Abstract
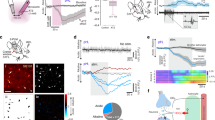
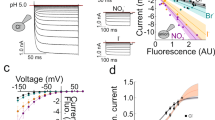
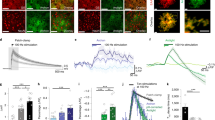
GLUTAMATE uptake into glial cells helps to keep the brain extracellular glutamate concentration, [glu]0, below levels that kill neurons. Uptake is powered1–4 by the transmembrane gradients of Na+, K+ and pH. When the extracellular [K+] rises in brain ischaemia, uptake reverses, releasing glutamate into the extracellular space5,6. Here we show, by monitoring glutamate transport electrically and detecting released glutamate with ion channels in neurons placed outside glial cells, that a raised [H+] inhibits both forward and reversed glutamate uptake. No electroneutral reversed uptake was detected, contradicting the idea7 that forward and reversed uptake differ fundamentally. Suppression of reversed uptake by the low pH occurring in ischaemia8,9 will slow the Ca2+-independent release of glutamate10 which can raise [glu]0 to a neurotoxic level 11,12, and will thus protect the brain during a transient loss of blood supply.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanner, B. I. & Sharon, I. Biochemistry 17, 3949–3953 (1978).
Bouvier, M., Szatkowski, M., Amato, A. & Attwell, D. Nature 360, 471–474 (1992).
Erecinska, M., Wantorsky, D. & Wilson, D. F. J. biol. Chem. 258, 9069–9077 (1983).
Nelson, P. J., Dean, G. E., Aronson, P. S. & Rudnick, G. Biochemistry 22, 5459–5463 (1983).
Szatkowski, M., Barbour, B. & Attwell, D. Nature 348, 443–446 (1990).
Madl, J. E. & Burgesser, K. J. Neurosci. 13, 4429–4444 (1993).
Schwartz, E. A. & Tachibana, M. J. Physiol., Lond. 426, 43–80 (1990).
Silver, I. A. & Erecinska, M. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 12, 759–772 (1992).
Mutch, W. A. C. & Hansen, A. J. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 4, 17–27 (1984).
Ikeda, M., Nakawaza, T., Abe, K., Kaneko, T. & Yamatsu, K. Neurosci. Lett. 96, 202–206 (1989).
Szatkowski, M. & Attwell, D. Trends Neurosci. 17, 359–365 (1994).
Choi, D. W. & Rothman, S. M. A. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 171–182 (1990).
Brew, H. & Attwell, D. Nature 327, 707–709 (1987).
Kanai, Y. et al. J. biol. Chem. 270, 16561–16568 (1995).
Storck, T., Schulte, S., Hofmann, K. & Stoffel, W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 10955–10959 (1992).
Pines, G. et al. Nature 360, 464–467 (1992).
Kanai, Y. & Hediger, M. A. Nature 360, 467–471 (1992).
Attwell, D. & Mobbs, P. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 4, 353–359 (1994).
Schwartz, E. A. Neuron 10, 1141–1149 (1993).
Barbour, B., Brew, H. & Attwell, D. J. Physiol., Lond. 436, 169–193 (1991).
Sarantis, M., Everett, K. & Attwell, D. Nature 332, 451–453 (1988).
Eliasof, S. & Werblin, F. S. J. Neurosci. 13, 402–411 (1993).
Fairman, W. A., Vandenberg, R. J., Arriza, J. L., Kavanaugh, M. P. & Amara, S. G. Nature 375, 599–603 (1995).
Attwell, D., Barbour, B. & Szatkowski, M. Neuron 11, 401–407 (1993).
Yamada, K. A. & Tang, C.-M. J. Neurosci. 13, 3904–3915 (1993).
Nadeau, S. E. J. Fam. Pract. 38, 495–504 (1994).
Lord, R. S. Aust. N. Z. J. Ophthal. 18, 299–305 (1990).
Traynelis, S. F. & Cull-Candy, S. G. Nature 345, 347–350 (1990).
Mobbs, P., Brew, H. & Attwell, D. Brain Res. 460, 235–245 (1988).
Newman, E. A. & Odette, L. L. J. Neurophysiol. 51, 164–182 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Billups, B., Attwell, D. Modulation of non-vesicular glutamate release by pH. Nature 379, 171–174 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/379171a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/379171a0
This article is cited by
-
Different effects of monophasic pulses and biphasic pulses applied by a bipolar stimulation electrode in the rat hippocampal CA1 region
BioMedical Engineering OnLine (2021)
-
Neurobiology, Functions, and Relevance of Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters (EAATs) to Treatment of Refractory Epilepsy
CNS Drugs (2020)
-
Glutamate Transporters (EAAT-1–3) as a Factor in the Pathogenesis and a Potential Therapeutic Target in Epilepsy
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2020)
-
Are glutamate transporters neuroprotective or neurodegenerative during cerebral ischemia?
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2019)
-
Regenerative Glutamate Release by Presynaptic NMDA Receptors Contributes to Spreading Depression
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (2013)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.