Abstract
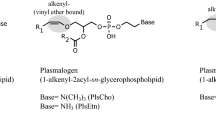
Studies have demonstrated alterations in brain membrane phospholipid metabolite levels in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The changes in phospholipid metabolite levels correlate with neuropathological hallmarks of the disease and measures of cognitive decline. This 31P nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of Folch extracts of autopsy material reveals significant reductions in AD brain levels of phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn) and phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns), and elevations in sphingomyelin (SPH) and the plasmalogen derivative of PtdEtn. In the superior temporal gyrus, there were additional reductions in the levels of diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG) and phosphatidic acid (PtdA). The findings are present in 3/3 as well as 3/4 and 4/4 apolipoprotein E (apoE) genotypes. The AD findings do not appear to reflect non-specific neurodegeneration or the presence of gliosis. The present findings could possibly contribute to an abnormal membrane repair in AD brains which ultimately results in synaptic loss and the aggregation of Aβ peptide.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Pettegrew, J. W., Minshew, N. J., Cohen, M. M., Kopp, S. J., and Glonek, T. 1984. P-31 NMR changes in Alzheimer's and Huntington's disease brain (abstract). Neurology 34(Suppl 1):281.
Pettegrew, J. W., Withers, G., Panchalingam, K., and Post, J. F. 1987. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy of brain in aging and Alzheimer's disease. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 24:261–268.
Pettegrew, J. W., Moossy, J., Withers, G., McKeag, D., and Panchalingam, K. 1988. 31P Nuclear Magnetic Resonance study of the brain in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 47:235–248.
Brown, G. G., Levine, S. R., Gorell, J. M., Pettegrew, J. W., Gdowski, J. W., Bueri, J. A., Helpern, J. A., and Welch, K. M. 1989. In vivo 31P NMR profiles of Alzheimer's disease and multiple subcortical infarct dementia. Neurology 39:1423–1427.
Nitsch, R. M., Blusztajn, J. K., Pittas, A. G., Slack, B. E., Growdon, J. H., and Wurtman, R. J. 1992. Evidence for a membrane defect in Alzheimer disease brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:1671–1675.
Smith, C. D., Gallenstein, L. G., Layton, W. J., Kryscio, R. J., and Markesbery, W. R. 1993. 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in Alzheimer's and Pick's disease. Neurobiol. Aging 14:85–92.
Cuenod, C.-A., Kaplan, D. B., Michot, J.-L., Jehenson, P., Leroy-Willig, A., Forette, F., Syrota, A., and Boller, F. 1995. Phospholipid abnormalities in early Alzheimer's disease. Arch. Neurol. 52:89–94.
Pettegrew, J. W., Panchalingam, K., Klunk, W. E., McClure, R. J., and Muenz, L. R. 1994. Alterations of cerebral metabolism in probable Alzheimer's disease: A preliminary study. Neurobiol. Aging 15:117–132.
Klunk, W. E., Panchalingam, K., McClure, R. J., and Pettegrew, J. W. 1996. Quantitative 1H and 31P MRS of PCA extracts of postmortem Alzheimer's disease brain. Neurobiol. Aging 17:349–357.
Pettegrew, J. W., Panchalingam, K., Withers, G., McKeag, D., and Strychor, S. 1990. Changes in brain energy and phospholipid metabolism during development and aging in the Fischer 344 rat. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 49:237–249.
Vance, D. E. 1991. Phospholipid metabolism and cell signalling in eucaryotes. Pages 205–240, in Vance, D. E., and Vance, J. (eds.), Biochemistry of lipids, lipoproteins and membranes, Volume 20, Elsevier, New York.
Pettegrew, J. W., McClure, R. J., Keshavan, M. S., Minshew, N. J., Panchalingam, K., and Klunk, W. E. 1997. 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of developing brain. Pages 71–92, in Keshavan, M. S., and Murray, R. M. (eds.), Neurodevelopement & Adult Psychopathology, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Geddes, J. W., Panchalingam, K., Keller, J. N., and Pettegrew, J. W. 1997. Elevated phosphocholine and phosphatidyl choline following rat entorhinal cortex lesions. Neurobiol. Aging 18:305–308.
