tang B et al (2016a) Estrogen receptor-alpha is localized to neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep 6:20352. doi:10.1038/srep20352
Gerenu G, Liu K, Chojnacki JE, Saathoff JM, Martinez-Martin P, Perry G, Zhu X, Lee HG et al (2015) Curcumin/melatonin hybrid 5-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-3-oxo-pentanoic acid [2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)-ethyl]-amide ameliorates AD-like pathology in the APP/PS1 mouse model. ACS Chem Neurosci 6(8):1393–1399
Wang W, Wang X, Fujioka H, Hoppel C, Whone AL, Caldwell MA, Cullen PJ, Liu J et al (2016b) Parkinson’s disease-associated mutant VPS35 causes mitochondrial dysfunction by recycling DLP1 complexes. Nat Med 22(1):54–63. doi:10.1038/nm.3983
Shankar GM, Leissring MA, Adame A, Sun X, Spooner E, Masliah E, Selkoe DJ, Lemere CA et al (2009) Biochemical and immunohistochemical analysis of an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model reveals the presence of multiple cerebral Abeta assembly forms throughout life. Neurobiol Dis 36(2):293–302. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.021
Li N, Liu K, Qiu Y, Ren Z, Dai R, Deng Y, Qing H (2016) Effect of presenilin mutations on APP cleavage; insights into the pathogenesis of FAD. Front Aging Neurosci 8:51
Barnwell E, Padmaraju V, Baranello R, Pacheco-Quinto J, Crosson C, Ablonczy Z, Eckman E, Eckman CB et al (2014) Evidence of a novel mechanism for partial gamma-secretase inhibition induced paradoxical increase in secreted amyloid beta protein. PLoS One 9(3):e91531
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Tago H, McGeer EG (1987) Reactive microglia in patients with senile dementia of the Alzheimer type are positive for the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR. Neurosci Lett 79(1–2):195–200
Styren SD, Civin WH, Rogers J (1990) Molecular, cellular, and pathologic characterization of HLA-DR immunoreactivity in normal elderly and Alzheimer’s disease brain. Exp Neurol 110(1):93–104
Bellucci A, Westwood AJ, Ingram E, Casamenti F, Goedert M, Spillantini MG (2004) Induction of inflammatory mediators and microglial activation in mice transgenic for mutant human P301S tau protein. Am J Pathol 165(5):1643–1652
Janelsins MC, Mastrangelo MA, Oddo S, LaFerla FM, Federoff HJ, Bowers WJ (2005) Early correlation of microglial activation with enhanced tumor necrosis factor-alpha and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression specifically within the entorhinal cortex of triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease mice. J Neuroinflammation 2:23
Heneka MT, Golenbock DT, Latz E (2015) Innate immunity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Immunol 16(3):229–236
Wyss-Coray T, Loike JD, Brionne TC, Lu E, Anankov R, Yan F, Silverstein SC, Husemann J (2003) Adult mouse astrocytes degrade amyloid-beta in vitro and in situ. Nat Med 9(4):453–457
Terwel D, Steffensen KR, Verghese PB, Kummer MP, Gustafsson JA, Holtzman DM, Heneka MT (2011) Critical role of astroglial apolipoprotein E and liver X receptor-alpha expression for microglial Abeta phagocytosis. J Neurosci 31(19):7049–7059
Bonda DJ, Wang X, Lee HG, Smith MA, Perry G, Zhu X (2014) Neuronal failure in Alzheimer’s disease: a view through the oxidative stress looking-glass. Neurosci Bull 30(2):243–252. doi:10.1007/s12264-013-1424-x
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Latz E (2014) Innate immune activation in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev 14(7):463–477
Chen L, Na R, Boldt E, Ran Q (2015) NLRP3 inflammasome activation by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species plays a key role in long-term cognitive impairment induced by paraquat exposure. Neurobiol Aging 36(9):2533–2543. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.05.018
Arendt T (2009) Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 118(1):167–179
Dempsey C, Rubio Araiz A, Bryson KJ, Finucane O, Larkin C, Mills EL, Robertson AA, Cooper MA et al (2016) Inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome with MCC950 promotes non-phlogistic clearance of amyloid-beta and cognitive function in APP/PS1 mice. Brain Behav Immun. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2016.12.014
Daniels MJ, Rivers-Auty J, Schilling T, Spencer NG, Watremez W, Fasolino V, Booth SJ, White CS et al (2016) Fenamate NSAIDs inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome and protect against Alzheimer’s disease in rodent models. Na Commun 7:12504. doi:10.1038/ncomms12504
Sastre M, Dewachter I, Rossner S, Bogdanovic N, Rosen E, Borghgraef P, Evert BO, Dumitrescu-Ozimek L et al (2006) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs repress beta-secretase gene promoter activity by the activation of PPARgamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(2):443–448
Kummer MP, Vogl T, Axt D, Griep A, Vieira-Saecker A, Jessen F, Gelpi E, Roth J et al (2012) Mrp14 deficiency ameliorates amyloid beta burden by increasing microglial phagocytosis and modulation of amyloid precursor protein processing. J Neurosci 32(49):17824–17829
Kummer MP, Hermes M, Delekarte A, Hammerschmidt T, Kumar S, Terwel D, Walter J, Pape HC et al (2011) Nitration of tyrosine 10 critically enhances amyloid beta aggregation and plaque formation. Neuron 71(5):833–844
Vom Berg J, Prokop S, Miller KR, Obst J, Kalin RE, Lopategui-Cabezas I, Wegner A, Mair F et al (2012) Inhibition of IL-12/IL-23 signaling reduces Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and cognitive decline. Nat Med 18(12):1812–1819
Pihlaja R, Koistinaho J, Malm T, Sikkila H, Vainio S, Koistinaho M (2008) Transplanted astrocytes internalize deposited beta-amyloid peptides in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Glia 56(2):154–163
Mucke L, Selkoe DJ (2012) Neurotoxicity of amyloid beta-protein: synaptic and network dysfunction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2(7):a006338
DeKosky ST, Scheff SW (1990) Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer’s disease: correlation with cognitive severity. Ann Neurol 27(5):457–464
Tong L, Prieto GA, Kramar EA, Smith ED, Cribbs DH, Lynch G, Cotman CW (2012) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent synaptic plasticity is suppressed by interleukin-1beta via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Neurosci 32(49):17714–17724
Youm YH, Grant RW, McCabe LR, Albarado DC, Nguyen KY, Ravussin A, Pistell P, Newman S et al (2013) Canonical Nlrp3 inflammasome links systemic low-grade inflammation to functional decline in aging. Cell Metab 18(4):519–532
Acknowledgements
The work was supported in part by the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health [R01NS083385 and RFAG049479 to X.Z. and R01AG041161 to S.Z.]; Alzheimer’s Association [AARG-16-443584 to X.Z.]; Dr. Robert M. Kohrman Memorial Fund to X.Z., Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation [20150601 to S.Z.]; and the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China [81100594 to J.Y.].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, J., Zhao, F., Chojnacki, J.E. et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitor Ameliorates Amyloid Pathology in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 55, 1977–1987 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0467-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0467-9