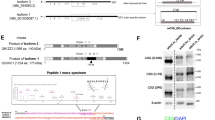
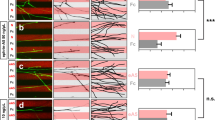
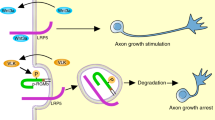
Abstract
Neuregulins (also called ARIA1, GGF2, heregulin3 or NDF4) are a group of polypeptide factors that arise from alternative RNA splicing of a single gene. Through their interaction with the ErbB family of receptors (ErbB2, ErbB3 and ErbB4), neuregulins help to regulate cell growth and differentiation in many tissues5–7. Here we report the cloning of a second neuregulin-like gene, neuregulin-2. The encoded product of the neuregulin-2 gene has a motif structure similar to that of neuregulins and an alternative splicing site in the epidermal growth factor(EGF)-like domain gives rise to two isoforms (α and β). Northern blot and in situ hybridization analysis of adult rat tissues indicate that expression of neuregulin-2 is highest in the cerebellum, and the expression pattern is different from that of neuregulins. Recombinant neuregulin-2β induces the tyrosine-phosphorylation of ErbB2, ErbB3 and ErbB4 in cell lines expressing all of these ErbB-family receptors. However, in cell lines with defined combinations of ErbBs, neuregulin-2βonly activates those with ErbB3 and/or ErbB4, suggesting that signalling by neuregulin-2 is mediated by ErbB3 and/or ErbB4 receptors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Falls, D. L., Rosen, K. M., Corfas, G., Lane, W. S. & Fischbach, G. D. ARIA, a protein that stimulates acetylcholine receptor synthesis, is a member of the neu ligand family. Cell 72, 801–815 (1993).
Marchionni, M. A. et al. Glial growth factors are alternatively spliced ErbB2 ligands expressed in the nervous system. Nature 362, 312–318 (1993).
Holmes, W. E. et al. Identification of heregulin, a specific activator of p185erbB2. Science 256, 1205–1210 (1992).
Wen, D. et al. Neu differentiation factor; a transmembrane glycoprotein containing an EGF domain and an immunoglobulin homology unit. Cell 69, 559–572 (1992).
Marchionni, M. A. Neu tack on neuregulin. Nature 378, 334–335 (1995).
Lemke, G. Recitative and ARIA. Nature 362, 291–292 (1993).
Carraway, K. L. & Burden, S. J. Neuregulins and their receptors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 5, 606–612 (1995).
Plowman, G. D. et al. Ligand-specific activation of HER4/pl80erbB4, a fourth member of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 1746–1750 (1993).
Kraus, M. H., Issing, W., Miki, T., Popescu, N. C. & Aaronson, S. A. Isolation and characterization of ErbB3, a third member of the ErbB/epidermal growth factor receptor family: evidence for over-expression in a subset of human mammary tumors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 9193–9197 (1989).
Schechter, A. L. et al. The neu oncogene: an erbB-related gene encoding a 185,000-Mr tumour antigen. Nature 312, 513–516 (1984).
Hynes, N. E. & Stern, D. F. The biology of erbB/neu//Her-2 and its role in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1198, 165–184 (1994).
Sliwkowski, M. X. et al. Coexpression of erbB2 and erbB3 proteins reconstitutes a high affinity receptor for heregulin. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 14661–14665 (1994).
Plowman, G. D. et al. Heregulin induces tyrosine phosphorylation of HER4/p180erbB4. Nature 366, 473–475 (1993).
Meyer, D. & Birchmeier, C. Multiple essential functions of neuregulin in development. Nature 378, 386–390 (1995).
Gassmann, M. et al. Aberrant neural and cardiac development in mice lacking the ErbB4 neuregulin receptor. Nature 378, 390–394 (1995).
Lee, K. F. et al. Requirement for neuregulin receptor erbB2 in neural and cardiac development. Nature 378, 394–398 (1995).
Chang, H. & Gilbert, W. Cloning and characterization of a new factor related to ARIA/NDF/GGF. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 20, 1694 (1994).
Williams, A. F. & Barclay, A. N. The immunoglobulin superfamily—domains for cell surface recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 6, 381–405 (1988).
Carpenter, G. & Cohen, S. Epidermal growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 7709–7712 (1990).
Wen, D. et al. Structural and functional aspects of the multiplicity of Neu differentiation factors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 1909–1919 (1994).
Corfas, G., Rosen, K. M., Aratake, H., Krauss, R. & Fischbach, G. D. Differential expression of ARIA isoforms in the rat brain. Neuron 14, 103–115 (1995).
Wallasch, C. et al. Heregulin-dependent regulation of HER2/neu oncogenic signaling by hetero-dimerization with HER3. EMBO J. 14, 4267–4275 (1995).
Beerli, R. R. et al. Neu differentiation factor activation of ErbB-3 and ErbB-4 is cell specific and displays a differential requirement for ErbB-2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 6496–6505 (1995).
Riese, D. J. et al. Betacellulin activates the epidermal growth factor receptor and erbB-4, and induces cellular response patterns distinct from those stimulated by epidermal growth factor or neuregulin-β. Oncogene 12, 345–353 (1996).
Schaeren-Wiemers, N. & Gerfin-Moser, A. A single protocol to detect transcripts of various types and expression levels in neural tissue and cultured cells: in situ hybridization using digoxigenin-labelled cRNA probes. Histochemistry 100, 431–440 (1993).
Riese, D. J., van Raaij, T. M., Plowman, G. D., Andrews, G. C. & Stern, D. F. The cellular response to neuregulins is governed by complex interactions of the erbB receptor family. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 5770–5776 (1995).
DiGiovanna, M. P. & Stern, D. F. Activation state-specific monoclonal antibody detects tyrosine phosphorylated p185neu/erbB-2 in a subset of human breast tumors overexpressing this receptor. Cancer Res. 55, 1946–1955 (1995).
Dobashi, Y. & Stern, D. F. Membrane-anchored forms of EGF stimulate focus formation and intercellular communication. Oncogene 6, 1151–1159 (1991).
Barbacci, E. G. et al. The structural basis for the specificity of epidermal growth factor and heregulin binding. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 9585–9589 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, H., Riese II, D., Gilbert, W. et al. Ligands for ErbB-family receptors encoded by a neuregulin-like gene. Nature 387, 509–512 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/387509a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/387509a0
This article is cited by
-
Fluorescent in situ hybridization has limitations in screening NRG1 gene rearrangements
Diagnostic Pathology (2024)
-
In vitro gene regulatory networks predict in vivo function of liver
BMC Systems Biology (2010)
-
The Neuregulin Family of Genes and their Multiple Splice Variants in Breast Cancer
Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia (2008)
-
Anti-erbB2 treatment induces cardiotoxicity by interfering with cell survival pathways
Breast Cancer Research (2006)
-
Neuregulins 1–4 are expressed in the cytoplasm or nuclei of ductal carcinoma (in situ) of the human breast
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2006)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.