Kanfer, J. N., Pettegrew, J. W., Moossy, J., and McCartney, D. G. 1993. Alterations of selected enzymes of phospholipid metabolism in Alzheimer's disease brain tissue as compared to non-Alzheimer's disease controls. Neurochem. Res. 18:331–334.
Pettegrew, J. W., Panchalingam, K., Moossy, J., Martinez, J., Rao, G., and Boller, F. 1988. Correlation of phosphorus-31 magnetic resonance spectroscopy and morphologic findings in Alzheimer's disease. Arch. Neurol. 45:1093–1096.
Klunk, W. E., Xu, C. J., McClure, R. J., Panchalingam, K., Stanley, J. A., and Pettegrew, J. W. 1997. Aggregation of β-amyloid peptide is promoted by membrane phospholipid metabolites elevated in Alzheimer's disease brain. J. Neurochem. 69:266–272.
Pettegrew, J. W., Klunk, W. E., Kanal, E., Panchalingam, K., and McClure, R. J. 1995. Changes in brain membrane phospholipid and high-energy phosphate metabolism precede dementia. Neurobiol. Aging 16:973–975.
Pettegrew, J. W., Klunk, W. E., Panchalingam, K., McClure, R. J., and Stanley, J. A. 1997. Magnetic resonance spectroscopic changes in Alzheimer's disease. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 826:282–306.
Mason, R. P., Shoemaker, W. J., Shajenko, L., Chambers, T. E., and Herbette, G. 1992. Structural changes in Alzheimer's disease brain membrane mediated by alteration in cholesterol. Neurobiol. Aging 13:413–419.
Mahley, R. W. 1988. Apolipoprotein E: Cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science 240:622–630.
Patrick, G. N., Zukerberg, L., Nikolic, M., de la Monte, S., Dikkes, P., and Tsai, L.-H. 1999. Conversion of p35 to p25 deregulates Cdk5 activity and promotes neurodegeneration. Nature 402:615–622.
Aronson, M. K., Ooi, W. L., Morgenstern, H., Hafner, M. S., Masur, D., and Crystal H. 1990. Women, myocardial infraction, and dementia in the very old. Neurology 40:1102–1106.
Sparks, D. L., Hunsaker, J. C., III, Scheff, S. W., Kryscio, R. J., Henson, J. L., and Markesbery, W. R. 1990. Cortical senile plaques in coronary artery diseases, aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Aging 11:601–607.
Khachaturian, Z. S. 1985. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch. Neurol. 42:1097–1105.
Moossy, J., Zubenko, G., Martinez, J., Rao, G. R., Kopp, U., and Hanin, I. 1988. Bilateral symmetry of morphologic lesions in Alzheimer's disease. Arch. Neurol. 45:251–254.
Meneses, P. and Glonek, T. 1988. High resolution 31P NMR of extracted phospholipids. J. Lipid Res. 29:679–690.
Pettegrew, J. W., Panchalingam, K., Levine, J., McClure, R. J., Gershon, S., and Yao, J. K. 2001. Chronic myo-inositol increases rat brain phosphatidylethanolamine plasmalogen. Biol. Psychiatry 49:444–453.
Steel, R. G. D. and Torrie, J. H. 1980. Principles and Procedures of Statistics a Biometrical Approach, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Klunk, W. E., Xu, C. J., Panchalingam, K., McClure, R. J., and Pettegrew, J. W. 1994. Analysis of magnetic resonance spectra by mole percent: Comparison to absolute units. Neurobiol. Aging 15:133–140.
Simons, K. and Ikonen, E. 1997. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 387:569–572.
Harder, T. and Simons, K. 1997. Caveolae, DIGs, and the dynamics of sphingolipid-cholesterol microdomains. Curr. Opinion Cell Biol. 9:534–542.
Pettegrew, J. W., Klunk, W. E., Panchalingam, K., McClure, R. J., and Stanley, J. A. 2000. Molecular insights into neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Bull. 53:455–469.
Maulik, P. R. and Shipley, G. G. 1996. Interactions of N-stearoyl sphingomyelin with cholesterol and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine in bilayer membranes. Biophys. J. 70:2256–2265.
Scott, H. L., Jakobsson, E., Mashl, J., and Chiu, S.-W. 2001. Combined molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulation of sphingomyelin lipid bylayers (abstract). Biophys. J. 80(Suppl):525a.
