Abstract
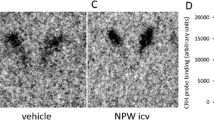
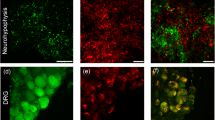
Neuromedin U (NMU) is a peptide isolated from the porcine spinal cord. Recently, two receptors for NMU have been identified and characterized. A recent study indicated that NMU is an anorectic chemical in the brain. The present study shows that NMU has an action in the brain to inhibit food intake in rats. Intracerebroventricular injection of NMU inhibited dark-phase feeding. Animals injected with NMU showed a strong increase in Fos-immunoreactive nuclei in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and supraoptic nucleus (SON) of the hypothalamus, and in the parabrachial nucleus of the brain stem. Double immunohistochemistry revealed that a high number of oxytocin-immunoreactive neurons in the PVN and SON contained Fos after intracerebroventricular injection of NMU. In addition, a small proportion of vasopressinergic cells within the PVN and SON were found to contain Fos. The effect of NMU on the hypothalamus and brain stem contributes to the inhibitory effects of NMU on feeding behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Minamino, N., Kangawa, K., and Matsuo, H. (1985). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 130, 1078–1085.
Conlon, J. M., Domin, J., Thim, L., Dimarzo, V., Morris, H. R., and Bloom, S. R. (1988). J. Neurochem. 51, 988–991.
Minamino, N., Kangawa, K., Honzawa, M., and Matsuo, H. (1988). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 156, 355–360.
Murphy, R., Turner, C. A., Furness, J. B., Parker, L., and Giraud, A. (1990). Peptides 11, 613–617.
O’Harte, F., Bockman, C. S., Abel, P. W., and Conlon, J. M. (1991). Peptides 12, 11–15.
Lo, G., Legon, S., Austin, C., Wallis, S., Wang, Z., and Bloom, S. R. (1992). Mol. Endocrinol. 6, 1538–1544.
Howard, A. D., Wang, R., Pong, S.-S., et al. (2000). Nature 406, 70–74.
Fujii, R., Hosoya, M., Fukusumi, S., Kawamata, Y., Habata, Y., Hinuma, S., Onda, H., Nishimura, O., and Fujino, M. (2000). J. Biol. Chem. 275, 21,068–21,074.
Szekeres, P. G., Muir, A. I., Spinage, L. D., et al. (2000). J. Biol. Chem. 275, 20,247–20,250.
Kojima, M., Haruno, R., Nakazato, M., Date, Y., Murakami, N., Hanada, R., Matsuo, H., and Kangawa, K. (2000). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 276, 435–438.
Malendowicz, L. K. (1998). Horm. Metab. Res. 30, 374–383.
Nakazato, M., Hanada, R., Murakami, N., Date, Y., Mondal, M. S., Kojima, M., and Yoshimatsu, H. (2000). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 277, 191–194.
Morgan, J. I. and Curran, T. (1989). Trends Neurosci. 12, 459–462.
Steel, J. H., Noorden, S., Ballesta, J., Gibson, S. J., Ghatei, M. A., Burrin, J., Leonhardt, U. R. S., Domin, J., Bloom, S. R., and Polak, J. M. (1988). Endocrinology 122, 270–282.
Olson, B. R., Drutarosky, M. D., Chow, M.-S., Hurby, V. J., Stricker, E. M., and Verbalis, J. G. (1991). Peptides 12, 113–118.
Olson, B. R., Drutarosky, M. D., Stricker, E. M., and Verbalis, J. G. (1991). Endocrinology 129, 260–272.
Sawchenko, P. E. and Swanson, L. W. (1982). J. Comp. Neurol. 205, 260–272.
Moga, M. M., Herbert, H., Hurley, K. M., Yasui, Y., Gray, T. S., and Saper, C. B. (1990). J. Comp. Neurol. 295, 624–661.
Moga, M. M., Saper, C. B., and Gray, T. S. (1990). J. Comp. Neurol. 295, 662–682.
Fulwiler, C. E. and Saper, C. B. (1985). Neurosci. Lett. 53, 289–296.
Niimi, M., Sato, M., Yokote, R., Tada, S., and Takahara, J. (1999). J. Neuroendocrinol. 11, 605–611.
Niimi, M., Sato, M., and Taminato, T. (2001). Endocrine 14, 269–273.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niimi, M., Murao, K. & Taminato, T. Central administration of neuromedin U activates neurons in ventrobasal hypothalamus and brainstem. Endocr 16, 201–206 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:16:3:201
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:16:3:201