Ballou, L. R., Laulederkind, S. J., Rosloniec, E. F., and Raghow, R. 1996. Ceramide signalling and the immune response. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1301:273–287.
Pyne, S., Tolan, D. G., Conway, A. M., and Pyne, N. 1997. Sphingolipids as differential regulators of cellular signalling processes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 25:549–556.
Haimovitz-Friedman, A., Kolesnick, R. N., and Fuks, Z. 1997. Ceramide signaling in apoptosis. Br. Med. Bull. 53:539–553.
Perry, D. K. and Hannun, Y. A. 1998. The role of ceramide in cell signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1436:233–243.
Merrill, A. H. J., Morgan, E. T., Nikolova-Karakashian, M., and Stewart, J. 1999. Sphingomyelin hydrolysis and regulation of the expression of the gene for cytochrome P450. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 27:383–387.
Levade, T. and Jaffrezou, J. P. 1999. Signalling sphingomyelinases: which, where, how and why? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1438:1–17.
Hannun, Y. A. and Luberto, C. 2000. Ceramide in the eukaryotic stress response. Trends Cell Biol. 10:73–80.
Gross, R. W. 1984. High plasmalogen and arachidonic acid content of canine myocardial sarcolemma: a fast atom bombardment mass spectroscopic and gas chromatography-mass spectroscopic characterization. Biochemistry 23:158–165.
Diagne, A., Fauvel, J., Record, M., Chap, H., and Douste-Blazy, L. 1984. Studies on ether phospholipids II. Comparative composition of various tissues from human, rat and guinea pig. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 793:221–231.
Lohner, K., Balgavy, P., Hermetter, A., Paltauf, F., and Laggner, P. 1991. Stabilization of non-bilayer structures by the etherlipid ethanolamine plasmalogen. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1061:132–140.
Ginsberg, L., Xuereb, J. H., and Gershfeld, N. L. 1998. Membrane instability, plasmalogen content, and Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 70:2533–2538.
Kaufman, A. E., Goldfine, H., Narayan, O., and Gruner, S. M. 1990. Physical studies on the membranes and lipids of plasmalogen-deficient Megasphaera elsdenii. Chem. Phys. Lipids 55:41–48.
Lohner, K. 1996. Is the high propensity of ethanolamine plasmalogens to form non-lamellar lipid structures manifested in the properties of biomembranes? Chem. Phys. Lipids 81: 167–184.
Glaser, P. E. and Gross, R. W. 1994. Plasmenylethanolamine facilitates rapid membrane fusion: a stopped-flow kinetic investigation correlating the propensity of a major plasma membrane constituent to adopt an HII phase with its ability to promote membrane fusion. Biochemistry 33:5805–5812.
Farooqui, A. A., Rapoport, S. I., and Horrocks, L. A. 1997. Membrane phospholipid alterations in Alzheimer's disease: deficiency of ethanolamine plasmalogens. Neurochem. Res. 22: 523–527.
Schu, P. V., Takegawa, K., Fry, M. J., Stack, J. H., Waterfield, M. D., and Emr, S. D. 1993. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase encoded by yeast VPS34 gene essential for protein sorting. Science 260:88–91.
Qiao, L., Nan, F., Kunkel, M., Gallegos, A., Powis, G., and Kozikowski, A. P. 1998. 3-Deoxy-D-myo-inositol 1-phosphate, 1-phosphonate, and ether lipid analogues as inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling and cancer cell growth. J. Med. Chem. 41:3303–3306.
Merrill, A. H. J. and Schroeder, J. J. 1993. Lipid modulation of cell function. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 13:539–559.
Turini, M. E. and Holub, B. J. 1994. The cleavage of plasmenylethanolamine by phospholipase A2 appears to be mediated by the low affinity binding site of the TxA2/PGH2 receptor in U46619-stimulated human platelets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1213:21–26.
Gross, R. W. 1985. Identification of plasmalogen as the major phospholipid constituent of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry 24:1662–1668.
Paltauf, F. 1994. Ether lipids in biomembranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 74:101–139.
Yavin, E. and Gatt, S. 1972. Oxygen-dependent cleavage of the vinyl-ether linkage of plasmologens. 1. Cleavage by rat-brain supernatant. Eur. J. Biochem. 25:431–436.
Reiss, D., Beyer, K., and Engelmann, B. 1997. Delayed oxidative degradation of polyunsaturated diacyl phospholipids in the presence of plasmalogen phospholipids in vitro. Biochem. J. 323:807–814.
Engelmann, B., Brautigam, C., and Thiery, J. 1994. Plasmalogen phospholipids as potential protectors against lipid peroxidation of low density lipoproteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 204:1235–1242.
Farooqui, A. A., Yang, H. C., and Horrocks, L. A. 1995. Plasmalogens, phospholipases A2 and signal transduction. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 21:152–161.
Holub, B. J. 1986. Metabolism and function of myo-inositol and inositol phospholipids. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 6:563–597.
Klunk, W. E., Panchalingam, K., McClure, R. J., Stanley, J. A., and Pettegrew, J. W. 1998. Metabolic alterations in postmortem Alzheimer's disease brain are exaggerated by Apo-E4. Neurobiol. Aging 19:511–515.
Schlame, M., Rua, D., and Greenberg, M. L. 2000. The biosynthesis and functional role of cardiolipin. Prog. Lipid Res. 39:257–288.
Lehninger, A. L., Nelson, D. L., and Cox, M. M. 1993. Principles of Biochemistry, Worth Publishers, New York.
Jope, R. S., Song, L., and Powers, R. E. 1997. Cholinergic activation of phosphoinositide signaling is impaired in Alzheimer's disease brain. Neurobiol. Aging 18:111–120.
Fowler, C. J. 1997. The role of the phosphoinositide signalling system in the pathgenesis of sporadic Alzheimer's disease: a hypothesis. Brain Res. Rev. 25:373–380.
McAuley, K. E., Fyfe, P. K., Ridge, J. P., Isaacs, N. W., Cogdell, R. J., and Jones, M. R. 1999. Structural details of an interaction between cardiolipin and an integral membrane protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:14706–14711.
Robinson, N. C. 1993. Functional binding of cardiolipin to cytochrome c oxidase. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 25:153–163.
Kish, S., Bergeron, C., Rajput, A., Dozic, S., Mastrogracosno, F., Chong, L. J., Wilson, J. M., DiStefano, L. M., and Nobregia, J. N. 1992. Brain cytochrome oxidase in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 59:776–779.
Sims, N. R., Finegan, J. M., Blass, J. P., Bowen, D. M., and Neary, D. 1987. Mitochondrial function in brain tissue in primary degenerative dementia. Brain Res. 436:30–38.
Chauhan, A., Ray. I., and Chauhan, V. P. S. 2000. Interaction of amyloid beta-protein with anionic phospholipids: Possible involvement of Lys28 and C-terminus aliphatic amino acids. Neurochem. Res. 25:423–429.
Vance, J. E., Campenot, R. B., and Vance, D. E. 2000. The synthesis and transport of lipids of axonal growth and nerve regeneration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1486:84–96.
Hirokawa, N. 1998. Kinesin and dynein superfamily proteins and teh mechanism of organelle transport. Science 279:519–526.
Ginsberg, L., Rafique, S., Xuereb, J. H., Rapoport, S. I., and Gershfeld, N. L. 1995. Disease and anatomic specificity of ethanolamine plasmalogen deficiency in Alzheimer's disease brain. Brain Res. 698:223–226.
Prasad, M. R., Lovell, M. A., Yatin, M., Dhillon, H., and Markesbery, W. R. 1998. Regional membrane phospholipid alterations in Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem. Res. 23:81–88.
Wells, K., Farooqui, A. A., Liss, L., and Horrocks, L. A. 1995. Neural membrane phospholipids in Alzheimer disease. Neurochem. Res. 20:1329–1333.
Guan, Z., Wang, Y., Cairns, N. J., Lantos, P. L., Dallner, G., and Sindelar, P. J. 1999. Decrease and structural modifications of phosphatidylethanolamine plasmalogen in the brain with Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 58:740–747.
McIlwain, H. and Bachelard, H. S. 1985. Biochemistry and the Central Nervous System, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pettegrew, J.W., Panchalingam, K., Hamilton, R.L. et al. Brain Membrane Phospholipid Alterations in Alzheimer's Disease. Neurochem Res 26, 771–782 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011603916962
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011603916962